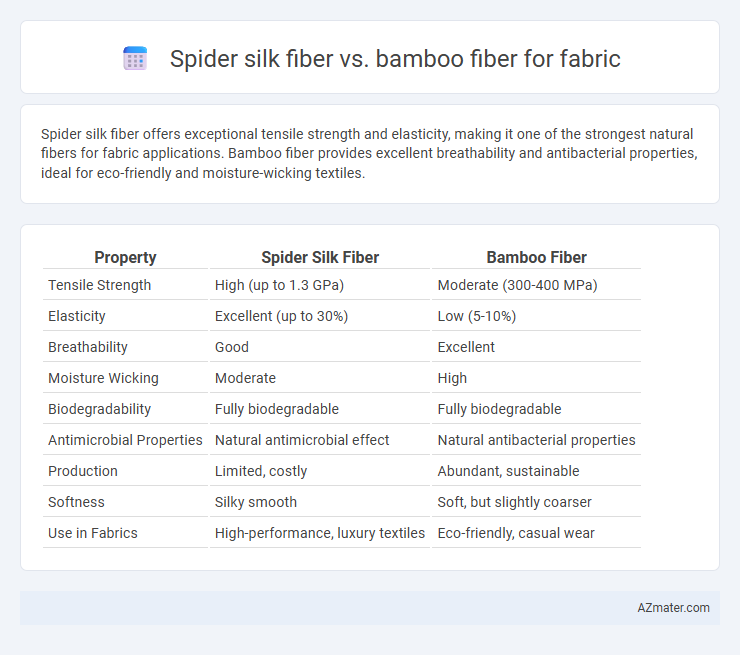
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it one of the strongest natural fibers for fabric applications. Bamboo fiber provides excellent breathability and antibacterial properties, ideal for eco-friendly and moisture-wicking textiles.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 1.3 GPa) | Moderate (300-400 MPa) |
| Elasticity | Excellent (up to 30%) | Low (5-10%) |
| Breathability | Good | Excellent |
| Moisture Wicking | Moderate | High |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Fully biodegradable |
| Antimicrobial Properties | Natural antimicrobial effect | Natural antibacterial properties |
| Production | Limited, costly | Abundant, sustainable |
| Softness | Silky smooth | Soft, but slightly coarser |
| Use in Fabrics | High-performance, luxury textiles | Eco-friendly, casual wear |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Bamboo Fibers
Spider silk fiber, renowned for its exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, outperforms many natural fibers, including bamboo, in durability and flexibility. Bamboo fiber, derived from the pulp of bamboo grass, is prized for its antimicrobial properties and sustainability but typically lacks the tensile resilience of spider silk. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic materials, with spider silk excelling in performance textiles and bamboo favored for softness and breathability in fabric production.
Origins and Production Processes
Spider silk fiber originates from the protein strands secreted by spiders, harvested through a careful and labor-intensive process involving the collection of silk from spider webs or genetically engineered microorganisms. Bamboo fiber is derived from bamboo plants, produced either mechanically by crushing bamboo culms and chemically treating the fibers or chemically through processes like viscose production to extract soft, textile-grade fibers. Spider silk's production is limited by low yield and complexity, whereas bamboo fiber benefits from rapid plant growth and scalable industrial manufacturing techniques.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength with tensile strength reaching up to 1.3 GPa, making it one of the strongest natural fibers available, while bamboo fiber typically shows tensile strength between 250 and 500 MPa. The durability of spider silk is enhanced by its elasticity and toughness, allowing it to withstand significant strain without breaking, whereas bamboo fiber offers good durability but tends to degrade more quickly under repeated stress or environmental exposure. Fabrics made from spider silk fibers deliver exceptional performance in strength and longevity compared to bamboo-based textiles, which are valued more for their sustainability and breathability.
Flexibility and Elasticity
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior elasticity compared to bamboo fiber, stretching up to five times its original length without breaking, which enhances fabric flexibility and durability. Bamboo fiber, while naturally soft and breathable, has limited stretchability, resulting in less elastic fabrics prone to deformation under stress. The remarkable combination of spider silk's tensile strength and elasticity makes it highly sought after for creating flexible, high-performance textiles compared to bamboo-based fabrics.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional biodegradability and requires minimal water and chemicals during production, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional textiles. Bamboo fiber, while renewable and fast-growing with low pesticide use, often involves energy-intensive processing methods that can generate pollutants. Comparatively, spider silk provides a more sustainable fabric option due to its natural production processes and lower environmental footprint.
Comfort and Breathability in Textiles
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional softness and a smooth texture that enhances comfort, while its natural moisture-wicking properties promote superior breathability in textiles. Bamboo fiber also provides a comfortable, silky feel with excellent breathability, thanks to its porous structure that allows better air circulation and moisture absorption. Compared to bamboo, spider silk is stronger and more elastic, resulting in fabrics that conform better to the body without sacrificing ventilation.
Moisture Management and Antimicrobial Properties
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional moisture management due to its ability to wick sweat away from the skin rapidly, maintaining a dry and comfortable fabric microclimate. Bamboo fiber also offers excellent moisture absorption and quick drying properties, enhancing breathability and sweat evaporation. Both fibers possess natural antimicrobial properties; spider silk contains antimicrobial peptides that inhibit bacterial growth, while bamboo fiber's inherent bio-agent, bamboo kun, effectively reduces odor-causing bacteria, making both ideal for hygienic fabric applications.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and natural biodegradability, making it ideal for high-performance textiles used in sportswear, medical sutures, and luxury fashion. Bamboo fiber provides excellent moisture-wicking properties, antibacterial benefits, and a smooth texture, which makes it popular in eco-friendly clothing, bedding, and activewear. Both fibers are valued in the textile industry for sustainable and functional fabric production, but spider silk's mechanical properties give it a unique edge in specialized technical applications.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Spider silk fiber remains significantly more expensive than bamboo fiber due to complex harvesting and low yield, limiting its commercial availability primarily to luxury and specialty textiles. Bamboo fiber, derived from fast-growing bamboo plants using eco-friendly processes, offers a cost-effective, abundant alternative widely available in mainstream fabric markets. Fabric manufacturers favor bamboo fiber for scalable production and affordability, while spider silk's high production costs restrict its use to niche applications despite superior strength and softness.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Spider silk fiber, renowned for its exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, is emerging as a revolutionary material in sustainable fabric innovation, with biotech companies advancing synthetic production methods to scale its commercial use. Bamboo fiber, valued for its natural antimicrobial properties, breathability, and rapid renewability, continues to gain popularity in eco-friendly textile markets, with innovations targeting enhanced softness and durability through advanced mechanical and chemical processing techniques. Future prospects for both fibers hinge on integrating cutting-edge nanotechnology and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes to meet increasing demands for high-performance, sustainable fabrics in fashion and technical applications.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Bamboo fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com