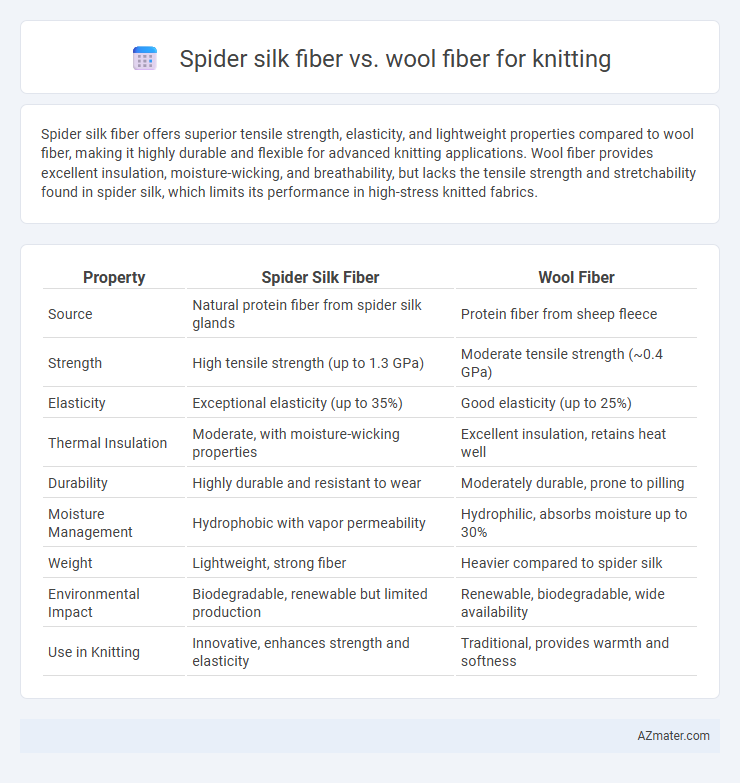
Spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties compared to wool fiber, making it highly durable and flexible for advanced knitting applications. Wool fiber provides excellent insulation, moisture-wicking, and breathability, but lacks the tensile strength and stretchability found in spider silk, which limits its performance in high-stress knitted fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spider Silk Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from spider silk glands | Protein fiber from sheep fleece |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 1.3 GPa) | Moderate tensile strength (~0.4 GPa) |
| Elasticity | Exceptional elasticity (up to 35%) | Good elasticity (up to 25%) |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate, with moisture-wicking properties | Excellent insulation, retains heat well |
| Durability | Highly durable and resistant to wear | Moderately durable, prone to pilling |
| Moisture Management | Hydrophobic with vapor permeability | Hydrophilic, absorbs moisture up to 30% |
| Weight | Lightweight, strong fiber | Heavier compared to spider silk |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable but limited production | Renewable, biodegradable, wide availability |
| Use in Knitting | Innovative, enhances strength and elasticity | Traditional, provides warmth and softness |
Introduction to Natural Fibers for Knitting
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties that make it a highly durable and smooth option for knitting. Wool fiber is renowned for its warmth, moisture-wicking ability, and natural insulation, providing comfort and breathability in knitted garments. Both natural fibers contribute unique qualities, with spider silk enhancing fiber strength and sheen, while wool enriches thermal regulation and texture in knitwear.
Overview of Spider Silk Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties, making it a highly durable and flexible material for knitting. Its protein-based structure provides superior moisture-wicking and temperature regulation compared to wool fiber, which is made from keratin and has natural insulation and breathability. While wool offers warmth and resilience, spider silk's combination of strength and softness presents a unique advantage for high-performance, lightweight knitted textiles.
Properties of Wool Fiber
Wool fiber offers excellent elasticity, moisture-wicking capabilities, and natural insulation, making it highly suitable for knitting warm, breathable garments. Unlike spider silk fiber, wool has a crimped structure that traps air, providing superior thermal regulation and comfort in various climates. Its durability and resilience allow knitted fabrics to maintain shape and resist wear over time.
Mechanical Strength: Spider Silk vs. Wool
Spider silk fiber exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and elasticity compared to wool fiber, making it exceptionally durable for knitting applications that require resilience and flexibility. The mechanical strength of spider silk, often measured at around 1.1 GPa, surpasses wool's tensile strength, which typically ranges between 0.1 and 0.5 GPa. This superior strength-to-weight ratio allows spider silk fiber to create lightweight yet robust knitted textiles, outperforming traditional wool in wear resistance and longevity.
Softness and Texture Comparison
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional softness and a smooth, lustrous texture, making it highly desirable for delicate knitting projects that require a gentle touch on the skin. Wool fiber, while also soft, typically has a coarser and more textured feel compared to the silky smoothness of spider silk, providing warmth and elasticity but sometimes causing slight itchiness for sensitive skin. The finer diameter and tensile strength of spider silk fibers contribute to a lightweight, breathable fabric that outperforms wool in softness and tactile comfort.
Thermal Insulation and Comfort
Spider silk fiber offers superior thermal insulation compared to wool fiber due to its lightweight, moisture-wicking properties that help regulate body temperature effectively. Unlike wool, spider silk is hypoallergenic and exceptionally smooth, enhancing comfort by reducing skin irritation during prolonged wear. Both fibers provide breathability, but spider silk's finer structure allows for better temperature control in diverse climates.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable biodegradability and requires minimal water and pesticides during production, making it a highly sustainable alternative to traditional fibers. Wool fiber, while renewable and biodegradable, involves land use, methane emissions from sheep, and significant water consumption, which impacts its overall environmental footprint. Choosing spider silk for knitting promotes lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduces ecological strain compared to conventional wool fibers.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Spider silk fiber offers superior dyeability compared to wool fiber due to its protein structure, which allows for vibrant and more consistent color absorption. Wool fiber, while also capable of holding dyes well, tends to fade faster over time because of its scale-like surface that can wear down with washing and exposure. Color retention in spider silk is enhanced by its strength and smooth texture, leading to longer-lasting and more vivid knitted garments.
Cost and Practicality for Knitting
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength and elasticity compared to traditional wool fiber but comes at a significantly higher cost due to complex harvesting processes and limited availability. Wool fiber remains more practical and affordable for knitting, providing natural warmth, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties that are well-suited for everyday garments. Cost-effectiveness and ease of care make wool the preferred choice for most knitters despite spider silk's superior performance in durability.
Future Trends and Innovations in Knitting Fibers
Spider silk fiber offers unparalleled strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary material for future knitting innovations compared to traditional wool fiber. Advances in biotechnology and synthetic biology are enabling scalable production of spider silk, enhancing its availability and affordability for eco-friendly, high-performance knitwear. Integration of spider silk with smart textiles and nanotechnology promises enhanced durability, moisture management, and thermal regulation, outpacing wool's conventional insulating properties in next-generation knit fabrics.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Wool fiber for Knitting
 azmater.com
azmater.com