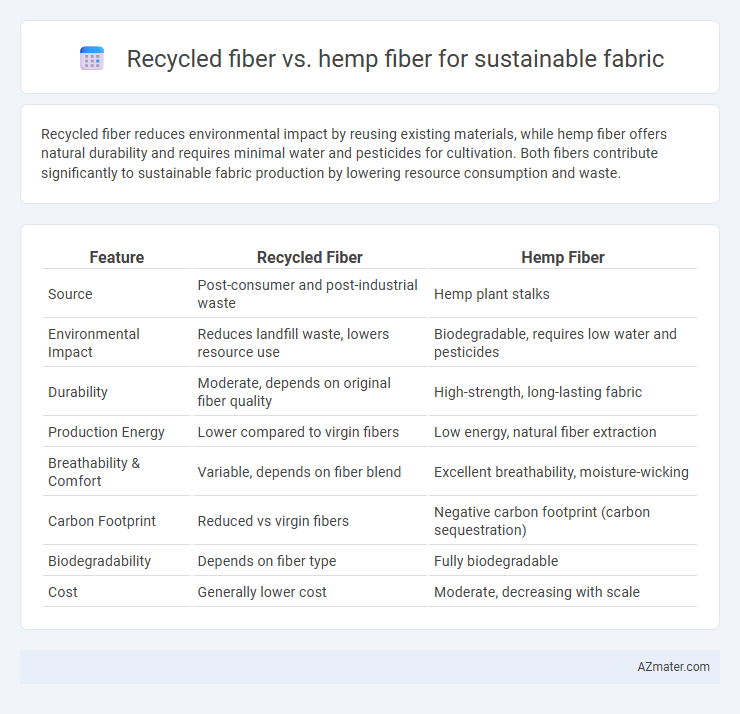
Recycled fiber reduces environmental impact by reusing existing materials, while hemp fiber offers natural durability and requires minimal water and pesticides for cultivation. Both fibers contribute significantly to sustainable fabric production by lowering resource consumption and waste.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Post-consumer and post-industrial waste | Hemp plant stalks |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers resource use | Biodegradable, requires low water and pesticides |
| Durability | Moderate, depends on original fiber quality | High-strength, long-lasting fabric |
| Production Energy | Lower compared to virgin fibers | Low energy, natural fiber extraction |
| Breathability & Comfort | Variable, depends on fiber blend | Excellent breathability, moisture-wicking |
| Carbon Footprint | Reduced vs virgin fibers | Negative carbon footprint (carbon sequestration) |
| Biodegradability | Depends on fiber type | Fully biodegradable |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate, decreasing with scale |
Introduction to Sustainable Fabrics
Recycled fiber and hemp fiber are leading materials in sustainable fabric innovation, offering environmentally friendly alternatives to conventional textiles. Recycled fibers reduce waste by reprocessing post-consumer and post-industrial materials, significantly lowering water consumption and energy use compared to virgin fibers. Hemp fiber stands out for its rapid growth, minimal pesticide requirements, and natural biodegradability, making it a highly renewable resource for eco-conscious fabric production.
What Are Recycled Fibers?
Recycled fibers are materials reclaimed from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, including textiles, plastics, and paper, processed to create new yarns and fabrics with reduced environmental impact. These fibers significantly lower resource consumption by diverting waste from landfills, reducing water use, and cutting greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin textile production. Incorporating recycled fibers into sustainable fabrics complements natural alternatives like hemp fiber, combining waste reduction with renewable, biodegradable properties for eco-friendly textile solutions.
Understanding Hemp Fiber Production
Hemp fiber production involves harvesting the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, followed by retting, decortication, and fiber extraction processes that yield long, strong, and biodegradable fibers suitable for sustainable fabric. Compared to recycled fiber, which relies on repurposing existing textiles or plastics, hemp fiber offers renewable and less chemically intensive cultivation with a lower environmental impact per kilogram produced. The natural durability and breathability of hemp fibers contribute to sustainable textile solutions by reducing the need for synthetic additives and promoting circular economy practices in fabric manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Fiber
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and decreasing the need for virgin raw materials, thereby conserving water and energy resources compared to traditional fibers. The production of recycled fiber generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and less pollution, contributing to a lower carbon footprint in the textile industry. By using post-consumer and post-industrial materials, recycled fiber supports circular economy principles and minimizes resource extraction, promoting a sustainable fabric solution.
Environmental Impact: Hemp Fiber
Hemp fiber offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to many traditional fibers due to its rapid growth rate, requiring minimal water and no pesticides, which reduces soil degradation and water pollution. It also captures more CO2 during cultivation than cotton or synthetic fibers, contributing to carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation. The biodegradability of hemp fiber ensures minimal microplastic pollution, enhancing its sustainability credentials in textile production.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Recycled fiber and hemp fiber each offer distinct advantages in durability and performance for sustainable fabric production. Hemp fiber is renowned for its exceptional strength, natural resistance to mold and UV damage, and long lifespan, making it highly durable for textiles requiring longevity. Recycled fiber varies in durability depending on the source material and processing, often providing moderate strength but superior sustainability through waste reduction and lower energy consumption compared to virgin fibers.
Water and Energy Usage in Production
Recycled fiber significantly reduces water consumption compared to hemp fiber, using up to 90% less water during production. Hemp fiber requires moderate water inputs but excels in energy efficiency, needing less energy for cultivation and processing than conventional cotton. Choosing recycled fiber or hemp fiber supports sustainable fabric production by minimizing resource-intensive water and energy consumption, crucial for eco-friendly textile manufacturing.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Recycled fiber offers sustainability benefits by reducing waste and conserving resources, but its biodegradability depends on the original material composition, with some synthetic fibers taking decades to decompose. Hemp fiber is naturally biodegradable and breaks down efficiently in soil, contributing to improved end-of-life environmental impact without releasing harmful microplastics. Choosing hemp fiber enhances circularity in sustainable fabric production through efficient composting and reduced landfill accumulation.
Economic Factors and Market Availability
Recycled fiber offers cost-effective production due to lower raw material expenses and established recycling infrastructures, making it widely accessible in global markets. Hemp fiber, while environmentally beneficial and highly durable, faces higher cultivation and processing costs, limiting its competitive pricing and availability. Market demand for recycled fibers grows rapidly given regulatory incentives and consumer preference, whereas hemp's expansion depends on agricultural regulations and scaling of fiber-processing technologies.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Sustainable Fashion
Recycled fiber plays a crucial role in sustainable fashion by reducing waste and lowering carbon emissions through the reuse of materials like plastic bottles and textile scraps. Hemp fiber offers exceptional environmental benefits due to its rapid growth, minimal water usage, and ability to enrich soil without pesticides. Choosing the right fiber depends on balancing recycled content for circularity with hemp's natural sustainability and durability to achieve eco-friendly and resilient fabric solutions.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Hemp fiber for Sustainable fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com