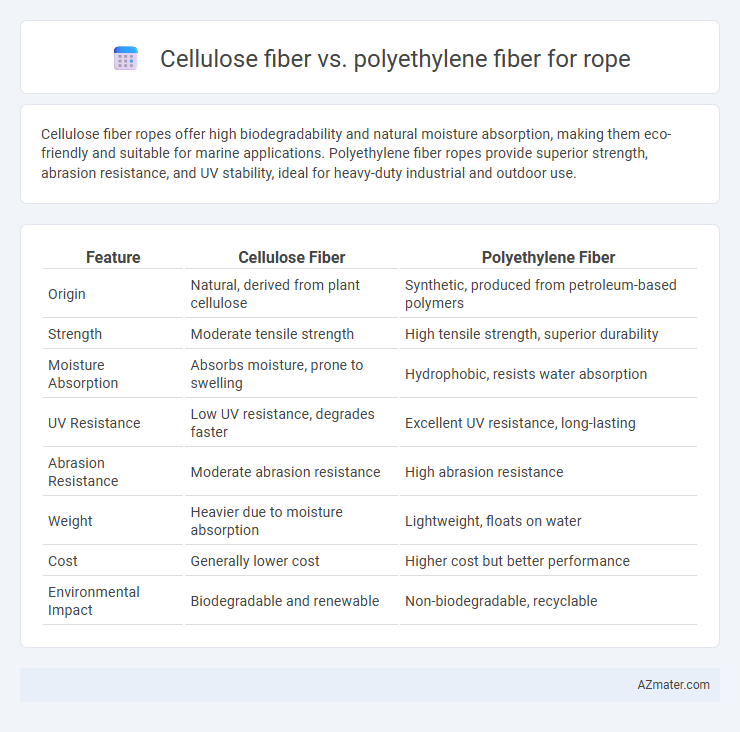
Cellulose fiber ropes offer high biodegradability and natural moisture absorption, making them eco-friendly and suitable for marine applications. Polyethylene fiber ropes provide superior strength, abrasion resistance, and UV stability, ideal for heavy-duty industrial and outdoor use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellulose Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, derived from plant cellulose | Synthetic, produced from petroleum-based polymers |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength, superior durability |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs moisture, prone to swelling | Hydrophobic, resists water absorption |
| UV Resistance | Low UV resistance, degrades faster | Excellent UV resistance, long-lasting |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance |
| Weight | Heavier due to moisture absorption | Lightweight, floats on water |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost but better performance |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable | Non-biodegradable, recyclable |
Introduction to Rope Fibers
Cellulose fiber and polyethylene fiber represent two distinct materials used in rope manufacturing, each offering unique properties suited to various applications. Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton or hemp, provide excellent biodegradability, breathability, and grip, making them ideal for traditional ropes in marine or agricultural settings. Polyethylene fibers, synthetic and known for their superior strength-to-weight ratio, resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation, are preferred in high-performance ropes used in industrial, climbing, and rescue operations.
Overview of Cellulose Fiber
Cellulose fiber, derived from natural plant sources like cotton, hemp, and flax, offers high biodegradability and excellent tensile strength, making it an eco-friendly option for rope manufacturing. Unlike polyethylene fiber, which is synthetic and resistant to UV and chemicals, cellulose fibers provide superior breathability and grip but have lower resistance to moisture and abrasion. These natural fibers are favored in applications prioritizing sustainability and environmental impact, though they may require more maintenance in harsh conditions.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber is a synthetic material known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for rope applications requiring high durability and low stretch. Unlike cellulose fiber, which is derived from natural plant sources and prone to moisture absorption, polyethylene fiber offers superior chemical resistance and excellent resistance to UV degradation. This fiber's low density and hydrophobic properties ensure ropes remain lightweight and perform consistently in wet or harsh environmental conditions.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Cellulose fiber ropes exhibit moderate tensile strength, typically ranging from 250 to 600 MPa, and provide good abrasion resistance but are prone to moisture absorption, which can reduce durability. Polyethylene fiber ropes, especially ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer exceptional mechanical strength with tensile strengths exceeding 2,400 MPa, combined with lightweight and excellent resistance to chemicals and UV degradation. The superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability of polyethylene fibers make them more suitable for high-performance rope applications compared to cellulose fibers.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Cellulose fiber ropes, made from natural materials like cotton or jute, exhibit moderate durability but are prone to degradation from moisture, UV exposure, and mold, reducing their lifespan in harsh weather conditions. Polyethylene fiber ropes, particularly those using high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offer superior durability with excellent resistance to UV rays, water, and chemicals, making them ideal for prolonged outdoor use. The synthetic nature of polyethylene fibers ensures minimal absorption and retention of water, enhancing weather resistance and maintaining rope strength under varying environmental stresses.
Flexibility and Handling
Cellulose fibers offer superior flexibility compared to polyethylene fibers, making ropes easier to bend and knot without compromising strength. Polyethylene fibers, while stiffer and more resistant to abrasion, can be less forgiving during handling, resulting in a firmer grip and reduced pliability. The natural texture of cellulose fibers enhances grip and maneuverability, ideal for applications requiring frequent tying and adjustment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose fiber ropes, derived from renewable plant sources like hemp, jute, or cotton, are biodegradable and decompose naturally, reducing long-term environmental pollution compared to polyethylene fiber ropes made from non-renewable petroleum-based polymers. Polyethylene fibers offer high durability and resistance to moisture and chemicals but persist in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to microplastic pollution when degraded. Choosing cellulose fiber ropes supports sustainable resource use and lowers ecological footprint, while polyethylene ropes require careful end-of-life management to mitigate environmental harm.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Cellulose fiber ropes generally offer lower initial costs due to the abundance and renewability of raw materials like cotton or hemp, making them an economical choice for short-term or light-duty applications. Polyethylene fiber ropes, while higher in upfront cost, provide superior durability, resistance to moisture, and longer service life, resulting in lower replacement frequency and potentially reduced long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership includes considering factors such as tensile strength, environmental resistance, and maintenance requirements, which often justify the investment in polyethylene fibers despite their higher price.
Applications and Best Use Cases
Cellulose fiber ropes excel in eco-friendly applications such as marine, agriculture, and climbing due to their natural biodegradability and high moisture absorption, providing secure grip even when wet. Polyethylene fiber ropes, commonly used in industrial, fishing, and safety sectors, offer superior tensile strength, resistance to UV degradation, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for heavy-duty and long-lasting performance in harsh environments. Selecting between cellulose and polyethylene fibers depends largely on environmental impact considerations and the required durability for specific rope applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Rope Fiber
Cellulose fiber ropes offer excellent biodegradability and natural grip, making them ideal for environmentally sensitive applications and traditional uses. Polyethylene fiber ropes provide superior strength, UV resistance, and durability, which are critical for heavy-duty marine and industrial environments. Selecting the right rope fiber depends on balancing environmental impact, tensile strength requirements, and exposure conditions specific to the intended use.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com