Ceramic fiber enhances concrete reinforcement by providing superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, ideal for high-temperature applications. Polypropylene fiber improves concrete toughness and crack resistance while reducing shrinkage, making it suitable for general structural use.
Table of Comparison
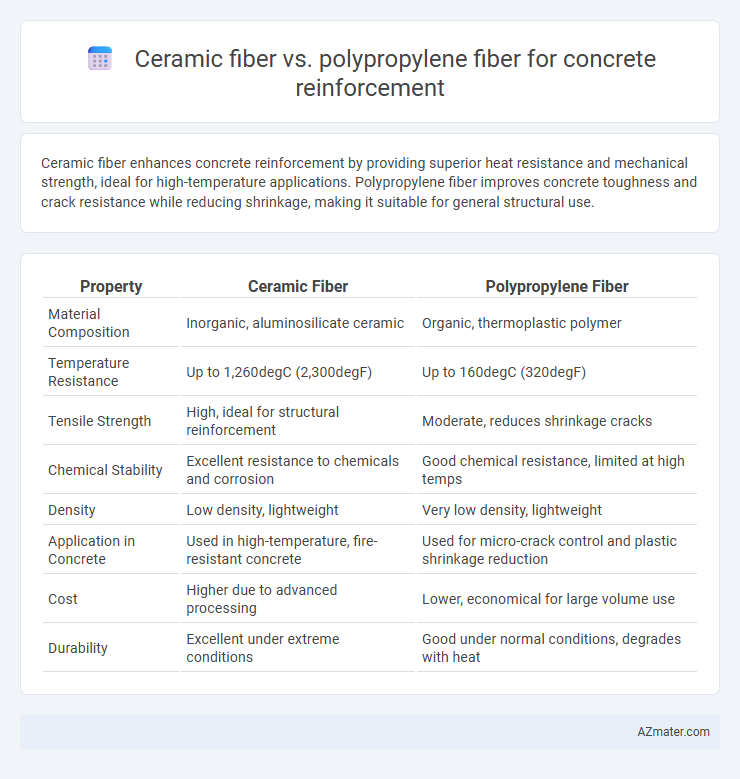
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic, aluminosilicate ceramic | Organic, thermoplastic polymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1,260degC (2,300degF) | Up to 160degC (320degF) |
| Tensile Strength | High, ideal for structural reinforcement | Moderate, reduces shrinkage cracks |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent resistance to chemicals and corrosion | Good chemical resistance, limited at high temps |
| Density | Low density, lightweight | Very low density, lightweight |
| Application in Concrete | Used in high-temperature, fire-resistant concrete | Used for micro-crack control and plastic shrinkage reduction |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced processing | Lower, economical for large volume use |
| Durability | Excellent under extreme conditions | Good under normal conditions, degrades with heat |
Introduction to Concrete Reinforcement Fibers
Concrete reinforcement fibers enhance mechanical properties by improving tensile strength, durability, and crack resistance. Ceramic fibers offer high heat resistance and chemical stability, making them ideal for high-temperature or harsh environments, while polypropylene fibers provide excellent flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to shrinkage and corrosion. Selection depends on specific application requirements such as thermal exposure, mechanical performance, and overall project budget.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber for Concrete
Ceramic fiber for concrete reinforcement offers high-temperature resistance, excellent thermal stability, and superior durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for refractory and high-performance concrete applications. These fibers improve concrete's mechanical strength and crack resistance while maintaining lightweight properties and chemical inertness. Compared to polypropylene fiber, ceramic fiber can withstand extreme heat and aggressive chemical exposure without degrading, enhancing the longevity and structural integrity of specialized concrete mixes.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber for Concrete
Polypropylene fiber is a synthetic material commonly used to enhance concrete's toughness by reducing shrinkage cracks and improving impact resistance. Its lightweight nature and high chemical resistance make it ideal for various concrete applications, including industrial floors, pavements, and shotcrete. Compared to ceramic fiber, polypropylene fiber offers better flexibility and is more cost-effective for controlling plastic shrinkage and improving durability in concrete structures.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature concrete applications. Polypropylene fiber, while having lower tensile strength, offers superior impact resistance and toughness, enhancing concrete's crack control and durability under dynamic loads. The modulus of elasticity is generally higher in ceramic fiber, providing improved stiffness, whereas polypropylene fiber contributes better flexibility and energy absorption in concrete reinforcement.
Durability and Longevity Factors
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior durability in concrete reinforcement due to its high resistance to heat, chemical corrosion, and alkaline environments, ensuring prolonged structural integrity in extreme conditions. Polypropylene fiber, while offering excellent toughness and crack resistance, is more susceptible to UV degradation and chemical breakdown over time, which can reduce its effectiveness in harsh environments. The long-term performance of ceramic fiber-reinforced concrete often surpasses that of polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring extended service life and high thermal stability.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion
Ceramic fiber offers superior resistance to chemicals and corrosion compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for concrete reinforcement in harsh environments exposed to acidic or alkaline substances. Polypropylene fiber, while resistant to certain chemicals and inert to most environments, can degrade under strong oxidizing conditions and elevated temperatures, reducing its durability in aggressive chemical exposures. The enhanced chemical stability of ceramic fiber ensures long-term structural integrity in concrete applications subjected to corrosive agents.
Impact on Concrete Workability and Setting
Ceramic fiber enhances concrete's heat resistance but tends to reduce workability due to its stiffness and lower water absorption, often requiring superplasticizers to maintain flow. Polypropylene fiber improves concrete workability by distributing evenly and absorbing minimal water, which helps preserve slump and facilitates easier placement. Setting times are marginally delayed by polypropylene fibers, while ceramic fibers have minimal impact on setting but can influence early hydration due to their physical properties.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Ceramic fiber offers high-temperature resistance but comes with a significantly higher cost compared to polypropylene fiber, making it less economical for widespread concrete reinforcement applications. Polypropylene fiber is readily available, widely produced, and cost-effective, providing an optimal balance for improving concrete toughness and crack resistance in most construction projects. The cost-efficiency and accessibility of polypropylene fibers make them the preferred choice for large-scale concrete reinforcement over the more expensive and niche ceramic fiber options.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Ceramic fibers excel in high-temperature concrete applications such as refractory linings, fireproof panels, and thermal insulation due to their exceptional heat resistance and stability. Polypropylene fibers are widely used in general concrete reinforcement for controlling plastic shrinkage, enhancing toughness, and improving impact resistance in structures like pavements, slabs, and precast elements. The choice depends on project requirements: ceramic fibers suit extreme thermal environments, while polypropylene fibers provide cost-effective durability and crack mitigation in standard construction.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Project
Ceramic fiber offers excellent heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature concrete applications such as refractory linings and industrial flooring. Polypropylene fiber enhances concrete's impact resistance and crack control, providing cost-effective solutions for general construction and infrastructure projects. Selecting the right fiber depends on project requirements including thermal exposure, mechanical strength, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Concrete reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com