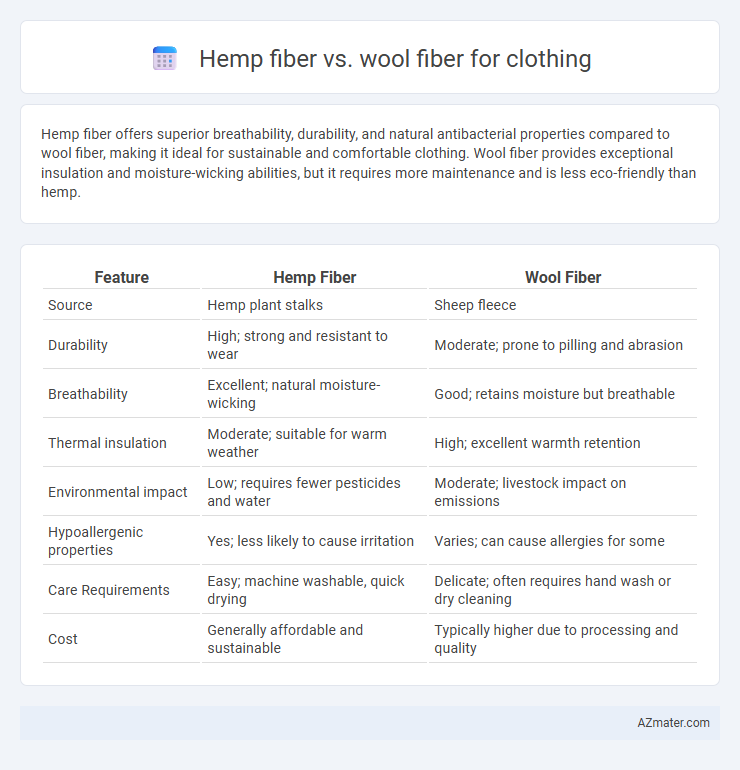
Hemp fiber offers superior breathability, durability, and natural antibacterial properties compared to wool fiber, making it ideal for sustainable and comfortable clothing. Wool fiber provides exceptional insulation and moisture-wicking abilities, but it requires more maintenance and is less eco-friendly than hemp.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp plant stalks | Sheep fleece |
| Durability | High; strong and resistant to wear | Moderate; prone to pilling and abrasion |
| Breathability | Excellent; natural moisture-wicking | Good; retains moisture but breathable |
| Thermal insulation | Moderate; suitable for warm weather | High; excellent warmth retention |
| Environmental impact | Low; requires fewer pesticides and water | Moderate; livestock impact on emissions |
| Hypoallergenic properties | Yes; less likely to cause irritation | Varies; can cause allergies for some |
| Care Requirements | Easy; machine washable, quick drying | Delicate; often requires hand wash or dry cleaning |
| Cost | Generally affordable and sustainable | Typically higher due to processing and quality |
Introduction to Hemp and Wool Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers exceptional durability, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties, making it increasingly popular in sustainable fashion. Wool fiber, sourced from the fleece of sheep, is renowned for its excellent insulation, moisture-wicking ability, and elasticity, contributing to superior warmth and comfort in garments. Both fibers provide unique textile qualities, with hemp excelling in strength and environmental benefits, while wool remains prized for its natural warmth and resilience.
Historical Context of Hemp and Wool in Textiles
Hemp fiber, cultivated for over 10,000 years, has historically been prized for its durability and breathability in textiles, especially in ancient Asia and Europe, while wool, sourced from sheep domesticated around 8000 BCE, became a staple in colder climates due to its excellent insulation properties. Both fibers played crucial roles in early textile development, with hemp often used for coarse fabrics and sails, and wool dominating garment production in medieval Europe for warmth. The resurgence of hemp in modern eco-friendly fashion highlights its sustainable qualities compared to traditional wool, which requires intensive animal husbandry.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Hemp fiber outperforms wool fiber in sustainability due to its rapid growth rate, minimal water requirements, and natural resistance to pests, reducing the need for harmful pesticides and fertilizers. Wool production, while renewable, involves high greenhouse gas emissions from sheep methane and requires significant land use, impacting biodiversity. Hemp's biodegradability and low-impact cultivation make it a more environmentally responsible choice for eco-conscious clothing brands and consumers.
Fiber Processing and Production Methods
Hemp fiber undergoes a retting process to separate the bast fibers from the stalk, followed by decortication and combing, resulting in durable, coarse fibers ideal for sustainable textile production. Wool fiber is harvested through shearing, then cleaned, carded, and spun into yarn, maintaining natural crimp and elasticity for insulation and comfort in clothing. Both fibers require specialized machinery, but hemp processing demands more water and time-intensive retting, whereas wool production focuses on managing lanolin and fiber consistency.
Durability and Longevity in Clothing
Hemp fiber exhibits exceptional durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting clothing that withstands repeated washing and harsh conditions. Wool fiber offers natural elasticity and resilience, allowing garments to maintain shape and integrity over time, particularly in cold and damp environments. Both fibers excel in longevity, but hemp's superior tensile strength provides enhanced abrasion resistance, while wool's lanolin content contributes to its moisture management and natural protection.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Hemp fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to wool, making it ideal for warm and humid climates. Wool fiber excels in thermal insulation and moisture retention, providing comfort in colder environments through its natural crimp structure. Both fibers are sustainable choices, but hemp's smooth texture is less likely to cause skin irritation, enhancing overall comfort for sensitive skin.
Thermal Insulation and Weather Suitability
Hemp fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it highly effective for thermal insulation in warm and humid climates. Wool fiber excels in retaining heat and regulating body temperature, providing exceptional insulation in cold and damp weather conditions. Combining hemp's durability and wool's insulating capabilities results in versatile clothing suited for diverse environmental challenges.
Allergenic Properties and Skin Sensitivity
Hemp fiber is naturally hypoallergenic and resists mold and mildew, making it ideal for sensitive skin and those prone to allergies. Wool fibers, particularly from sheep, contain lanolin, which can cause irritation or allergic reactions in individuals with sensitive skin. Choosing hemp clothing helps minimize skin irritation due to its breathability and antimicrobial properties, whereas wool requires careful treatment to reduce allergenic effects.
Care, Maintenance, and Longevity
Hemp fiber requires minimal care due to its natural resistance to mold, UV rays, and wear, making it highly durable and ideal for sustainable clothing with less frequent washing. Wool fiber demands careful maintenance, including gentle washing and proper storage to prevent shrinkage, moth damage, and loss of softness, ensuring long-lasting performance in garments. Both fibers offer longevity, but hemp's strength and resistance to environmental stressors give it an advantage in durability over time.
Cost, Availability, and Consumer Trends
Hemp fiber offers a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to wool fiber, with lower production expenses due to its fast-growing nature and minimal need for pesticides, making it increasingly popular among eco-conscious consumers. Wool fiber, while generally more expensive due to labor-intensive shearing and processing, remains widely available and favored for its natural warmth and moisture-wicking properties. Consumer trends show a growing shift toward hemp as demand rises for durable, breathable, and environmentally friendly clothing materials, especially in the sustainable fashion market.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Wool fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com