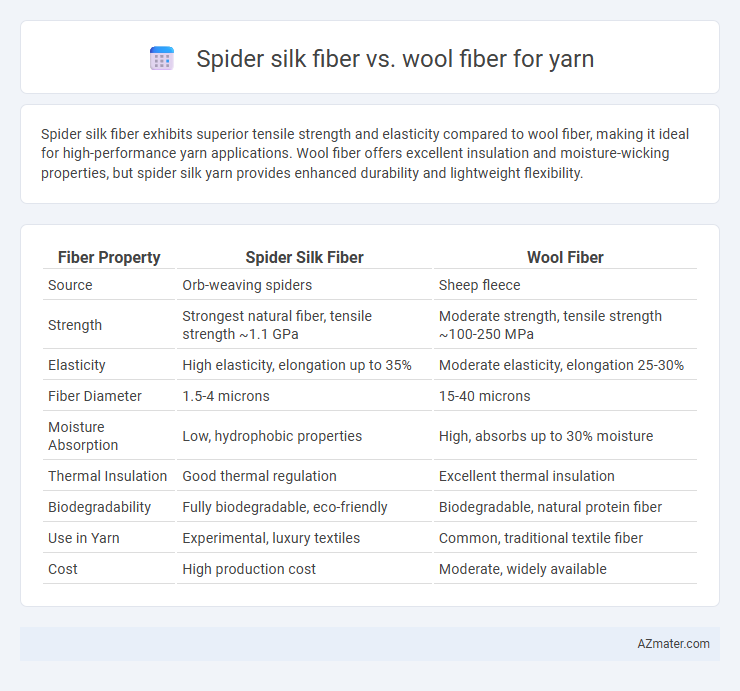
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to wool fiber, making it ideal for high-performance yarn applications. Wool fiber offers excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties, but spider silk yarn provides enhanced durability and lightweight flexibility.
Table of Comparison
| Fiber Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Orb-weaving spiders | Sheep fleece |
| Strength | Strongest natural fiber, tensile strength ~1.1 GPa | Moderate strength, tensile strength ~100-250 MPa |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, elongation up to 35% | Moderate elasticity, elongation 25-30% |
| Fiber Diameter | 1.5-4 microns | 15-40 microns |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, hydrophobic properties | High, absorbs up to 30% moisture |
| Thermal Insulation | Good thermal regulation | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable, eco-friendly | Biodegradable, natural protein fiber |
| Use in Yarn | Experimental, luxury textiles | Common, traditional textile fiber |
| Cost | High production cost | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Wool Fibers
Spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable tensile strength and elasticity, making it an exceptional material for advanced yarn applications, while wool fiber, derived from sheep fleece, is celebrated for its natural insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and softness. Spider silk's protein-based structure offers superior durability and lightweight characteristics compared to wool's keratin composition, which contributes to warmth and breathability in textiles. The sustainable harvesting of spider silk remains challenging, whereas wool is renewable and widely available, influencing their respective uses in the textile industry.
Origin and Production Methods
Spider silk fiber originates from the silk glands of spiders, harvested through either forcibly extracting silk from spider webs or genetically engineered production using recombinant DNA techniques in host organisms like bacteria or plants. Wool fiber is sourced from the fleece of sheep, obtained through shearing, followed by cleaning, carding, and spinning to produce yarn. Production of spider silk yarn remains less industrialized and more bioengineered compared to the well-established, large-scale, mechanical processing of wool fiber for textile applications.
Physical Properties Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, surpassing wool fiber, which is known for its coarse texture and moderate strength. Spider silk's lightweight, smooth surface and high moisture-wicking ability contrast with wool's heavier, insulating properties and natural crimp that provides warmth. The superior durability and flexibility of spider silk make it ideal for high-performance yarns, while wool offers excellent thermal insulation and resilience in textile applications.
Strength and Durability
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, often surpassing wool fiber, making it one of the strongest natural fibers available for yarn production. Its molecular structure enhances durability, providing resistance to wear, stretching, and environmental factors, whereas wool, composed of keratin, offers good elasticity but is more prone to abrasion and pilling over time. The innovative incorporation of spider silk into yarn results in materials that combine lightweight flexibility with superior longevity, outperforming traditional wool fibers in strength and durability metrics.
Softness and Texture
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional softness and a smooth, silk-like texture, making it one of the finest natural fibers available for yarn production. Wool fiber, while generally coarser, offers varying degrees of softness depending on the breed, with merino wool being renowned for its fine, soft texture and natural elasticity. The tensile strength and lightweight nature of spider silk contribute to a luxurious feel and delicate drape, whereas wool provides warmth and resilience with a more textured surface.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior moisture absorption compared to wool fiber, drawing moisture away from the skin while maintaining a dry feel. Its molecular structure allows enhanced breathability, facilitating efficient air circulation and temperature regulation. In contrast, wool fiber absorbs moisture more slowly and retains water longer, which can impact overall comfort in humid conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber exhibits superior environmental benefits over wool fiber due to its biodegradable nature and minimal resource requirements for production, including lower water consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. Wool fiber, while renewable, demands significant land use, water, and energy inputs, alongside methane emissions from sheep livestock, contributing to environmental degradation. Sustainable alternatives focusing on spider silk biofabrication offer promising eco-friendly yarn solutions by reducing ecological footprints compared to traditional wool-based yarns.
Applications in Yarn and Textiles
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it ideal for high-performance yarn used in sportswear and medical textiles, where durability and flexibility are crucial. Wool fiber offers excellent thermal insulation and moisture-wicking properties, commonly applied in yarn for winter clothing, upholstery, and traditional textiles. Combining spider silk with wool can enhance fabric resilience and comfort, catering to advanced textile applications requiring both strength and warmth.
Cost and Availability
Spider silk fiber commands a significantly higher cost than wool fiber due to its complex harvesting process and limited commercial production, making it a luxury material in the yarn market. Wool fiber is abundant and widely available, sourced from sheep globally, which drives its affordability and mass-market appeal. The scarcity and labor-intensive extraction of spider silk restrict its availability, contrasting with the well-established supply chains for wool.
Future Innovations and Potential
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a highly promising material for next-generation yarns in technical textiles and wearable technology. Innovations in bioengineering and synthetic biology aim to scale spider silk production through genetically modified organisms, potentially revolutionizing sustainable textile manufacturing with biodegradable and ultra-durable fabrics. Wool fiber remains a valuable natural resource, but its future potential lies in enhanced processing techniques and wool-synthetic blends that improve durability and functionality for performance-oriented yarns.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Wool fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com