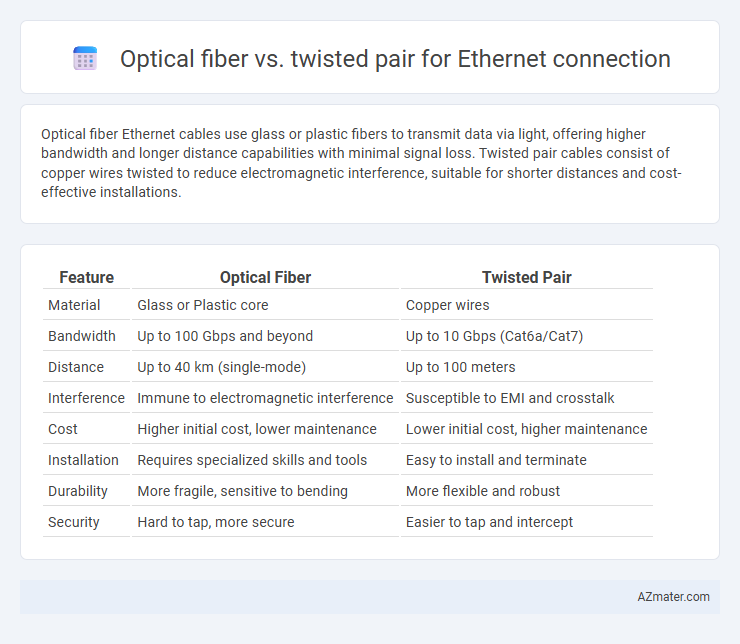
Optical fiber Ethernet cables use glass or plastic fibers to transmit data via light, offering higher bandwidth and longer distance capabilities with minimal signal loss. Twisted pair cables consist of copper wires twisted to reduce electromagnetic interference, suitable for shorter distances and cost-effective installations.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Optical Fiber | Twisted Pair |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Glass or Plastic core | Copper wires |
| Bandwidth | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond | Up to 10 Gbps (Cat6a/Cat7) |
| Distance | Up to 40 km (single-mode) | Up to 100 meters |
| Interference | Immune to electromagnetic interference | Susceptible to EMI and crosstalk |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance |
| Installation | Requires specialized skills and tools | Easy to install and terminate |
| Durability | More fragile, sensitive to bending | More flexible and robust |
| Security | Hard to tap, more secure | Easier to tap and intercept |
Introduction to Ethernet Cabling
Optical fiber and twisted pair cables serve as the primary mediums for Ethernet connections, each with distinct advantages and applications. Optical fiber offers higher bandwidth, longer transmission distances up to several kilometers, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for backbone networks and high-speed data transfers. Twisted pair cabling, such as Cat5e or Cat6, is cost-effective, easier to install, and commonly used for shorter-distance connections within local area networks (LANs), supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps over distances typically limited to 100 meters.
Overview of Optical Fiber Technology
Optical fiber technology uses thin strands of glass or plastic to transmit data as light signals, enabling significantly higher bandwidth and longer transmission distances compared to twisted pair cables. It offers immunity to electromagnetic interference, making it ideal for high-speed Ethernet networks in environments with heavy electrical noise. Optical fiber supports data rates up to 100 Gbps and beyond, suited for backbone and long-distance connections where low latency and high reliability are critical.
Understanding Twisted Pair Cables
Twisted pair cables, commonly used in Ethernet connections, consist of pairs of insulated copper wires twisted together to reduce electromagnetic interference and crosstalk. These cables are cost-effective, easy to install, and support data transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, making them ideal for local area networks (LANs). Compared to optical fiber, twisted pair cables have limited bandwidth and susceptibility to signal degradation over longer distances but remain popular for their balance of performance and affordability.
Speed and Bandwidth Comparison
Optical fiber offers significantly higher speed and bandwidth capabilities compared to twisted pair cables, supporting up to 100 Gbps and beyond for modern Ethernet networks. Twisted pair cables, such as Cat5e and Cat6, typically provide speeds up to 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps respectively, with limited bandwidth capacity over longer distances. The superior data transmission rate and minimal signal degradation of optical fiber make it the preferred choice for high-speed, high-bandwidth Ethernet connections in enterprise and data center environments.
Transmission Distance Capabilities
Optical fiber supports transmission distances up to 40 kilometers or more without signal degradation, making it ideal for long-range Ethernet connections. Twisted pair cables, specifically Cat5e or Cat6, are limited to approximately 100 meters before requiring signal boosters or switches. The superior distance capabilities of optical fiber enable high-speed data transmission over vast infrastructures with minimal latency and interference.
Resistance to Electromagnetic Interference
Optical fiber cables provide superior resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI) compared to twisted pair cables, as they transmit data using light rather than electrical signals, making them immune to external electrical noise. Twisted pair cables, especially unshielded varieties, are more susceptible to EMI, which can cause data corruption and signal degradation in environments with high electromagnetic activity. Shielded twisted pair (STP) cables offer improved EMI resistance but still fall short of the inherent immunity provided by optical fiber.
Installation Complexity and Flexibility
Optical fiber installation requires specialized tools and trained technicians due to its fragility and precise splicing needs, making it more complex compared to twisted pair cables. Twisted pair cables offer greater flexibility in installation, easily routed through walls and conduits with standard connectors like RJ45, simplifying the setup process. Fiber optic cables provide superior performance over long distances but pose challenges in initial deployment, whereas twisted pairs balance ease of installation with moderate distance capabilities.
Cost Comparison: Initial and Long-Term
Optical fiber Ethernet connections typically have higher initial costs due to expensive cables and installation requirements, while twisted pair cables like Cat5e or Cat6 offer a more affordable upfront investment. Over the long term, optical fiber provides greater durability, lower maintenance, and higher data transmission speeds, which can reduce expenses related to upgrades and network downtime. Twisted pair cables may incur additional costs from performance limitations and the need for more frequent replacements or signal boosters in extensive or high-speed networks.
Reliability and Maintenance Considerations
Optical fiber offers superior reliability for Ethernet connections due to its immunity to electromagnetic interference and lower attenuation over long distances, resulting in fewer signal degradations and less frequent repairs. Twisted pair cables, while easier to install and maintain, are more susceptible to noise and crosstalk, potentially causing higher error rates and increased downtime. Maintenance for optical fiber requires specialized skills and tools, whereas twisted pair cables benefit from simpler testing and replacement procedures, making them more cost-effective for shorter runs and less critical environments.
Choosing the Right Cable for Your Network
Choosing the right cable for your Ethernet network depends on factors such as distance, bandwidth, and environment. Optical fiber offers superior speed and longer transmission distances, making it ideal for high-performance networks and environments with electromagnetic interference. Twisted pair cables are cost-effective and easier to install, suitable for shorter distances and typical office or home networks requiring reliable connectivity under 100 meters.
Infographic: Optical fiber vs Twisted pair for Ethernet connection
 azmater.com
azmater.com