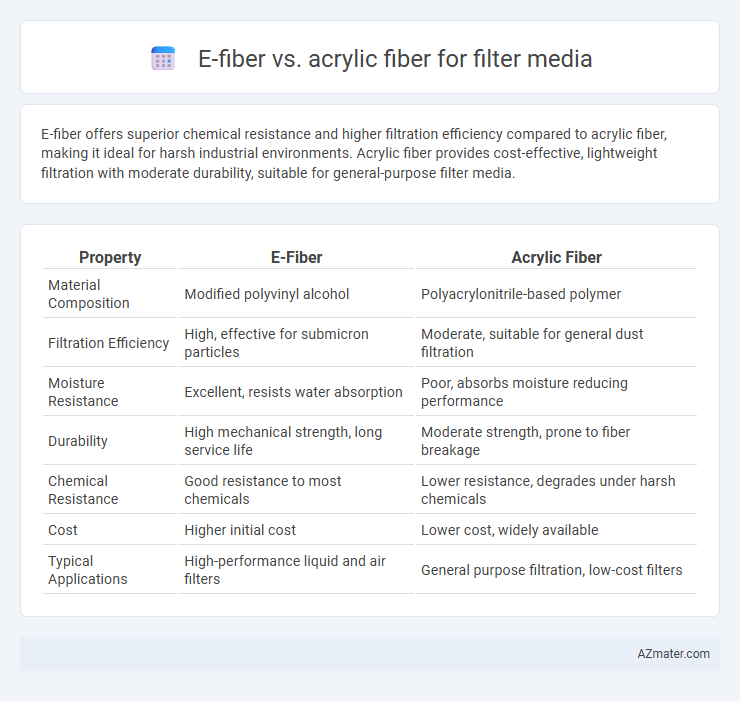
E-fiber offers superior chemical resistance and higher filtration efficiency compared to acrylic fiber, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Acrylic fiber provides cost-effective, lightweight filtration with moderate durability, suitable for general-purpose filter media.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Modified polyvinyl alcohol | Polyacrylonitrile-based polymer |
| Filtration Efficiency | High, effective for submicron particles | Moderate, suitable for general dust filtration |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, resists water absorption | Poor, absorbs moisture reducing performance |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, long service life | Moderate strength, prone to fiber breakage |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to most chemicals | Lower resistance, degrades under harsh chemicals |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Typical Applications | High-performance liquid and air filters | General purpose filtration, low-cost filters |
Introduction to Filter Media: E-Fiber vs Acrylic Fiber
E-fiber and acrylic fiber serve as essential materials in filter media, each offering distinct filtration efficiencies and durability. E-fiber, a type of fine glass fiber, provides superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for industrial filtration applications. Acrylic fiber offers excellent moisture management and softness, typically used in applications requiring fine particulate capture and comfort in air and liquid filtration.
Composition and Properties of E-Fiber
E-fiber, primarily composed of alumina-borosilicate glass, exhibits superior thermal stability and high tensile strength compared to acrylic fibers, which are synthetic polymers made from polyacrylonitrile. The inorganic nature of E-fiber imparts excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for demanding filtration applications. In contrast, acrylic fibers offer flexibility and moderate resistance but lack the durability and heat resistance crucial for high-performance filter media.
Composition and Properties of Acrylic Fiber
Acrylic fiber used in filter media is primarily composed of polyacrylonitrile (PAN), offering excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and hydrophobic properties that enhance filtration efficiency and durability. Unlike e-fiber, which is polyester-based and known for mechanical strength and moisture absorption, acrylic fibers maintain performance in harsh chemical environments and high-temperature applications. The fine denier and surface morphology of acrylic fibers contribute to superior particulate capture and extended filter lifespan in industrial filtration systems.
Filtration Efficiency: E-Fiber Compared to Acrylic Fiber
E-fiber offers superior filtration efficiency compared to acrylic fiber due to its finer fiber diameter and higher surface area, which enhances particle capture in filter media applications. The electrospun nanofibers in E-fiber create a dense, uniform matrix that effectively traps submicron particles, outperforming the relatively coarser and less uniform acrylic fibers. This results in E-fiber-based filters achieving higher contaminant retention and longer service life, making them ideal for high-performance filtration solutions.
Durability and Lifespan of Each Fiber Type
E-fiber, or glass fibers, exhibit superior durability and longer lifespan in filter media compared to acrylic fibers due to their high resistance to chemical degradation, heat, and mechanical stress. Acrylic fibers tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light and acidic environments, resulting in reduced filtration efficiency over time. The inherent thermal stability and robust structural integrity of E-fibers make them ideal for industrial filtration applications requiring sustained performance and frequent exposure to harsh operating conditions.
Chemical Resistance: E-Fiber vs Acrylic
E-fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to acrylic fiber, making it highly effective in aggressive chemical environments and industrial filtration applications. E-fiber maintains structural integrity and performance when exposed to acids, alkalis, and solvents, whereas acrylic fiber tends to degrade or weaken under similar conditions. This enhanced chemical resistance of E-fiber extends the lifespan and reliability of filter media in challenging chemical processing scenarios.
Cost Analysis: E-Fiber vs Acrylic Fiber
E-fiber generally incurs higher initial costs compared to acrylic fiber due to advanced manufacturing processes and superior filtration efficiency. Acrylic fiber offers a cost-effective alternative with lower production expenses, but may require more frequent replacement and maintenance, impacting long-term operational costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights E-fiber's durability and enhanced performance that can offset upfront investment over time.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-fiber, derived from renewable sources such as plant cellulose, offers significant environmental benefits over acrylic fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. The biodegradability of E-fiber reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions throughout its lifecycle, enhancing sustainability in filter media applications. E-fiber's renewable origin and reduced ecological footprint make it a preferable choice for eco-friendly filtration solutions compared to synthetic acrylic fibers.
Applications and Industry Usage
E-fiber, characterized by its high tensile strength and thermal resistance, is extensively used in high-performance filtration applications such as automotive exhaust systems, HVAC filters, and industrial dust collection where durability and heat tolerance are critical. Acrylic fiber, known for its excellent chemical resistance and softness, finds applications in liquid filtration, air filters for residential and commercial buildings, and fine particulate filtration in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. The choice between E-fiber and acrylic fiber filter media depends on specific industry requirements for temperature stability, chemical exposure, and filtration efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Filter Media
E-fiber offers superior filtration efficiency and durability due to its advanced electrostatic properties, making it ideal for high-performance filter media in HVAC and cleanroom applications. Acrylic fiber provides cost-effective filtration with good chemical resistance but generally lacks the longevity and fine particle capture capabilities of E-fiber. Selecting the right fiber depends on application-specific requirements such as filtration precision, budget constraints, and environmental conditions.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Filter Media
 azmater.com
azmater.com