Bamboo fiber is naturally antibacterial, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional cotton fiber, which is soft but requires extensive water and pesticide use during cultivation. Clothing made from bamboo fiber offers enhanced breathability and durability compared to conventional cotton garments.
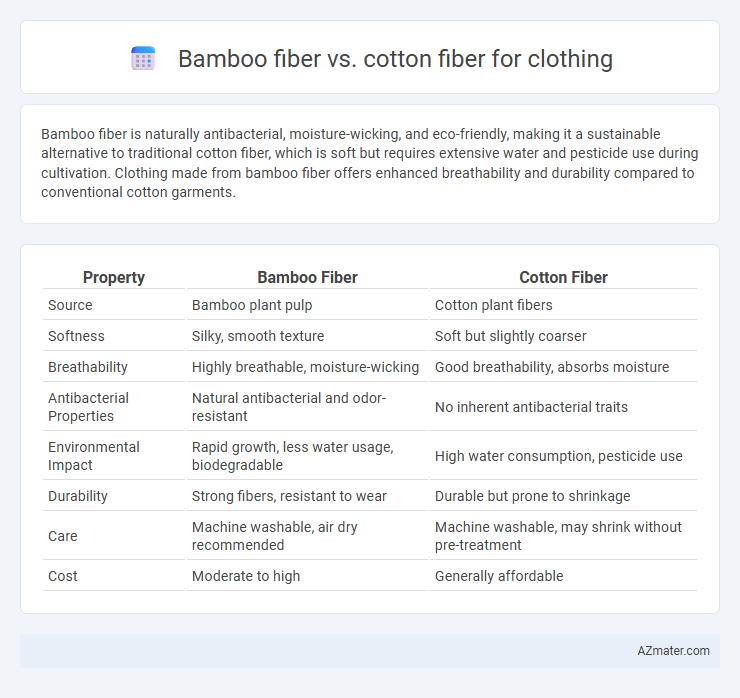
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bamboo plant pulp | Cotton plant fibers |
| Softness | Silky, smooth texture | Soft but slightly coarser |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Good breathability, absorbs moisture |
| Antibacterial Properties | Natural antibacterial and odor-resistant | No inherent antibacterial traits |
| Environmental Impact | Rapid growth, less water usage, biodegradable | High water consumption, pesticide use |
| Durability | Strong fibers, resistant to wear | Durable but prone to shrinkage |
| Care | Machine washable, air dry recommended | Machine washable, may shrink without pre-treatment |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally affordable |
Introduction to Bamboo and Cotton Fibers
Bamboo fiber is derived from the pulp of bamboo grass and is known for its natural antibacterial properties, moisture-wicking ability, and eco-friendly production process compared to traditional fibers. Cotton fiber, sourced from the cotton plant's seed hairs, is celebrated for its softness, breathability, and widespread availability in the textile industry. Both fibers play significant roles in clothing manufacturing, with bamboo offering sustainable benefits and cotton providing comfort and durability.
Source and Production Processes
Bamboo fiber originates from the cellulose of bamboo plants, extracted through mechanical or chemical processes such as viscose production, while cotton fiber is harvested directly from the cotton plant's seed hairs through mechanical ginning. Bamboo fiber production often involves chemical treatments that can impact environmental sustainability, whereas cotton cultivation requires significant water, pesticides, and labor-intensive harvesting. The source and processing methods define the environmental footprint and texture differences between bamboo and cotton fibers in clothing manufacturing.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Bamboo fiber production requires 3-5 times less water than cotton, significantly reducing water consumption in clothing manufacturing. Bamboo grows rapidly without pesticides or fertilizers, minimizing soil degradation and chemical runoff, whereas conventional cotton relies heavily on agrochemicals that harm ecosystems. The biodegradability of bamboo fiber also exceeds that of cotton, promoting a lower environmental footprint from production through disposal.
Texture and Comfort Differences
Bamboo fiber offers a silky, smooth texture that feels softer and cooler against the skin compared to cotton's naturally coarse but durable feel. Its moisture-wicking and breathable properties enhance comfort by reducing sweat and odor, whereas cotton absorbs moisture but can retain it longer, potentially causing a clammy sensation. Bamboo fiber's hypoallergenic qualities also make it ideal for sensitive skin, providing a gentler alternative to traditional cotton fabrics.
Moisture Wicking and Breathability
Bamboo fiber outperforms cotton in moisture-wicking due to its natural micro-gaps that absorb and evaporate sweat quickly, keeping the skin dry and comfortable during physical activity. Cotton, while breathable, tends to retain moisture, leading to a damp and heavy feel in humid conditions or intense workouts. Bamboo's superior breathability and moisture management make it an ideal choice for activewear and hot climates.
Durability and Longevity
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior durability compared to cotton due to its natural strength and resistance to wear and tear, making it an excellent choice for long-lasting clothing. Cotton fiber, while soft and breathable, tends to weaken and lose integrity after multiple washes, reducing its lifespan. Bamboo fabric also has antimicrobial properties that help maintain fabric quality over time, enhancing its longevity relative to traditional cotton garments.
Skin Sensitivity and Hypoallergenic Properties
Bamboo fiber is naturally hypoallergenic, making it an excellent choice for sensitive skin by reducing irritation and allergic reactions compared to cotton. Its moisture-wicking and antimicrobial properties further enhance comfort for individuals prone to skin sensitivities. Cotton fiber, while breathable and soft, may cause irritation in some cases due to chemical treatments unless it is organic and untreated.
Cost and Market Availability
Bamboo fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to cotton fiber due to lower water and pesticide requirements in cultivation, resulting in reduced production expenses and competitive pricing in the textile market. Cotton fiber remains widely available and dominates the global clothing market, supported by established supply chains and massive production volumes. Bamboo fiber is gaining market availability through increased demand for sustainable textiles, though it still lags behind cotton in global market penetration and retail presence.
Maintenance and Care Instructions
Bamboo fiber clothing requires gentle washing in cold water with mild detergent to maintain its softness and antimicrobial properties, avoiding bleach and high heat drying to prevent fiber damage. Cotton fiber garments can withstand warmer wash cycles and higher drying temperatures but may experience shrinkage and color fading without proper care such as turning clothes inside out. Both fibers benefit from air drying when possible to extend fabric lifespan and preserve texture.
Summary: Which Fiber is Better for Clothing?
Bamboo fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to cotton, making it ideal for activewear and sensitive skin. Cotton fiber excels in breathability and durability, providing a natural softness preferred for everyday clothing. Choosing between bamboo and cotton depends on specific needs such as environmental impact, comfort, and garment use.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Cotton fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com