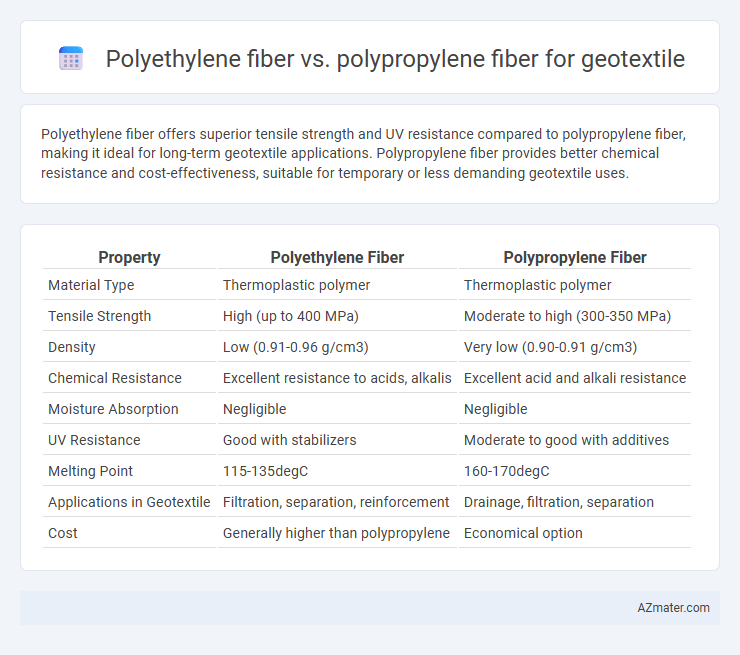
Polyethylene fiber offers superior tensile strength and UV resistance compared to polypropylene fiber, making it ideal for long-term geotextile applications. Polypropylene fiber provides better chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, suitable for temporary or less demanding geotextile uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 400 MPa) | Moderate to high (300-350 MPa) |
| Density | Low (0.91-0.96 g/cm3) | Very low (0.90-0.91 g/cm3) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to acids, alkalis | Excellent acid and alkali resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Negligible | Negligible |
| UV Resistance | Good with stabilizers | Moderate to good with additives |
| Melting Point | 115-135degC | 160-170degC |
| Applications in Geotextile | Filtration, separation, reinforcement | Drainage, filtration, separation |
| Cost | Generally higher than polypropylene | Economical option |
Introduction to Geotextile Fibers
Polyethylene fiber and polypropylene fiber are widely used materials in geotextile manufacturing due to their excellent chemical resistance, durability, and lightweight properties. Polypropylene fibers offer superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and biological degradation, making them ideal for soil stabilization and drainage applications. Polyethylene fibers provide higher tensile strength and UV resistance, enhancing the performance and longevity of geotextile products in harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high tensile strength and excellent chemical resistance, is a popular choice for geotextile applications requiring durability and long-term performance. Its low density and hydrophobic nature make it effective in drainage and filtration systems by preventing water absorption and maintaining structural integrity. Compared to polypropylene fiber, polyethylene offers superior resistance to UV degradation and abrasion, enhancing the lifespan of geotextile products in harsh environmental conditions.
Overview of Polypropylene Fiber
Polypropylene fiber is a synthetic polymer widely used in geotextile applications due to its excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high tensile strength. It offers superior durability against moisture, UV exposure, and microbial attacks compared to polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for soil stabilization and erosion control. Polypropylene fibers provide cost-effective solutions with enhanced filtration and drainage properties essential for geotechnical engineering projects.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and better elongation at break compared to polypropylene fiber, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility in geotextiles. Polypropylene fiber offers superior resistance to chemical degradation and UV exposure, though it generally has lower abrasion resistance and tensile modulus. The choice between polyethylene and polypropylene fibers for geotextiles depends on the specific mechanical performance needs, with polyethylene favored for high-strength applications and polypropylene preferred for cost-effective solutions with moderate mechanical demands.
Chemical Resistance and Durability
Polyethylene fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to polypropylene fibers, making them ideal for geotextile applications exposed to harsh chemicals and aggressive environments. Polypropylene fibers offer excellent durability under mechanical stress but tend to degrade more rapidly when exposed to UV radiation and certain chemicals. Selecting polyethylene fiber enhances the longevity and performance of geotextiles in chemically demanding conditions, while polypropylene remains cost-effective for less aggressive environments.
UV Resistance and Weathering Performance
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior UV resistance and weathering performance compared to polypropylene fiber in geotextile applications, making it more suitable for long-term exposure to sunlight and harsh environmental conditions. Polyethylene's molecular structure offers enhanced durability against UV degradation, reducing brittleness and maintaining mechanical strength over time. In contrast, polypropylene fibers tend to degrade faster under UV exposure, which limits their longevity in outdoor geotextile use.
Cost Analysis of Polyethylene vs Polypropylene
Polypropylene fibers generally offer a more cost-effective solution for geotextile applications compared to polyethylene fibers due to lower raw material and production expenses. Polyethylene fibers, while providing higher tensile strength and chemical resistance, tend to have higher manufacturing costs that increase the overall price of polyethylene-based geotextiles. For large-scale projects prioritizing budget constraints, polypropylene geotextiles often deliver the best value without compromising essential performance parameters.
Applications in Geotextile Engineering
Polyethylene fiber offers high tensile strength and resistance to UV degradation, making it ideal for geotextile applications requiring durability and long-term stability in soil reinforcement and erosion control. Polypropylene fiber is widely favored for its chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in filtration, drainage, and separation functions within geotextile engineering. Both fibers contribute to different performance criteria, with polyethylene enhancing structural reinforcement while polypropylene excels in lightweight and flexible geosynthetic solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber in geotextiles offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, leading to a longer lifespan and reduced environmental waste. Polypropylene fiber is lighter and more cost-effective but less UV resistant, causing faster degradation and higher replacement rates, which impacts sustainability negatively. Both materials are recyclable, but polyethylene's greater resilience typically results in a lower overall environmental footprint in geotechnical applications.
Recommendations for Geotextile Selection
Polyethylene fiber offers excellent resistance to UV radiation and chemical degradation, making it ideal for long-term geotextile applications in harsh environmental conditions. Polypropylene fiber provides superior tensile strength and better drainage properties, suitable for soil stabilization and erosion control in moderate climates. Select polyethylene fiber geotextiles for durability and chemical resistance, while polypropylene fiber is recommended for cost-effective performance and efficient water permeability in geotechnical projects.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Geotextile
 azmater.com
azmater.com