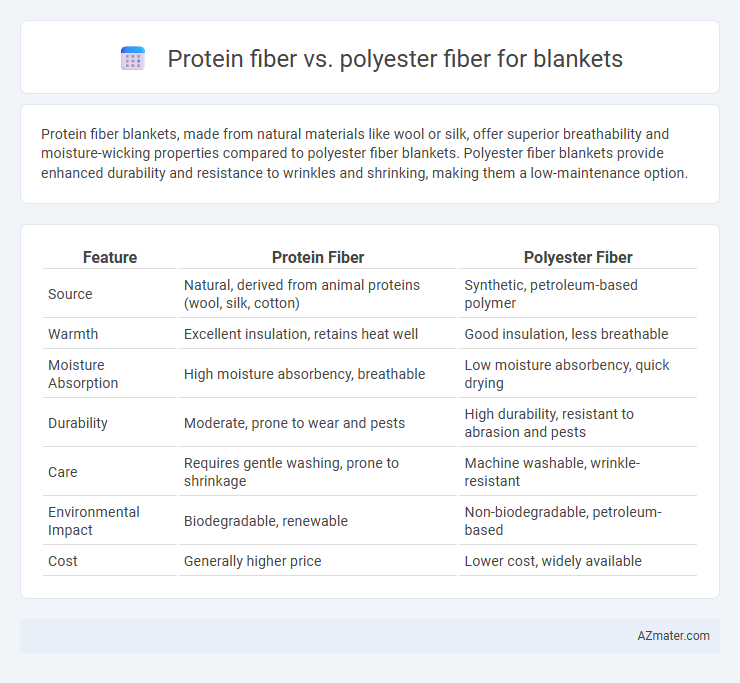
Protein fiber blankets, made from natural materials like wool or silk, offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester fiber blankets. Polyester fiber blankets provide enhanced durability and resistance to wrinkles and shrinking, making them a low-maintenance option.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Protein Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural, derived from animal proteins (wool, silk, cotton) | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Warmth | Excellent insulation, retains heat well | Good insulation, less breathable |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture absorbency, breathable | Low moisture absorbency, quick drying |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear and pests | High durability, resistant to abrasion and pests |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, prone to shrinkage | Machine washable, wrinkle-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Generally higher price | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Protein Fiber and Polyester Fiber Blankets
Protein fiber blankets, crafted from natural materials such as wool, silk, and alpaca, offer superior breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and hypoallergenic benefits, making them ideal for sensitive skin. Polyester fiber blankets, made from synthetic polymers, provide high durability, wrinkle resistance, and affordability, suitable for everyday use and easy maintenance. Choosing between protein fiber and polyester fiber blankets depends on preferences for natural comfort versus practical durability.
Source and Composition of Protein Fibers
Protein fibers used in blankets primarily originate from natural animal sources such as wool from sheep, alpaca, and cashmere from goats, each containing complex keratin proteins that provide warmth and breathability. These fibers are composed of long chains of amino acids forming fibrous proteins, which contribute to their softness, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties. In contrast, polyester fibers are synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals, lacking the natural protein structure and often offering greater durability and water resistance but less comfort and thermal regulation.
Characteristics of Polyester Fiber
Polyester fiber in blankets is known for its durability, resistance to shrinking and stretching, and quick-drying properties, making it ideal for long-lasting use and easy maintenance. Unlike protein fibers such as wool or silk, polyester is a synthetic polymer that offers excellent wrinkle resistance and retains color vibrancy after multiple washes. Its lightweight and moisture-wicking capabilities enhance comfort, while being hypoallergenic ensures suitability for sensitive skin.
Warmth and Insulation Properties Compared
Protein fibers such as wool and alpaca offer superior warmth and natural insulation due to their ability to trap air within their crimped structure, regulating body temperature effectively. Polyester fibers, while less breathable, provide efficient moisture-wicking and insulation when densely woven, making them resistant to cold and quick-drying. Compared to polyester, protein fibers excel in maintaining warmth in cold conditions through better thermal regulation and moisture absorption.
Softness and Comfort: Feel of Both Fibers
Protein fibers like wool and silk offer natural softness and breathability, making blankets cozy and comfortable for extended use. Polyester fibers, while more durable and wrinkle-resistant, tend to lack the natural softness of protein fibers and may feel less breathable against the skin. The inherent moisture-wicking properties of protein fibers contribute to superior comfort compared to the synthetic texture of polyester fibers in blankets.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability Differences
Protein fibers like wool and silk naturally excel in moisture absorption, with wool able to absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet, offering superior breathability that regulates body temperature effectively. Polyester fibers, being synthetic, have low moisture absorption, often less than 1%, causing poor breathability and trapping heat and sweat, which can lead to discomfort during extended use. Blankets made from protein fibers provide a more comfortable, breathable experience, especially in varying climates, whereas polyester blankets are less effective at moisture management.
Durability and Longevity of the Blankets
Protein fibers, such as wool or silk, offer excellent durability with natural resilience and resistance to wear, maintaining blanket integrity over extended use. Polyester fibers provide superior longevity through high tensile strength and resistance to stretching, shrinking, and abrasions, ensuring the blanket remains intact over time. While protein fiber blankets excel in breathability and comfort, polyester blankets outperform in moisture resistance and long-term durability.
Care, Maintenance, and Washing Requirements
Protein fibers, such as wool and silk, require gentle care including hand washing with mild detergents or dry cleaning to maintain softness and prevent shrinkage, while avoiding high heat during drying. Polyester fibers are durable and machine washable, resisting wrinkles and shrinking, and they dry quickly, making maintenance easier and more convenient. Proper care of protein fiber blankets extends their lifespan, whereas polyester blankets offer low-maintenance functionality suitable for everyday use.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Protein fibers such as wool and silk are naturally biodegradable and renewable, reducing environmental pollution compared to synthetic polyester fibers derived from petroleum. Polyester fiber production relies heavily on fossil fuels, emits greenhouse gases, and contributes to microplastic pollution during washing. Choosing protein fibers for blankets supports sustainable agriculture practices and minimizes long-term ecological damage, making them a more eco-friendly option.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Protein fibers like wool and silk generally have higher production costs compared to polyester fibers, leading to increased prices in the blanket market. Polyester fibers benefit from lower manufacturing expenses and widespread industrial production, making them more affordable and readily available in various blanket options. Market availability favors polyester due to its synthetic origin and mass production capabilities, while protein fiber blankets tend to occupy premium segments with limited availability.
Infographic: Protein fiber vs Polyester fiber for Blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com