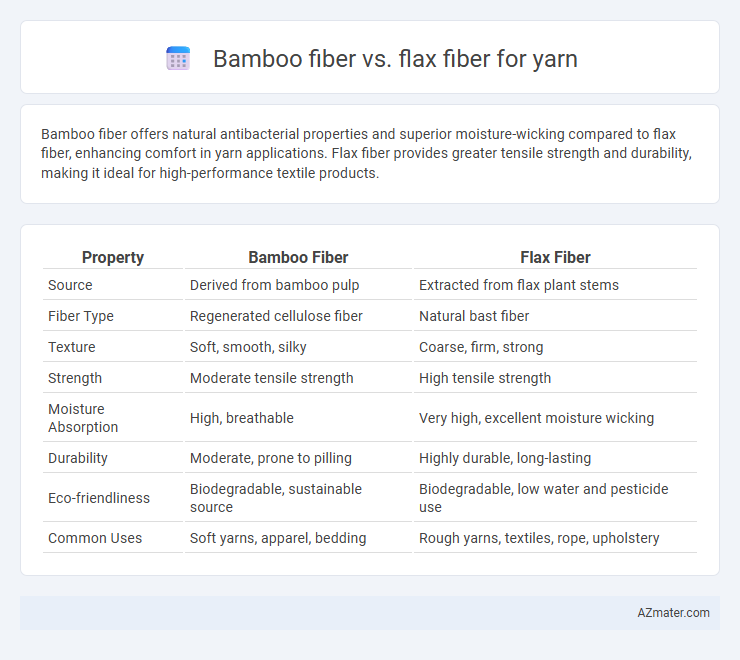
Bamboo fiber offers natural antibacterial properties and superior moisture-wicking compared to flax fiber, enhancing comfort in yarn applications. Flax fiber provides greater tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for high-performance textile products.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bamboo Fiber | Flax Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from bamboo pulp | Extracted from flax plant stems |
| Fiber Type | Regenerated cellulose fiber | Natural bast fiber |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silky | Coarse, firm, strong |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Moisture Absorption | High, breathable | Very high, excellent moisture wicking |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to pilling | Highly durable, long-lasting |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable source | Biodegradable, low water and pesticide use |
| Common Uses | Soft yarns, apparel, bedding | Rough yarns, textiles, rope, upholstery |
Introduction to Bamboo and Flax Fibers
Bamboo fiber, derived from the cellulose of bamboo plants, offers natural antibacterial properties, high moisture absorption, and a soft texture, making it ideal for breathable yarn in textile production. Flax fiber, extracted from the stalks of the flax plant, is renowned for its strength, durability, and moisture-wicking abilities, commonly used in linen yarn for its crisp and sturdy characteristics. Both fibers provide sustainable alternatives to synthetic yarns with distinct properties tailored for eco-friendly and performance-driven fabric applications.
Origin and Sustainability of Bamboo vs Flax
Bamboo fiber originates from the fast-growing bamboo plant, known for its rapid renewability and minimal water requirements, making it a highly sustainable resource. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant cultivated primarily in Europe, boasts a centuries-old tradition with low pesticide use and biodegradable properties, contributing to eco-friendly textile production. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives to conventional materials but differ in growth cycles and environmental impact, with bamboo's rapid growth and regenerative qualities often giving it a sustainability edge over flax.
Fiber Extraction Processes Compared
Bamboo fiber extraction typically involves chemical or mechanical processes, with chemical methods using solvents like sodium hydroxide to break down bamboo into viscose or rayon, yielding softer and finer fibers for yarn production. Flax fiber extraction relies on retting, a natural microbial process that separates fibers from the stalk, followed by scutching and hackling to refine long, strong fibers ideal for durable yarns. Mechanical extraction of flax preserves fiber strength but is labor-intensive, whereas bamboo's chemical process enhances softness but may reduce environmental sustainability.
Yarn Texture and Feel: Bamboo vs Flax
Bamboo fiber yarn is renowned for its silky smooth texture and natural sheen, offering a soft, breathable, and moisture-wicking feel ideal for sensitive skin. Flax fiber yarn, derived from flax plants, features a coarser, stiffer texture with a matte finish, providing a strong and durable yarn that softens with use but retains a slightly crisp hand. Bamboo yarn is typically smoother and cooler to the touch than flax yarn, making it preferable for lightweight, luxurious textiles.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent tensile strength and natural antimicrobial properties, making it highly durable for yarn applications in moisture-prone environments. Flax fiber, known for its superior stiffness and resilience, offers exceptional wear resistance and longevity, especially in high-stress textile uses. Comparative studies indicate flax fiber outperforms bamboo fiber in mechanical strength, but bamboo's flexibility enhances durability in dynamic fabric conditions.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Bamboo fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption due to its micro-gaps and micro-holes structure, which enhances breathability and keeps the fabric dry and comfortable. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, offers moderate moisture-wicking properties with excellent breathability attributed to its natural lignin and cellulose content. Yarn made from bamboo fiber excels in moisture management for activewear, while flax fiber yarn provides breathable comfort in lightweight, casual textiles.
Environmental Impact: Bamboo Fiber vs Flax Fiber
Bamboo fiber production requires less water and grows rapidly without pesticides, making it a highly renewable resource with a low environmental footprint, while flax fiber cultivation also benefits the environment by needing minimal water and fewer agrochemicals. Processing bamboo into yarn often involves chemical treatments that can impact ecosystems, whereas flax fiber processing tends to be more eco-friendly due to its natural retting process. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives to synthetic yarns, but flax fiber generally ranks higher in biodegradability and lower chemical use, contributing to a cleaner environmental impact.
Dyeing Properties and Colorfastness
Bamboo fiber exhibits excellent dye absorption due to its porous structure, resulting in vibrant and deep colors, while flax fiber has moderate dye affinity but offers superior color retention under sunlight. Bamboo yarn tends to have better moisture-wicking qualities, enhancing dye penetration and fastness, whereas flax yarn provides stronger resistance to fading after multiple washes. Both fibers support eco-friendly dyeing processes, but bamboo's natural antibacterial properties can reduce the need for chemical mordants, improving overall color durability.
Popular Uses in Yarn and Textiles
Bamboo fiber is popular in yarn production for its softness, moisture-wicking properties, and natural antibacterial qualities, making it ideal for activewear, baby clothing, and eco-friendly textiles. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, is highly valued for its strength, durability, and breathability, commonly used in linen fabrics, home textiles, and summer apparel. Both fibers serve distinct markets, with bamboo favored for comfort and sustainability, while flax is preferred for its texture and longevity in traditional and high-end textile applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Project
Bamboo fiber offers exceptional softness, moisture-wicking properties, and natural antibacterial benefits, making it ideal for projects requiring breathable, eco-friendly yarn with a silky texture. Flax fiber, derived from the flax plant, provides superior strength, durability, and subtle luster, perfect for sturdy, lightweight yarn suited to linen-like textiles and accessories. Selecting bamboo fiber or flax fiber for yarn depends on whether your project prioritizes softness and moisture management or resilience and a crisp finish.
Infographic: Bamboo fiber vs Flax fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com