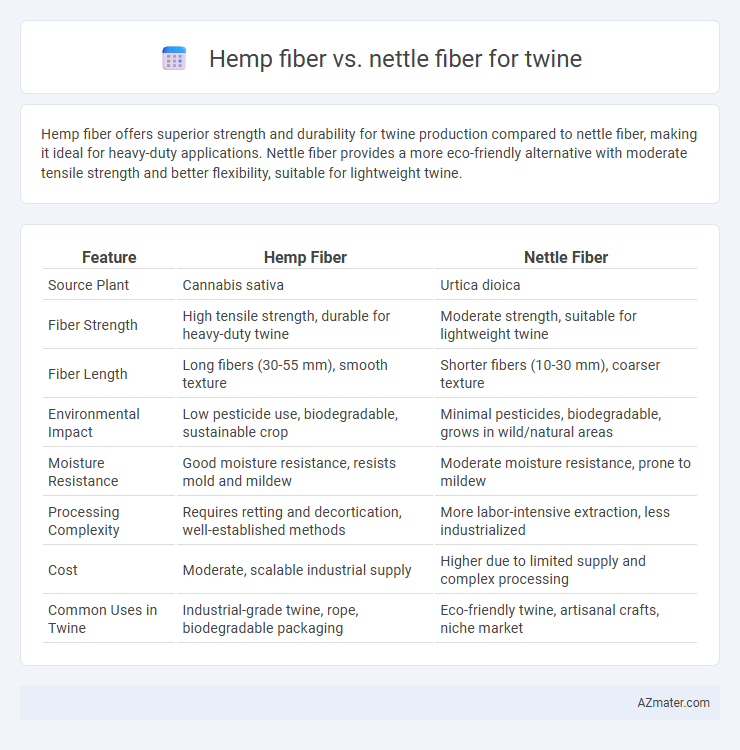
Hemp fiber offers superior strength and durability for twine production compared to nettle fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Nettle fiber provides a more eco-friendly alternative with moderate tensile strength and better flexibility, suitable for lightweight twine.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Nettle Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Plant | Cannabis sativa | Urtica dioica |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength, durable for heavy-duty twine | Moderate strength, suitable for lightweight twine |
| Fiber Length | Long fibers (30-55 mm), smooth texture | Shorter fibers (10-30 mm), coarser texture |
| Environmental Impact | Low pesticide use, biodegradable, sustainable crop | Minimal pesticides, biodegradable, grows in wild/natural areas |
| Moisture Resistance | Good moisture resistance, resists mold and mildew | Moderate moisture resistance, prone to mildew |
| Processing Complexity | Requires retting and decortication, well-established methods | More labor-intensive extraction, less industrialized |
| Cost | Moderate, scalable industrial supply | Higher due to limited supply and complex processing |
| Common Uses in Twine | Industrial-grade twine, rope, biodegradable packaging | Eco-friendly twine, artisanal crafts, niche market |
Introduction to Hemp and Nettle Fibers
Hemp fiber is derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its robust strength, durability, and resistance to rotting, making it ideal for twine production. Nettle fiber, extracted from the stems of the Urtica dioica plant, offers a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative with a smooth texture and comparable tensile strength. Both fibers exhibit excellent biodegradability and versatility, but hemp twine is often preferred for heavier-duty applications due to its higher lignin content and tensile resilience.
Historical Uses of Hemp and Nettle in Twine Making
Hemp fiber has been historically prized for twine making due to its exceptional strength and durability, dating back to ancient civilizations where it was used for ship rigging and agricultural binding. Nettle fiber, while less common, was also utilized in Europe for twine and cordage, valued for its fine texture and flexibility in delicate tasks. Both fibers played crucial roles in traditional crafts, with hemp dominating large-scale industrial uses and nettle serving more specialized, artisanal purposes.
Botanical Differences Between Hemp and Nettle
Hemp fiber, derived from Cannabis sativa, is characterized by its bast fibers that grow in long, strong bundles within the stalk's outer layer, offering high durability ideal for twine production. Nettle fiber originates from Urtica dioica, featuring finer bast fibers with a more delicate, softer texture, resulting in twine with increased flexibility but less tensile strength compared to hemp. The botanical distinction lies in their fiber structure and composition; hemp fibers contain higher cellulose content and lignin, contributing to greater rigidity, whereas nettle fibers have lower lignin levels, enhancing pliability and ease of processing for specific twine applications.
Fiber Extraction and Processing Methods
Hemp fiber extraction primarily involves retting, either water or dew retting, followed by mechanical decortication to separate bast fibers, resulting in durable and strong twine. Nettle fiber extraction uses a similar process, with dew retting preferred for its dual bast and core fiber yield, and requires careful mechanical separation to preserve fiber length and quality. Both fibers demand thorough drying and combing to enhance tensile strength and produce high-quality twine suitable for various industrial applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and durability compared to nettle fiber, making it ideal for heavy-duty twine applications. Hemp's long, coarse fibers resist wear and environmental degradation, ensuring longevity under stress. Nettle fiber, while strong, is generally finer and less abrasion-resistant, limiting its use in high-strength twine but offering more flexibility for lighter tasks.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber and nettle fiber both offer sustainable alternatives for twine production, with hemp demonstrating superior environmental benefits due to its rapid growth and minimal need for pesticides or herbicides. Nettle fiber, while also renewable, requires careful harvesting to prevent overharvesting and maintain biodiversity, making its sustainability dependent on responsible management. Both fibers are biodegradable and contribute to reducing reliance on synthetic materials, but hemp's higher yield per acre often results in a lower overall environmental impact.
Texture, Appearance, and Handle
Hemp fiber offers a coarse texture with a sturdy, rough appearance ideal for durable twine needing strong grip and resilience, while nettle fiber presents a smoother, finer texture with a natural sheen that lends a visually appealing finish and softer handle. The handle of hemp twine feels rigid and abrasive, suited for heavy-duty applications, whereas nettle twine delivers a gentle, flexible touch making it preferred for delicate wrapping and artisanal crafts. Both fibers provide sustainable options, but hemp's robust structure contrasts with nettle's lightweight elegance in texture and overall tactile experience.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp fiber is generally more cost-effective and widely available in the market compared to nettle fiber, which remains niche and less commercially produced. The established hemp industry benefits from large-scale cultivation and processing infrastructure, driving down prices and ensuring steady supply. In contrast, nettle fiber, valued for its eco-friendly properties, commands higher prices due to limited production and less developed market channels.
Applications in Modern Twine Production
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty twine applications such as agriculture and shipping. Nettle fiber, valued for its natural softness and flexibility, is increasingly used in eco-friendly packaging and craft twine where biodegradability and comfort are prioritized. Both fibers contribute to sustainable twine production, with hemp excelling in structural performance and nettle supporting niche markets focused on environmental impact.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Twine
Hemp fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty twine applications requiring long-lasting performance. Nettle fiber provides a softer texture and natural resistance to pests and mildew, suitable for eco-friendly and lightweight twine uses. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing the needed strength and environmental benefits, with hemp excelling in robustness and nettle favored for sustainability and gentleness.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Nettle fiber for Twine
 azmater.com
azmater.com