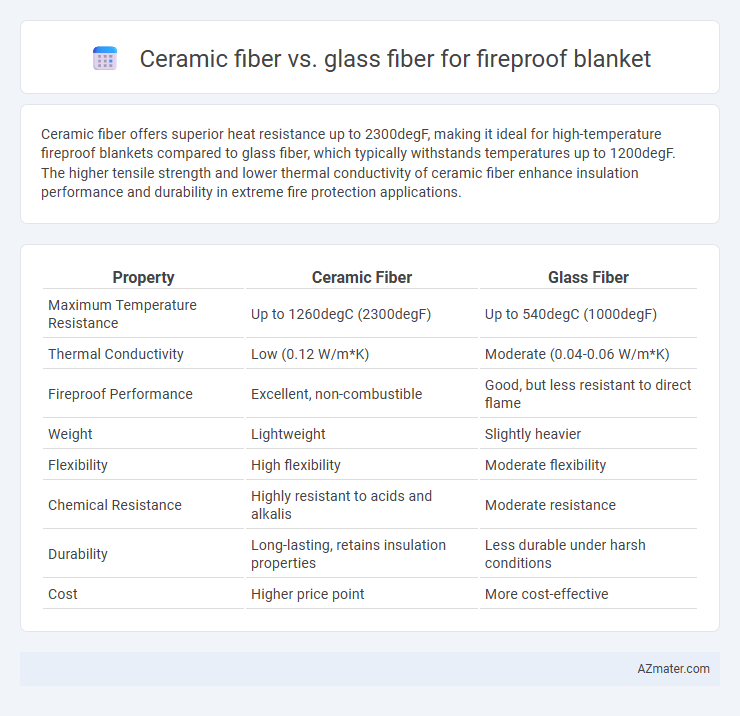
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance up to 2300degF, making it ideal for high-temperature fireproof blankets compared to glass fiber, which typically withstands temperatures up to 1200degF. The higher tensile strength and lower thermal conductivity of ceramic fiber enhance insulation performance and durability in extreme fire protection applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 540degC (1000degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.12 W/m*K) | Moderate (0.04-0.06 W/m*K) |
| Fireproof Performance | Excellent, non-combustible | Good, but less resistant to direct flame |
| Weight | Lightweight | Slightly heavier |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Highly resistant to acids and alkalis | Moderate resistance |
| Durability | Long-lasting, retains insulation properties | Less durable under harsh conditions |
| Cost | Higher price point | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Fireproof Blankets
Fireproof blankets made from ceramic fiber offer superior heat resistance and insulation compared to those made from glass fiber, making them ideal for high-temperature applications exceeding 1800degF (982degC). Glass fiber fireproof blankets provide satisfactory thermal protection up to 1200degF (649degC) and are valued for their lightweight and cost-effective properties. Both materials are essential in industries requiring effective fire containment and personal safety during emergency fire situations.
Understanding Ceramic Fiber: Properties and Uses
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance with operating temperatures up to 1800degF compared to glass fiber's lower threshold around 1200degF, making it ideal for high-temperature fireproof blankets. Its low thermal conductivity and excellent thermal shock resistance provide effective insulation and durability during rapid temperature changes. Commonly used in industrial furnaces, kiln linings, and fireproof blankets, ceramic fiber ensures enhanced fire protection and energy efficiency in extreme heat environments.
Overview of Glass Fiber: Features and Applications
Glass fiber fireproof blankets offer excellent thermal insulation with a melting point around 1,400degC, making them suitable for high-temperature fire protection. They provide strong chemical resistance, durability, and flexibility, ensuring long-lasting performance in industrial, construction, and automotive applications. Commonly used for heat containment, pipe insulation, and fire barriers, glass fiber blankets balance cost-effectiveness and reliable fireproofing.
Thermal Resistance Comparison
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance for fireproof blankets, withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC) compared to glass fiber's maximum tolerance around 1200degF (650degC). This enhanced thermal stability makes ceramic fiber blankets ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnaces and kilns. Glass fiber, while effective at moderate heat levels, offers lower insulation efficiency and degrades faster under extreme thermal exposure.
Fireproof Performance Analysis
Ceramic fiber offers superior fireproof performance compared to glass fiber, withstanding temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC) versus glass fiber's limit around 1000degF (540degC). Its low thermal conductivity ensures enhanced insulation and minimal heat transfer, making it ideal for high-temperature fireproof blankets. Glass fiber, while more affordable and resistant to moisture, cannot match ceramic fiber's durability and long-term fire resistance in extreme conditions.
Durability and Lifespan
Ceramic fiber fireproof blankets exhibit superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to glass fiber counterparts due to their higher resistance to extreme temperatures up to 2300degF (1260degC) and minimal fiber degradation over time. Glass fiber blankets typically withstand temperatures up to 1000degF (538degC) but are prone to fiber breakage and reduced structural integrity with prolonged heat exposure. The enhanced thermal stability and mechanical strength of ceramic fiber make it the preferred choice for applications demanding long-term fire resistance and durability.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Ceramic fiber fireproof blankets are significantly lighter than glass fiber variants, often weighing up to 30% less, enhancing ease of handling and installation. Their superior flexibility allows ceramic fibers to conform more easily to irregular surfaces without cracking or breaking, making them ideal for applications requiring tight seals and contours. In contrast, glass fiber blankets, while durable, tend to be thicker and stiffer, which can limit their adaptability in complex fireproofing scenarios.
Safety and Health Considerations
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance and lower off-gassing compared to glass fiber, making it safer for prolonged exposure in fireproof blanket applications. Glass fiber may release respirable fibers that can irritate skin, eyes, and respiratory systems, necessitating protective equipment during handling. Both materials require adherence to safety regulations, but ceramic fiber's low bio-persistence reduces long-term health risks, enhancing workplace safety.
Cost Effectiveness: Ceramic vs Glass Fiber
Ceramic fiber fireproof blankets typically offer higher temperature resistance but come at a premium cost compared to glass fiber options, which are more affordable and suitable for moderate heat applications. Glass fiber blankets provide cost-effective fire protection with decent durability, ideal for budget-conscious projects with lower temperature requirements. Evaluating long-term expenses, ceramic fiber's superior thermal performance can reduce maintenance and replacement costs, making it cost-effective for high-heat industrial environments despite its initial higher price.
Best Choice for Fireproof Blanket Applications
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance and higher melting points compared to glass fiber, making it the best choice for fireproof blanket applications requiring exposure to extreme temperatures above 1260degC (2300degF). It offers excellent insulation properties, low thermal conductivity, and greater durability under prolonged high-heat conditions, which ensures enhanced fire protection and longevity in industrial and firefighting settings. Glass fiber, while more cost-effective and flexible, is better suited for moderate temperature ranges below 540degC (1000degF) and provides less thermal stability and durability for demanding fireproof blanket uses.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Glass fiber for Fireproof Blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com