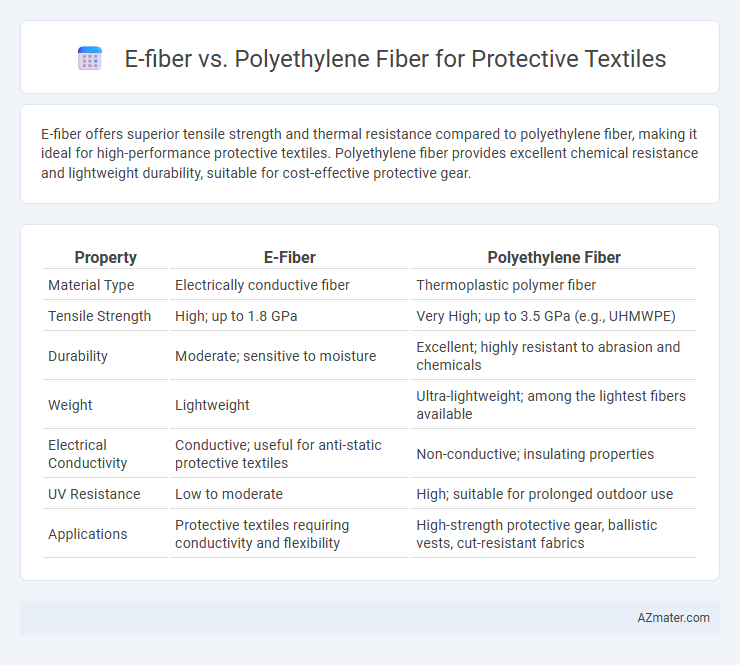
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for high-performance protective textiles. Polyethylene fiber provides excellent chemical resistance and lightweight durability, suitable for cost-effective protective gear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Electrically conductive fiber | Thermoplastic polymer fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High; up to 1.8 GPa | Very High; up to 3.5 GPa (e.g., UHMWPE) |
| Durability | Moderate; sensitive to moisture | Excellent; highly resistant to abrasion and chemicals |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight; among the lightest fibers available |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive; useful for anti-static protective textiles | Non-conductive; insulating properties |
| UV Resistance | Low to moderate | High; suitable for prolonged outdoor use |
| Applications | Protective textiles requiring conductivity and flexibility | High-strength protective gear, ballistic vests, cut-resistant fabrics |
Introduction to Protective Textiles
Protective textiles incorporating E-fiber and polyethylene fiber offer distinct advantages in durability and resistance to environmental hazards. E-fiber, known for its exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, enhances protective gear against mechanical impacts and heat exposure. Polyethylene fiber provides superior chemical resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for protective clothing in hazardous chemical and ballistic applications.
Overview of E-fiber Technology
E-fiber technology utilizes ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) fibers that offer exceptional tensile strength, lightweight properties, and superior cut resistance, making them ideal for protective textiles. Compared to traditional polyethylene fibers, E-fibers deliver enhanced durability and higher performance in impact and abrasion resistance while maintaining flexibility. The advanced molecular alignment in E-fibers ensures greater energy absorption, boosting wearer protection in ballistic and stab-resistant applications.
Polyethylene Fiber: Characteristics and Uses
Polyethylene fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for protective textiles in hazardous environments. Its low moisture absorption and excellent UV resistance enhance durability and performance in outdoor applications such as ballistic vests and cut-resistant gloves. Compared to E-fiber, polyethylene fiber offers superior abrasion resistance and lighter weight, which improve wearer comfort without compromising safety.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
E-fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polyethylene fiber, with tensile strength typically exceeding 4 GPa, making it highly effective for protective textiles requiring high durability. Polyethylene fiber, especially ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers tensile strength around 2.5 to 3.5 GPa but provides better impact resistance and lighter weight. The stiffness of E-fiber is significantly higher, enhancing load-bearing capacity in protective gear, whereas polyethylene fibers excel in flexibility and abrasion resistance.
Flexibility and Comfort Differences
E-fiber offers superior flexibility compared to polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for protective textiles that require enhanced movement and adaptability. Polyethylene fibers tend to be stiffer, which can compromise comfort during prolonged wear in protective gear. The advanced pliability of E-fiber contributes to better ergonomic performance without sacrificing protective capabilities.
Thermal Stability and Flame Resistance
E-fiber exhibits superior thermal stability with a decomposition temperature often exceeding 500degC, making it highly suitable for protective textiles exposed to extreme heat. Polyethylene fiber, while lightweight and strong, has a lower melting point around 130degC and tends to ignite more easily, limiting its flame resistance in high-temperature applications. Protective textiles incorporating E-fibers demonstrate enhanced flame retardancy and sustained mechanical integrity under thermal stress compared to their polyethylene fiber counterparts.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
E-fiber offers superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene fiber, effectively minimizing water absorption and maintaining structural integrity in wet environments. Polyethylene fiber excels in chemical resistance, especially against acids and alkalis, outperforming many other fibers including E-fiber in harsh chemical exposures. Protective textiles combining E-fiber and polyethylene fiber provide balanced advantages, ensuring durability against moisture while resisting a broad spectrum of chemical agents.
Applications in Protective Apparel
E-fiber, known for its high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, is widely used in protective apparel for fire-resistant clothing and ballistic vests, offering enhanced durability and heat resistance. Polyethylene fiber, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), provides exceptional impact resistance and lightweight comfort, making it ideal for stab-proof vests and cut-resistant gloves. Both fibers contribute to advanced protective textiles by optimizing strength-to-weight ratio and performance in extreme environments.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
E-fiber, derived from renewable sources like cellulose, offers superior biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based polyethylene fiber, making it a more sustainable choice for protective textiles. Polyethylene fibers, while durable and resistant to chemicals, pose significant environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradability and reliance on fossil fuels. The shift toward E-fiber integration in protective textiles supports circular economy principles and reduces microplastic pollution in ecosystems.
Future Trends in Protective Fiber Development
E-fiber, derived from ethylene, offers lightweight and high tensile strength properties, positioning it as a promising material for next-generation protective textiles. Polyethylene fiber, particularly ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), continues to dominate due to its exceptional impact resistance and durability in ballistic and cut-resistant applications. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid composites combining E-fiber and polyethylene fibers to enhance multifunctional protection while maintaining comfort and flexibility in protective gear.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Protective Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com