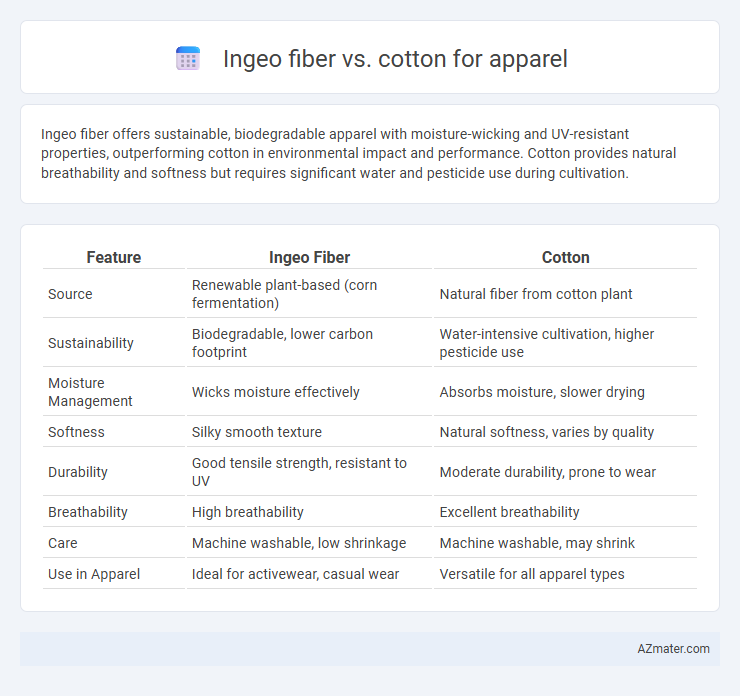
Ingeo fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable apparel with moisture-wicking and UV-resistant properties, outperforming cotton in environmental impact and performance. Cotton provides natural breathability and softness but requires significant water and pesticide use during cultivation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn fermentation) | Natural fiber from cotton plant |
| Sustainability | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Water-intensive cultivation, higher pesticide use |
| Moisture Management | Wicks moisture effectively | Absorbs moisture, slower drying |
| Softness | Silky smooth texture | Natural softness, varies by quality |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, resistant to UV | Moderate durability, prone to wear |
| Breathability | High breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Care | Machine washable, low shrinkage | Machine washable, may shrink |
| Use in Apparel | Ideal for activewear, casual wear | Versatile for all apparel types |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Cotton
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional cotton in apparel manufacturing. Cotton, a natural fiber known for its softness and breathability, remains widely used but requires significant water and pesticide inputs. Ingeo fiber provides enhanced moisture management and biodegradability, positioning it as an eco-friendly choice in textile production.
Overview of Ingeo Fiber: Properties and Production
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional cotton in apparel production. This biopolymer fiber boasts properties like high moisture-wicking ability, breathability, and a softer texture, enhancing comfort and durability in textiles. Manufactured through a closed-loop process with low carbon emissions, Ingeo fiber supports eco-friendly fashion by reducing reliance on water-intensive cotton cultivation and synthetic fibers.
Cotton: Characteristics and Manufacturing Process
Cotton, a natural fiber derived from the seed hairs of the cotton plant, is renowned for its breathability, softness, and moisture absorption, making it a popular choice for apparel. The manufacturing process involves harvesting cotton bolls, ginning to separate fibers from seeds, spinning the fibers into yarn, and weaving or knitting into fabric. This traditional process emphasizes sustainability when combined with organic farming practices, but cotton cultivation typically requires significant water and pesticide inputs compared to Ingeo, a plant-based biopolymer fiber produced through fermentation of corn sugars.
Environmental Impact: Ingeo Fiber vs Cotton
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn starch, emits significantly lower greenhouse gases during production compared to conventional cotton, which requires extensive water usage and pesticides. Cotton cultivation accounts for roughly 20% of global insecticide use and consumes about 2,700 liters of water per kilogram, intensifying environmental strain. Ingeo's biodegradable nature and reduced reliance on irrigation make it a more sustainable choice for environmentally conscious apparel manufacturing.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant sources, offers superior moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional cotton, enhancing comfort by keeping the skin dry and cool. Cotton, known for its natural softness and breathability, provides a lightweight and airy feel, but may retain moisture longer, potentially causing discomfort in humid conditions. The sustainable profile of Ingeo fiber combined with advanced moisture management makes it an increasingly popular choice for high-performance apparel focused on comfort and breathability.
Durability and Longevity in Apparel
Ingeo fiber offers superior durability compared to cotton, maintaining fabric integrity through repeated washing and wear due to its biopolymer structure derived from renewable resources. Cotton, while natural and breathable, tends to weaken over time, showing signs of wear such as thinning and pilling more quickly than Ingeo-based textiles. The long-lasting resilience of Ingeo fiber makes it an excellent choice for apparel designed for extended use and sustained performance.
Moisture Management and Absorbency
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers superior moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional cotton, allowing apparel to dry faster and maintain comfort during physical activities. Cotton, known for its high absorbency, effectively retains moisture but dries slowly, which can lead to a clammy feel in activewear. Ingeo's ability to manage moisture more efficiently makes it an ideal choice for performance apparel requiring both breathability and quick-drying characteristics.
Allergies and Skin Sensitivity Considerations
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn, offers hypoallergenic properties that make it suitable for sensitive skin and individuals prone to allergies. Compared to cotton, which can sometimes trigger irritation due to pesticide residues or chemical treatments, Ingeo fabric provides a softer, smoother texture that reduces the risk of skin discomfort. Its moisture-wicking and breathable characteristics also help prevent bacterial buildup, enhancing comfort for allergy-sensitive wearers.
Cost and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, tends to be more costly than traditional cotton due to its complex manufacturing process and limited large-scale production. Cotton benefits from extensive global cultivation and established supply chains, making it widely available and generally more affordable for apparel manufacturing. Market availability of Ingeo fiber is growing steadily as demand for sustainable textiles rises, but it remains less accessible than cotton in many regions.
Which is Better for Sustainable Fashion?
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable corn starch, offers a lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to conventional cotton, which demands extensive water and pesticide use. While cotton remains popular for its natural softness and breathability, Ingeo's closed-loop production minimizes environmental impact, positioning it as a superior choice for sustainable fashion. Brands prioritizing eco-friendly apparel increasingly prefer Ingeo for its renewable origin and reduced resource consumption over traditional cotton.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Cotton for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com