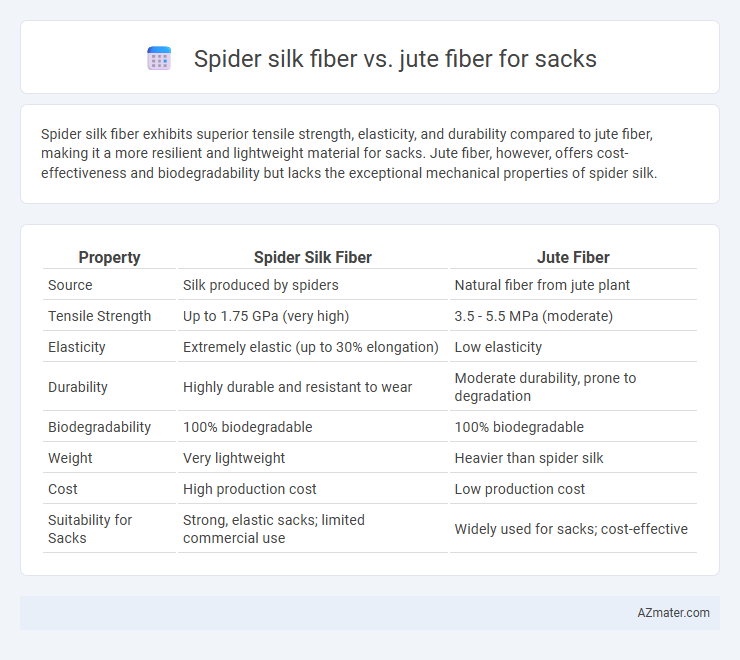
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, elasticity, and durability compared to jute fiber, making it a more resilient and lightweight material for sacks. Jute fiber, however, offers cost-effectiveness and biodegradability but lacks the exceptional mechanical properties of spider silk.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Silk produced by spiders | Natural fiber from jute plant |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.75 GPa (very high) | 3.5 - 5.5 MPa (moderate) |
| Elasticity | Extremely elastic (up to 30% elongation) | Low elasticity |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to wear | Moderate durability, prone to degradation |
| Biodegradability | 100% biodegradable | 100% biodegradable |
| Weight | Very lightweight | Heavier than spider silk |
| Cost | High production cost | Low production cost |
| Suitability for Sacks | Strong, elastic sacks; limited commercial use | Widely used for sacks; cost-effective |
Introduction to Natural Fibers for Sacks
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a highly durable and resilient material for sacks. Jute fiber, a traditional natural fiber, provides cost-effective, biodegradable, and breathable sacks with moderate strength suitable for agricultural and industrial use. Comparing these fibers highlights the advantages of spider silk's superior mechanical properties against jute's widespread availability and eco-friendliness in natural fiber sack applications.
Overview of Spider Silk Fiber Properties
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, surpassing many natural fibers, including jute, while maintaining remarkable elasticity and toughness. Its lightweight and biodegradable nature make it an eco-friendly alternative for sack production, offering superior durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. Unlike jute fiber, spider silk demonstrates excellent moisture-wicking properties and a high strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing sack performance for heavy-duty use.
Jute Fiber: Characteristics and Applications
Jute fiber, known for its high tensile strength and biodegradability, offers excellent moisture retention and breathability, making it ideal for sack production. Unlike spider silk fiber, which is rare and expensive, jute is abundant, cost-effective, and widely used in packaging, agriculture, and textiles due to its durability and eco-friendly properties. Its natural resistance to pests and ability to decompose without harming the environment further enhance its suitability for sustainable sack manufacturing.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, often surpassing steel by weight, making it exceptionally strong for sack applications. In comparison, jute fiber provides good strength but is more prone to wear and tear under heavy loads or prolonged usage. Spider silk's remarkable durability and elasticity contribute to longer-lasting sacks, whereas jute fibers may deteriorate faster in harsh environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber offers superior biodegradability and minimal environmental footprint compared to jute fiber, which, while natural and renewable, often requires high water usage and extensive pesticide application in cultivation. The production of spider silk involves less land and chemical input, making it a more sustainable option for eco-friendly sacks. Jute's rapid growth cycle contributes to carbon sequestration, but spider silk's potential for biodegradability and lower resource consumption positions it as a cutting-edge material for sustainable packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis: Spider Silk vs. Jute Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits significantly higher production costs due to complex harvesting and limited scalability compared to widely available jute fiber. Jute fiber costs remain low owing to large-scale cultivation and simpler extraction processes, making it more economically viable for sack manufacturing. Despite spider silk's superior strength and durability, jute fiber remains the preferred choice for cost-sensitive applications.
Biodegradability and Eco-friendliness
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior biodegradability and eco-friendliness compared to jute fiber due to its protein-based natural polymer structure, which decomposes rapidly without releasing harmful substances. Jute fiber, although also biodegradable, often undergoes chemical treatments during processing, potentially reducing its overall environmental benefits. The sustainable cultivation of jute coupled with minimal resource use supports eco-friendly practices, but spider silk's renewable production and minimal ecological footprint make it ideal for green packaging applications like sacks.
Weight, Flexibility, and Handling
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it significantly lighter than jute fiber for sack production while maintaining durability. Its superior flexibility allows for easy manipulation and shaping, enhancing the handling experience during manufacturing and use. In contrast, jute fiber is coarser and heavier, which can reduce flexibility and make sacks bulkier and less comfortable to handle over extended periods.
Industrial Scalability and Production Challenges
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, but its industrial scalability is hindered by low yield and complex harvesting processes, limiting mass production for sacks. In contrast, jute fiber benefits from established large-scale cultivation and processing infrastructure, enabling cost-effective and scalable production despite lower mechanical properties. Production challenges for spider silk include bioengineering constraints and high costs, whereas jute faces issues like moisture sensitivity and variability in fiber quality affecting sack durability.
Future Prospects in Sack Manufacturing
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary material for future sack manufacturing with enhanced durability and environmental benefits. Jute fiber, while sustainable and cost-effective, faces limitations in tensile strength and moisture resistance, which may constrain its application as sack demands evolve. Advancements in bioengineering spider silk production could lead to scalable, eco-friendly sacks that outperform jute in longevity and versatility, driving a shift in the packaging industry.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Jute fiber for Sack
 azmater.com
azmater.com