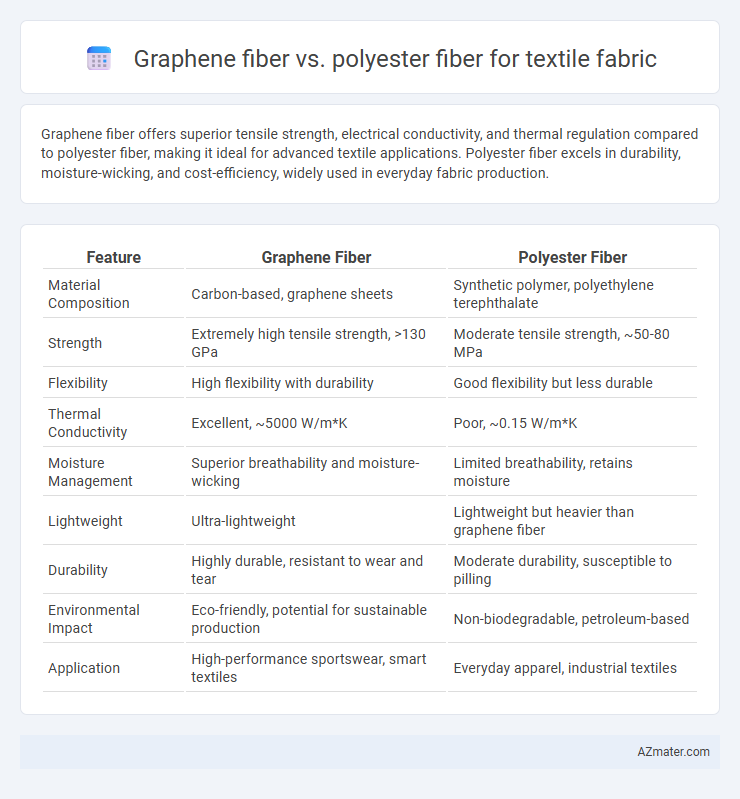
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal regulation compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for advanced textile applications. Polyester fiber excels in durability, moisture-wicking, and cost-efficiency, widely used in everyday fabric production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based, graphene sheets | Synthetic polymer, polyethylene terephthalate |
| Strength | Extremely high tensile strength, >130 GPa | Moderate tensile strength, ~50-80 MPa |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with durability | Good flexibility but less durable |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent, ~5000 W/m*K | Poor, ~0.15 W/m*K |
| Moisture Management | Superior breathability and moisture-wicking | Limited breathability, retains moisture |
| Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight | Lightweight but heavier than graphene fiber |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear and tear | Moderate durability, susceptible to pilling |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, potential for sustainable production | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Application | High-performance sportswear, smart textiles | Everyday apparel, industrial textiles |
Introduction to Graphene Fiber and Polyester Fiber
Graphene fiber, derived from graphene's single-layer carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offers exceptional mechanical strength, lightweight properties, and advanced conductivity compared to conventional fibers. Polyester fiber, a synthetic polymer made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is widely used in textiles for its durability, resistance to wrinkles, and moisture-wicking capabilities. In textile fabric applications, graphene fiber's enhanced thermal and electrical conductivity presents innovative opportunities over polyester's established cost-effectiveness and ease of processing.
Material Composition and Structure
Graphene fiber consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, offering exceptional tensile strength, conductivity, and flexibility, whereas polyester fiber is a synthetic polymer primarily made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) with a semi-crystalline structure contributing to its durability and moisture resistance. The atomic-scale thickness and unique two-dimensional structure of graphene fibers enable superior thermal and electrical properties compared to the amorphous and semi-crystalline regions found in polyester fibers. Textile fabrics utilizing graphene fibers exhibit enhanced mechanical performance and electrical conductivity, while polyester fabrics benefit from affordability, ease of production, and resistance to chemicals and UV degradation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Graphene fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyester fiber, with tensile strength reaching up to 1300 MPa, significantly enhancing fabric durability under stress. Its exceptional flexibility and resistance to wear and tear surpass polyester, which typically offers tensile strength around 60-80 MPa but is prone to degradation from UV exposure and abrasion. The incorporation of graphene fiber in textile fabrics results in materials that maintain structural integrity longer in demanding environments, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Flexibility and Comfort in Fabrics
Graphene fiber exhibits superior flexibility compared to polyester fiber, enhancing the fabric's ability to conform to body movements without losing shape. Its exceptional thermal conductivity and breathability contribute to increased comfort in textiles, making it ideal for activewear and performance garments. In contrast, polyester fiber is less breathable and can trap heat, leading to reduced comfort during prolonged wear.
Thermal Conductivity and Temperature Regulation
Graphene fiber exhibits superior thermal conductivity compared to polyester fiber, enabling faster heat dissipation and enhanced temperature regulation in textile fabrics. This high thermal conductivity promotes improved breathability and moisture management, keeping the wearer cooler in warm conditions. Polyester fiber, while durable and cost-effective, has lower thermal conductivity, resulting in less efficient heat transfer and reduced temperature regulation capabilities.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Graphene fiber exhibits superior moisture management compared to polyester fiber, effectively wicking sweat away from the skin and accelerating evaporation due to its high thermal conductivity and hydrophobic properties. Polyester fiber, while lightweight and durable, tends to trap moisture and offers lower breathability, which can lead to discomfort in hot or active conditions. Textile fabrics incorporating graphene fiber enhance airflow and maintain dryness, making them ideal for performance and athletic wear.
Weight and Fabric Thickness Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly lower weight compared to traditional polyester fiber, enhancing comfort and reducing garment bulk. Despite its ultralight characteristics, graphene fiber maintains superior durability and strength, allowing for thinner fabric constructions without compromising performance. Polyester fiber, while heavier and thicker, offers cost-effective mass production but falls short in lightweight and high-strength applications crucial for advanced textile innovation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber exhibits superior environmental benefits compared to polyester fiber due to its biodegradability and lower carbon footprint during production. Polyester fiber, derived from petrochemicals, contributes significantly to microplastic pollution and has a higher energy consumption in manufacturing. Sustainable textile fabric choices increasingly favor graphene fiber for its recyclability and reduced ecological impact.
Cost and Market Availability
Graphene fiber, known for its exceptional strength and conductivity, remains significantly more expensive than polyester fiber due to high production costs and limited large-scale manufacturing. Polyester fiber dominates the textile market with cost-effectiveness, widespread availability, and established supply chains, making it the preferred choice for mass production. The high price and scarcity of graphene fiber restrict its current use to niche applications and premium textile products.
Future Prospects in Textile Applications
Graphene fiber offers superior strength, conductivity, and flexibility compared to polyester fiber, making it a game-changer for future textile applications in smart fabrics and wearable technology. Its lightweight and durable properties enhance performance in sportswear, protective clothing, and medical textiles, while polyester remains dominant due to cost-effectiveness and ease of production. Advances in scalable graphene fiber manufacturing promise to reduce costs and enable mass adoption, positioning graphene as a transformative material in next-generation textile innovations.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Polyester fiber for Textile fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com