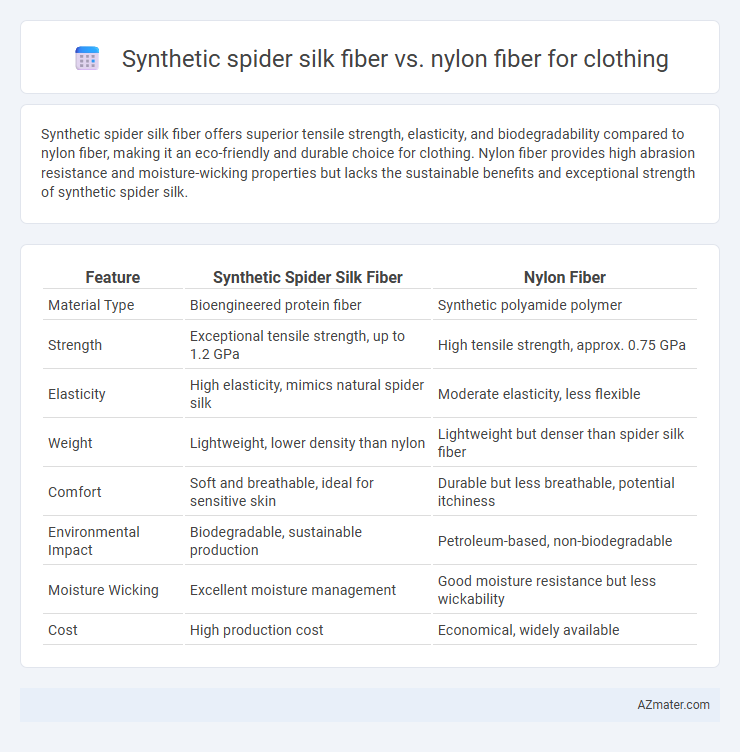
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to nylon fiber, making it an eco-friendly and durable choice for clothing. Nylon fiber provides high abrasion resistance and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the sustainable benefits and exceptional strength of synthetic spider silk.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bioengineered protein fiber | Synthetic polyamide polymer |
| Strength | Exceptional tensile strength, up to 1.2 GPa | High tensile strength, approx. 0.75 GPa |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, mimics natural spider silk | Moderate elasticity, less flexible |
| Weight | Lightweight, lower density than nylon | Lightweight but denser than spider silk fiber |
| Comfort | Soft and breathable, ideal for sensitive skin | Durable but less breathable, potential itchiness |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, sustainable production | Petroleum-based, non-biodegradable |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent moisture management | Good moisture resistance but less wickability |
| Cost | High production cost | Economical, widely available |
Introduction to Synthetic Spider Silk and Nylon Fibers
Synthetic spider silk fiber mimics the natural protein structure of spider silk, offering exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a promising material for sustainable clothing. Nylon fiber, a synthetic polyamide, is widely used in textiles for its durability, abrasion resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. The unique molecular composition of synthetic spider silk enables superior comfort and environmental benefits compared to conventional nylon clothing fibers.
History and Development of Spider Silk and Nylon
Synthetic spider silk fiber traces its roots to the early 2000s when scientists began replicating the natural protein structure of orb-weaver spider silk, known for its remarkable tensile strength and elasticity; innovations in genetic engineering allowed bacteria and yeast to produce silk proteins, enabling scalable fiber production. Nylon fiber, developed in 1935 by Wallace Carothers at DuPont, marked the first commercially successful synthetic polymer for textiles, revolutionizing the clothing industry with its durability, elasticity, and ease of manufacture. Both fibers have evolved through extensive research and development efforts, with synthetic spider silk emerging as a sustainable, high-performance alternative to traditional nylon materials.
Production Methods: Bioengineering vs Synthetic Polymerization
Synthetic spider silk fiber is produced through bioengineering techniques that involve genetically modifying organisms such as bacteria, yeast, or plants to produce silk proteins, followed by controlled spinning processes that mimic natural spider silk formation. Nylon fiber, in contrast, is manufactured via synthetic polymerization, involving the chemical reaction of monomers like adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine to form long polymer chains, followed by extrusion and drawing into fibers. Bioengineered synthetic spider silk offers advantages in biodegradability and strength-to-weight ratio, while nylon production relies on petrochemical sources and energy-intensive polymerization methods.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Elasticity, and Durability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength compared to nylon fiber, offering enhanced resistance to breaking under stress. Its elasticity allows for greater stretch and recovery without deformation, providing improved comfort and fit in clothing applications. Durability-wise, synthetic spider silk resists wear and environmental degradation more effectively than nylon, ensuring longer-lasting garments.
Comfort and Wearability in Clothing
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to nylon fiber, enhancing overall comfort during prolonged wear. Its lightweight and hypoallergenic nature minimizes skin irritation, making it ideal for sensitive skin and activewear applications. Nylon fiber, while durable and elastic, often traps heat and moisture, which can reduce comfort and increase wearability challenges in high-performance clothing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits significantly lower environmental impact compared to nylon fiber due to its biodegradability and production process that requires less energy and water. Unlike nylon, which is derived from petrochemicals and contributes to microplastic pollution, synthetic spider silk is made through bioengineered protein synthesis, reducing carbon emissions and waste. This sustainable alternative supports circular fashion by decomposing naturally and promoting reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior biodegradability compared to nylon fiber, breaking down more efficiently in natural environments and reducing long-term plastic pollution associated with clothing waste. Nylon fibers, derived from petrochemicals, resist decomposition and contribute significantly to microplastic contamination in ecosystems during washing and landfill degradation. End-of-life considerations favor synthetic spider silk, as its natural protein structure supports composting and eco-friendly disposal methods, whereas nylon requires energy-intensive recycling or ends up persisting in landfills for centuries.
Cost and Commercial Scalability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior strength and elasticity compared to nylon fiber, making it a highly durable option for clothing applications. However, its high production costs and complex biosynthetic processes currently limit commercial scalability, whereas nylon benefits from well-established, cost-effective manufacturing and widespread availability. As advancements in biotechnology reduce expenses, synthetic spider silk has the potential to challenge nylon's dominance in the textile industry.
Applications in Fashion and Activewear
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional nylon fiber, making it ideal for high-performance activewear and luxury fashion garments. Its lightweight and biodegradable nature enhance comfort and sustainability, catering to eco-conscious consumers seeking durable, breathable fabrics. Nylon fiber remains popular for its cost-effectiveness and abrasion resistance but falls short in biodegradability and elasticity, limiting its use in innovative, sustainable fashion applications.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Fiber Technology
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers promising future prospects over nylon fiber due to its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, biodegradability, and enhanced comfort in clothing applications. Innovations in fiber technology focus on scalable bioengineering methods to produce synthetic spider silk that can outperform nylon's durability and elasticity while reducing environmental impact. Continued research aims to integrate nanotechnology and smart textile capabilities into synthetic spider silk fibers, providing superior performance and sustainability in next-generation apparel.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Nylon fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com