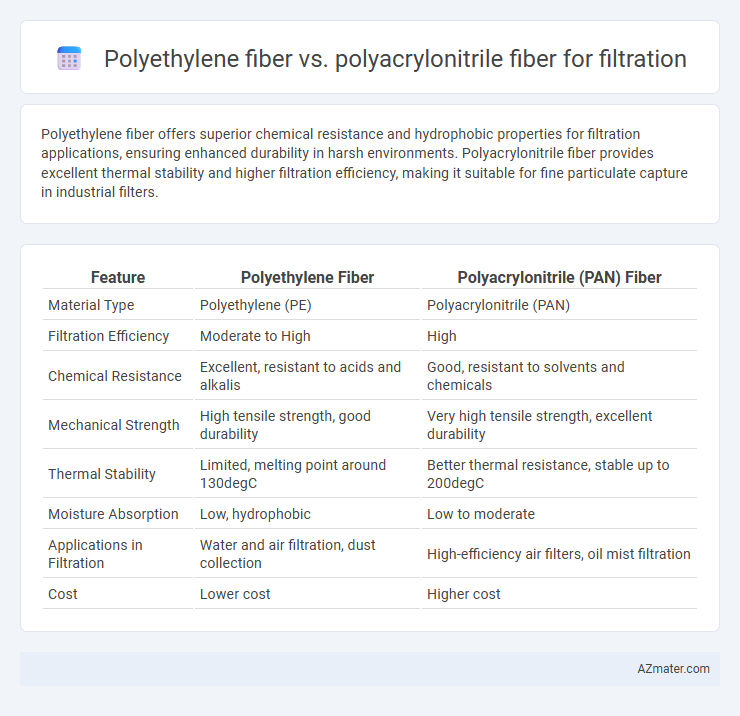
Polyethylene fiber offers superior chemical resistance and hydrophobic properties for filtration applications, ensuring enhanced durability in harsh environments. Polyacrylonitrile fiber provides excellent thermal stability and higher filtration efficiency, making it suitable for fine particulate capture in industrial filters.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyethylene Fiber | Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyethylene (PE) | Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) |
| Filtration Efficiency | Moderate to High | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids and alkalis | Good, resistant to solvents and chemicals |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good durability | Very high tensile strength, excellent durability |
| Thermal Stability | Limited, melting point around 130degC | Better thermal resistance, stable up to 200degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, hydrophobic | Low to moderate |
| Applications in Filtration | Water and air filtration, dust collection | High-efficiency air filters, oil mist filtration |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Filtration Fiber Materials
Polyethylene fiber offers high chemical resistance and hydrophobic properties, making it suitable for filtration applications involving oily or acidic substances. Polyacrylonitrile fiber exhibits excellent thermal stability and fine fiber diameter, providing superior filtration efficiency in capturing fine particulate matter. Selection between these fibers depends on the specific filtration requirements such as chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and desired particle retention.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent chemical resistance, is widely used in filtration applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance. Its hydrophobic nature and low moisture absorption make it ideal for filtering liquids and gases without compromising filter efficiency or structural integrity. Compared to polyacrylonitrile fiber, polyethylene fiber offers superior resistance to alkaline and acidic environments, enhancing filter lifespan in aggressive processing conditions.
Overview of Polyacrylonitrile Fiber
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber is widely used in filtration due to its excellent chemical resistance, thermal stability, and superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene fiber. PAN fibers offer high surface area and porosity, enabling efficient capture of fine particulate matter and improved filtration performance in air and water applications. The inherent hydrophobicity and resistance to solvents make PAN fibers ideal for industrial filtration systems requiring durability and longevity under harsh conditions.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance and hydrophobicity, making it ideal for filtration applications involving oily or aqueous environments, while Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber offers higher tensile strength and thermal stability, which suits high-temperature filtration processes. The lower density of polyethylene fiber contributes to a lighter filtration medium, whereas PAN fiber's inherent flame resistance enhances safety in industrial filtration systems. Both fibers possess distinct morphological structures affecting pore size control and filtration efficiency, with PAN fibers typically providing finer filtration due to their smaller diameter and higher surface area.
Chemical Resistance and Stability
Polyethylene fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making it highly suitable for harsh filtration environments. Polyacrylonitrile fiber offers excellent thermal stability and resistance to oxidative degradation but is less resistant to strong acids and bases compared to polyethylene. The chemical inertness and stability of polyethylene fibers provide longer service life in aggressive chemical filtration applications, while polyacrylonitrile fibers excel in high-temperature filtration where oxidative stability is critical.
Filtration Efficiency and Performance
Polyethylene fiber offers high filtration efficiency due to its hydrophobic nature and fine fiber diameter, which enhances particle capture in air and liquid filtration applications. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber exhibits superior chemical resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for filtration tasks under harsh conditions and high temperatures. In performance comparison, polyethylene fibers provide lower pressure drop and longer filter life in standard environments, while PAN fibers excel in aggressive chemical filtration and elevated temperature durability.
Application Suitability in Filtration
Polyethylene fiber offers excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, making it ideal for filtration applications involving aggressive chemicals and moisture-laden environments. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber provides superior thermal stability and fine fiber diameter, enhancing its ability to filter fine particulate matter in high-temperature industrial processes. The application suitability depends on the specific filtration environment, with polyethylene favored for chemical inertness and polyacrylonitrile for thermal resistance and particulate precision.
Durability and Longevity
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional chemical resistance and tensile strength, making it highly durable and ideal for filtration applications exposed to harsh environments. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber excels in thermal stability and abrasion resistance, contributing to its long service life in high-temperature filtration systems. The choice between polyethylene and PAN fibers depends on the specific filtration requirements, with polyethylene favored for durability in corrosive conditions and PAN preferred for longevity under thermal stress.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyethylene fiber offers excellent chemical resistance and durability in filtration but is less biodegradable, contributing to long-term environmental persistence. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fiber, while also durable and efficient in capturing particles, tends to have higher energy consumption during production, impacting its sustainability profile. Sustainable filtration solutions increasingly favor fibers with recyclability and lower carbon footprints, positioning advancements in biodegradable or bio-based PAN alternatives as promising for environmental improvements.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers a cost-effective solution for filtration due to its low production expenses and widespread availability, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications. Polyacrylonitrile fiber, while generally more expensive because of complex manufacturing processes, provides superior chemical resistance and thermal stability but is less accessible in bulk quantities. The choice between polyethylene and polyacrylonitrile fibers depends heavily on budget constraints and the need for specific filtration performance characteristics.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Polyacrylonitrile fiber for Filtration
 azmater.com
azmater.com