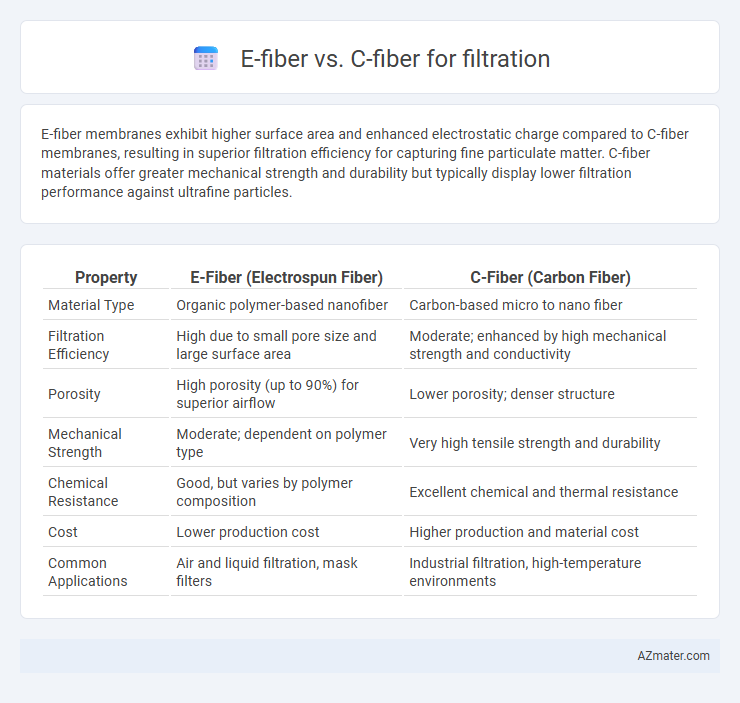
E-fiber membranes exhibit higher surface area and enhanced electrostatic charge compared to C-fiber membranes, resulting in superior filtration efficiency for capturing fine particulate matter. C-fiber materials offer greater mechanical strength and durability but typically display lower filtration performance against ultrafine particles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber (Electrospun Fiber) | C-Fiber (Carbon Fiber) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Organic polymer-based nanofiber | Carbon-based micro to nano fiber |
| Filtration Efficiency | High due to small pore size and large surface area | Moderate; enhanced by high mechanical strength and conductivity |
| Porosity | High porosity (up to 90%) for superior airflow | Lower porosity; denser structure |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate; dependent on polymer type | Very high tensile strength and durability |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but varies by polymer composition | Excellent chemical and thermal resistance |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production and material cost |
| Common Applications | Air and liquid filtration, mask filters | Industrial filtration, high-temperature environments |
Introduction to Fiber Types in Filtration
E-fiber and C-fiber represent two distinct fiber types commonly used in filtration applications, each offering unique structural and functional properties. E-fibers, typically characterized by their electrospun nanofiber morphology, provide high surface area and fine pore structures ideal for capturing ultrafine particles. C-fibers, often conventional microfibers, deliver robust mechanical strength and larger pore sizes suitable for high-flow filtration systems targeting larger particulate matter.
What are E-fibers?
E-fibers, or electrospun fibers, are ultra-fine fibers created through electrospinning, characterized by high surface area and porosity, which make them highly effective for filtration applications. Unlike traditional C-fibers (cellulose fibers), E-fibers offer superior mechanical strength, enhanced filtration efficiency, and the ability to capture nanoscale particles. These properties enable E-fiber filters to provide improved particulate matter removal and longer service life in air and liquid filtration systems.
What are C-fibers?
C-fibers are ultrafine synthetic fibers derived from cellulose acetate, known for their exceptional filtration efficiency due to their nanoscale diameter and high surface area. These fibers create dense, uniform filter media that effectively trap submicron particles, making them ideal for advanced air and liquid filtration applications. Compared to E-fibers, C-fibers offer superior aerosol capture and longer filter service life, driven by their fine fiber matrix and enhanced mechanical properties.
Key Differences Between E-fiber and C-fiber
E-fiber and C-fiber differ primarily in diameter and filtration efficiency, with E-fiber featuring ultra-fine diameters around 1-2 microns that enhance particulate capture, whereas C-fiber typically has thicker diameters ranging from 5 to 15 microns. E-fiber materials offer higher surface area-to-volume ratios, resulting in improved mechanical trapping and electrostatic retention of contaminants compared to C-fiber. While E-fiber excels in removing submicron particles with lower pressure drop, C-fiber provides durability and strength suitable for coarse filtration applications.
Filtration Efficiency: E-fiber vs C-fiber
E-fibers exhibit superior filtration efficiency compared to C-fibers due to their smaller diameter and greater surface area, enabling enhanced capture of fine particulate matter. The electrostatic properties of E-fibers further improve their ability to attract and retain submicron particles, which makes them ideal for high-performance filtration applications. In contrast, C-fibers, with larger diameters and lower surface charge, provide less effective filtration, particularly for ultrafine particles.
Applications of E-fiber in Filtration
E-fiber filtration media excels in applications requiring fine particulate capture and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for air and liquid filtration systems in medical, pharmaceutical, and cleanroom environments. Its electrospun nanofiber structure enables high surface area and enhanced filtration efficiency, particularly for submicron particles and pathogens. E-fibers are also increasingly utilized in HVAC filters and personal protective equipment, providing superior breathability and contaminant removal compared to conventional C-fibers.
Applications of C-fiber in Filtration
C-fiber membranes exhibit superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them ideal for aggressive solvent filtration and high-temperature applications. Their nonwoven structure provides high tensile strength and durability, suitable for industrial liquid filtration and air purification systems. These properties enable C-fiber filters to effectively remove contaminants in harsh environments where E-fiber membranes might degrade.
Durability and Lifespan: Comparative Analysis
E-fiber filters exhibit superior durability and extended lifespan compared to C-fiber filters due to their enhanced resistance to chemical degradation and mechanical wear. The structural stability of E-fibers maintains filtration efficiency over prolonged use in harsh industrial environments, resulting in reduced replacement frequency and lower operational costs. In contrast, C-fiber filters tend to degrade faster under similar conditions, limiting their effective service life and increasing maintenance demands.
Cost Considerations: E-fiber vs C-fiber
E-fibers offer a cost-effective solution in filtration due to their synthetic origin, which allows for consistent production and lower raw material expenses compared to natural C-fibers, which often involve higher procurement costs. The longer lifespan and durability of E-fiber filters reduce replacement frequency, further decreasing long-term operational expenses. While C-fibers provide superior biodegradability, their fluctuating supply and processing costs make E-fibers more economically favorable for large-scale filtration applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Optimal Filtration
E-fiber membranes provide high mechanical strength and chemical resistance, making them ideal for aggressive filtration environments and extended use in harsh conditions. C-fiber membranes offer superior filtration precision and biocompatibility, suited for delicate applications such as pharmaceutical and medical-grade filtrations. Selecting the right fiber type hinges on balancing filtration efficiency, chemical compatibility, and operational durability to achieve optimal performance.
Infographic: E-fiber vs C-fiber for Filtration
 azmater.com
azmater.com