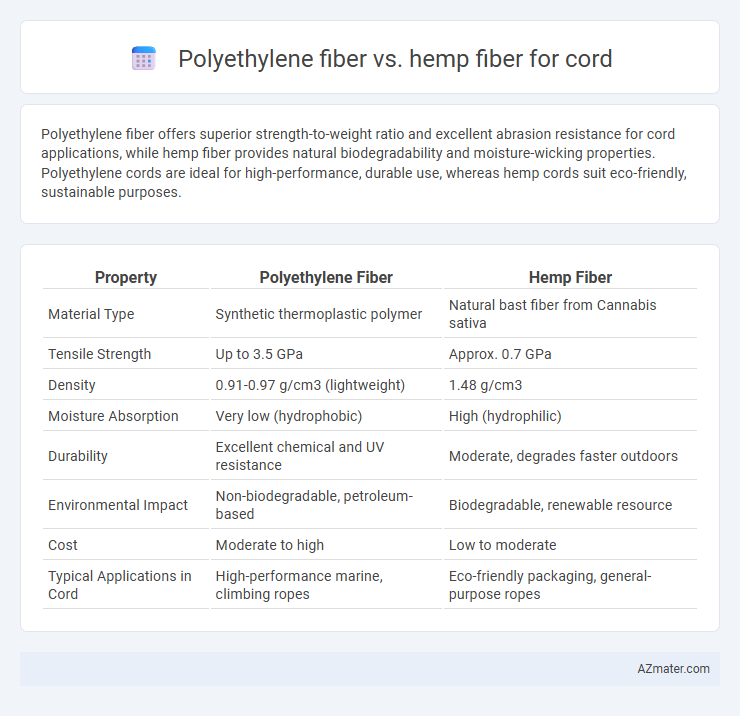
Polyethylene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and excellent abrasion resistance for cord applications, while hemp fiber provides natural biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties. Polyethylene cords are ideal for high-performance, durable use, whereas hemp cords suit eco-friendly, sustainable purposes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic thermoplastic polymer | Natural bast fiber from Cannabis sativa |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.5 GPa | Approx. 0.7 GPa |
| Density | 0.91-0.97 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 1.48 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low (hydrophobic) | High (hydrophilic) |
| Durability | Excellent chemical and UV resistance | Moderate, degrades faster outdoors |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Typical Applications in Cord | High-performance marine, climbing ropes | Eco-friendly packaging, general-purpose ropes |
Introduction to Polyethylene and Hemp Fibers
Polyethylene fiber, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to chemicals and moisture, offers superior durability and flexibility for cord applications. Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, provides natural biodegradability, high tensile strength, and resistance to ultraviolet light, making it an eco-friendly alternative for sustainable cord production. Both fibers deliver unique advantages in cord manufacturing, with polyethylene emphasizing synthetic performance and hemp prioritizing environmental benefits.
Overview of Cord Applications
Polyethylene fiber cords offer exceptional tensile strength, chemical resistance, and lightweight properties, making them ideal for high-performance marine, climbing, and industrial applications. Hemp fiber cords, valued for their natural biodegradability, durability, and resistance to UV light, are commonly used in eco-friendly packaging, agricultural twine, and crafts. Both fibers serve critical roles in various industries, with polyethylene favored for demanding technical uses and hemp prioritized for sustainable, environmentally conscious applications.
Material Composition and Production
Polyethylene fiber, composed mainly of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), is a synthetic fiber known for its high tensile strength and resistance to moisture and chemicals, produced through gel-spinning or melt-spinning processes. Hemp fiber, derived from the bast of the Cannabis sativa plant, is a natural cellulose-based fiber valued for its biodegradability, breathability, and durability, harvested through retting, decortication, and scutching. Production of polyethylene cord emphasizes advanced polymer technology and precision extrusion, while hemp cord manufacturing relies on traditional mechanical processing and eco-friendly treatment methods.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength with tensile strength values reaching up to 3.6 GPa, making it highly resistant to stretching and breaking under load in cord applications. Hemp fiber, while having a lower tensile strength around 800 MPa, offers excellent durability through natural resistance to UV degradation and moisture, ensuring long-term performance in outdoor environments. The synthetic nature of polyethylene results in enhanced wear resistance and longer lifespan, whereas hemp provides eco-friendly advantages with biodegradability and sustainable growth.
Flexibility and Handling
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior flexibility and excellent tensile strength, making it highly maneuverable and ideal for dynamic cord applications requiring resistance to bending and abrasion. Hemp fiber, though natural and eco-friendly, provides moderate flexibility but tends to be stiffer and less elastic, resulting in harsher handling and reduced durability under repetitive stress. For demanding uses where flexibility and easy handling are critical, polyethylene fiber cords outperform hemp fibers due to their enhanced pliability and resilience.
Environmental Impact
Polyethylene fiber, derived from petroleum, has a significant carbon footprint and is non-biodegradable, contributing to long-term environmental pollution. Hemp fiber is a sustainable alternative, being biodegradable, renewable, and requiring fewer pesticides and water during cultivation. Choosing hemp fiber for cord production reduces plastic waste and supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices, making it a preferable option for minimizing environmental impact.
Weather and Chemical Resistance
Polyethylene fiber offers superior weather resistance with excellent UV stability and moisture repellency, making it ideal for outdoor cord applications exposed to harsh sunlight and rain. Hemp fiber demonstrates strong chemical resistance to many solvents and biodegradable properties but is more susceptible to degradation from prolonged moisture and UV exposure. For long-term durability in extreme weather and chemical environments, polyethylene fiber provides a more reliable performance than hemp fiber.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers cost-effective production with widespread availability due to its synthetic manufacturing process, making it a common choice for cord applications. Hemp fiber, derived from natural sources, typically incurs higher costs influenced by agricultural factors and limited large-scale industrial supply. Although hemp provides eco-friendly advantages, polyethylene's affordability and consistent availability often drive preference in cost-sensitive markets.
Maintenance and Longevity
Polyethylene fiber cords exhibit exceptional resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation, resulting in minimal maintenance and a significantly longer lifespan compared to hemp fiber cords. Hemp fibers, while biodegradable and eco-friendly, tend to absorb water and degrade faster when exposed to harsh environmental conditions, requiring more frequent upkeep such as drying and treatment to prevent mold and rot. The superior durability and low maintenance of polyethylene fibers make them a preferred choice for applications demanding extended longevity and resilience.
Best Uses and Recommendations
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to moisture and chemicals, is ideal for marine ropes, fishing lines, and outdoor cords requiring durability and low stretch. Hemp fiber, a natural and biodegradable option, offers excellent abrasion resistance and UV stability, making it suitable for eco-friendly applications such as gardening, decorative cords, and sustainable packaging. For heavy-duty, long-lasting performance in harsh environments, polyethylene fiber is recommended, while hemp fiber excels in environmentally conscious projects and light-to-moderate load uses.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Hemp fiber for Cord
 azmater.com
azmater.com