Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers superior biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional cotton fiber, making it ideal for sustainable nonwoven wipes. Nonwoven wipes made with Ingeo fiber exhibit enhanced strength, softness, and environmental benefits over cotton-based alternatives.
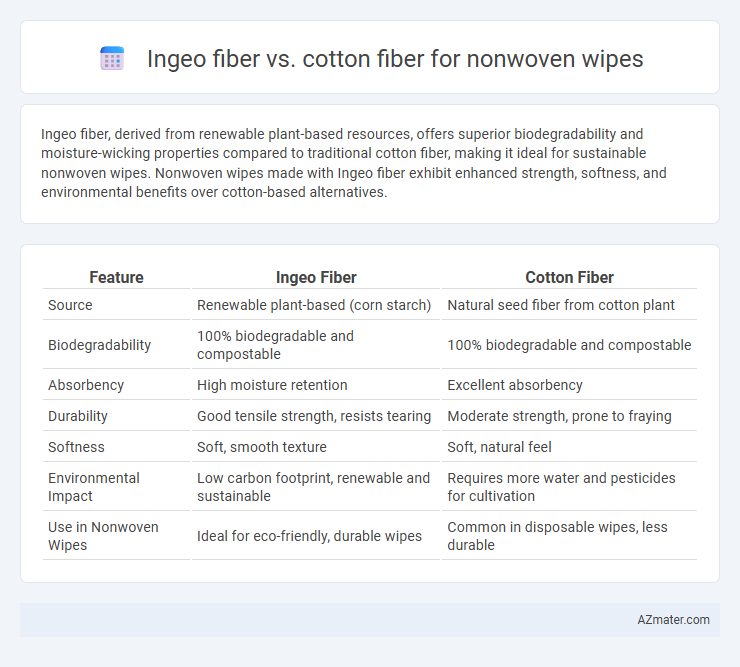
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable plant-based (corn starch) | Natural seed fiber from cotton plant |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable and compostable | 100% biodegradable and compostable |
| Absorbency | High moisture retention | Excellent absorbency |
| Durability | Good tensile strength, resists tearing | Moderate strength, prone to fraying |
| Softness | Soft, smooth texture | Soft, natural feel |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, renewable and sustainable | Requires more water and pesticides for cultivation |
| Use in Nonwoven Wipes | Ideal for eco-friendly, durable wipes | Common in disposable wipes, less durable |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Cotton Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers biodegradability and sustainability advantages for nonwoven wipes compared to conventional cotton fiber, which is natural but resource-intensive to produce. Cotton fibers are known for their softness, absorbency, and strength, making them a traditional choice for wipes, while Ingeo fibers provide a lower environmental footprint due to renewable sourcing and compostability. The distinct molecular structure of Ingeo fibers enhances moisture management and durability in nonwoven applications, positioning it as a competitive alternative to cotton in eco-friendly wipe products.
What Are Nonwoven Wipes?
Nonwoven wipes are fabric-like materials constructed from fibers bonded through chemical, mechanical, heat, or solvent treatments rather than woven or knitted processes. Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources such as polylactic acid (PLA), offers biodegradability and sustainability advantages over traditional cotton fibers commonly used in nonwoven wipes. Nonwoven wipes made with Ingeo fibers provide effective cleaning performance with an eco-friendly profile, making them suitable for disposable hygiene products and sustainable cleaning applications.
Origins and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant-based sources such as corn starch through a fermentation and polymerization process that produces polylactic acid (PLA) biopolymer, which is then spun into fibers. Cotton fiber originates from the natural cellulose of cotton plants, harvested and processed through ginning, carding, and spinning to create soft, absorbent textile fibers. The Ingeo fiber's biotechnological production emphasizes sustainability and reduced carbon footprint, whereas cotton production is traditionally agriculture-dependent with significant water and land usage impacts.
Physical Properties Comparison
Ingeo fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and superior elasticity compared to cotton fiber, enhancing durability and flexibility in nonwoven wipes. Its uniform fiber diameter and hydrophobic nature contribute to improved liquid repellency and faster drying times, while cotton fibers provide greater absorbency but lower wet strength. The biodegradability of Ingeo fiber offers sustainable performance without compromising functionality, making it a competitive alternative to traditional cotton in wipe applications.
Environmental Impact: Ingeo vs Cotton
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, offers a lower carbon footprint and faster biodegradability compared to traditional cotton fiber used in nonwoven wipes. Cotton cultivation demands significant water, pesticide inputs, and arable land, contributing to environmental strain and biodiversity loss. Ingeo's sustainable production process and compostability enhance eco-friendly waste management, making it a preferable choice over cotton for reducing the environmental impact of nonwoven wipes.
Performance in Wipe Applications
Ingeo fiber offers superior moisture absorption and quick-drying capabilities compared to cotton fiber, enhancing wipe efficiency for cleaning and sanitizing tasks. Its inherent biodegradability and softness provide a gentle yet durable texture, ideal for sensitive surfaces and skin contact in nonwoven wipes. Cotton fiber, while naturally strong and breathable, tends to retain more moisture and requires chemical treatments to achieve similar antimicrobial performance found in Ingeo-based wipes.
Biodegradability and Compostability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based polylactic acid (PLA), offers superior biodegradability and industrial compostability compared to traditional cotton fiber, which decomposes naturally but at a slower rate and often requires specific conditions to break down effectively. Ingeo fibers biodegrade within 90 to 180 days under industrial composting, releasing minimal greenhouse gases, whereas cotton fibers, while natural, may resist quick degradation due to chemical treatments and processing additives. Choosing Ingeo fiber for nonwoven wipes supports sustainable waste management by aligning with circular economy goals through certified compostability standards like EN 13432 and ASTM D6400.
Cost and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers a competitive cost structure compared to conventional cotton fiber, primarily due to scalable fermentation-based production processes. Market availability of Ingeo fiber is expanding rapidly as manufacturers prioritize sustainable materials, while cotton fiber remains widely accessible but faces price volatility linked to agricultural conditions. Nonwoven wipe producers increasingly favor Ingeo fiber for its consistent supply and environmental benefits, positioning it as a cost-effective alternative in growing green textile markets.
Skin Safety and Allergenicity
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based polylactic acid, offers superior skin safety compared to traditional cotton fiber due to its hypoallergenic and antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of irritation and allergic reactions in nonwoven wipes. Cotton fibers, while natural, can retain impurities and pesticides that may trigger sensitivities or skin allergies. Nonwoven wipes made from Ingeo fiber provide a cleaner, gentler alternative for sensitive skin, enhancing overall user comfort and minimizing allergen exposure.
Future Trends in Nonwoven Wipe Materials
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable polylactic acid, offers superior biodegradability and sustainability compared to traditional cotton fiber, making it a preferred choice for future nonwoven wipe materials. Advancements in Ingeo fiber technology enhance its softness, strength, and moisture absorption, aligning with increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly and high-performance wipes. The shift towards bio-based fibers like Ingeo is driven by stringent environmental regulations and growing market trends favoring sustainable, compostable, and non-toxic nonwoven wipes.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Cotton fiber for Nonwoven wipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com