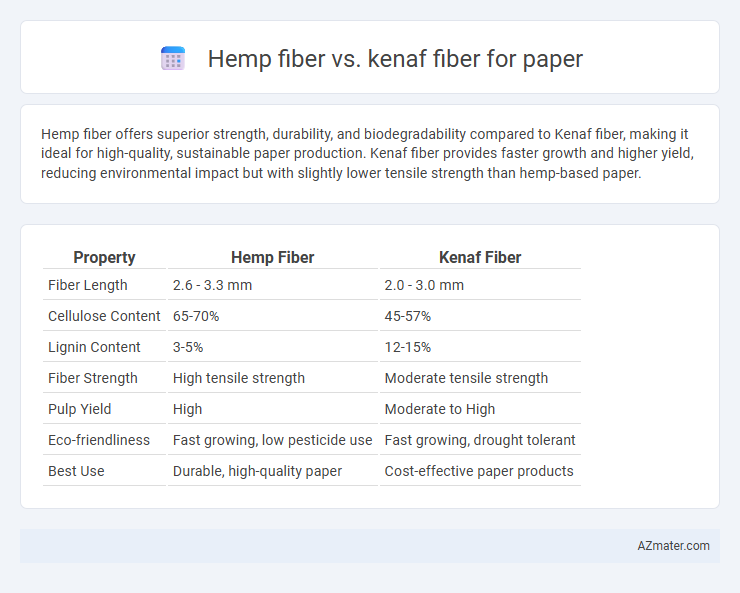
Hemp fiber offers superior strength, durability, and biodegradability compared to Kenaf fiber, making it ideal for high-quality, sustainable paper production. Kenaf fiber provides faster growth and higher yield, reducing environmental impact but with slightly lower tensile strength than hemp-based paper.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Kenaf Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Length | 2.6 - 3.3 mm | 2.0 - 3.0 mm |
| Cellulose Content | 65-70% | 45-57% |
| Lignin Content | 3-5% | 12-15% |
| Fiber Strength | High tensile strength | Moderate tensile strength |
| Pulp Yield | High | Moderate to High |
| Eco-friendliness | Fast growing, low pesticide use | Fast growing, drought tolerant |
| Best Use | Durable, high-quality paper | Cost-effective paper products |
Introduction to Hemp Fiber and Kenaf Fiber
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its long, strong fibers ideal for producing durable, high-quality paper with excellent tensile strength and resistance to tearing. Kenaf fiber comes from the Hibiscus cannabinus plant and is characterized by its fast-growing nature and high cellulose content, making it a sustainable and cost-effective raw material for paper production. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to wood pulp, with hemp fibers providing superior fiber length and kenaf fibers delivering efficient production cycles and reduced environmental impact.
Botanical Origins and Growth Characteristics
Hemp fiber, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, exhibits rapid growth with a typical maturing cycle of 90-120 days, thriving in temperate climates and yielding long, strong bast fibers ideal for paper production. Kenaf fiber originates from Hibiscus cannabinus, a fast-growing annual that matures in about 4-5 months and is well-suited for subtropical to tropical regions, producing a high cellulose content favorable for pulp. Both fibers share high lignin content and cellulose levels essential for paper strength, but hemp's superior fiber length generally offers enhanced tensile properties compared to kenaf.
Fiber Extraction and Processing Methods
Hemp fiber extraction for paper involves both retting and decortication processes, where water or chemical retting separates bast fibers, followed by mechanical processing to obtain long, strong fibers ideal for durable paper. Kenaf fiber extraction primarily uses water retting or chemical treatment to separate bast and core fibers, with mechanical refining enhancing fiber length and flexibility, making it suitable for lightweight, porous paper products. Processing methods for hemp tend to yield higher cellulose content with less lignin, resulting in paper with superior strength, while kenaf processing requires rigorous debarking to reduce lignin and optimize fiber quality for printing and packaging materials.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Hemp fiber exhibits higher cellulose content (around 70-74%) compared to kenaf fiber (approximately 45-57%), contributing to superior tensile strength and durability in paper production. Kenaf fiber typically contains more lignin (15-20%) than hemp (4-10%), affecting the ease of pulping and requiring more intensive chemical processing. Physically, hemp fibers are longer (average length 15-55 mm) and coarser, which enhances paper strength but may reduce smoothness compared to shorter and finer kenaf fibers (5-35 mm).
Pulping Efficiency and Yield Differences
Hemp fiber exhibits higher pulping efficiency compared to kenaf fiber due to its lower lignin content and longer cellulose fibers, resulting in a cleaner and more durable pulp. Kenaf fiber, however, offers a higher overall pulp yield because of its rapid growth and higher cellulose concentration despite requiring more intensive chemical processing. The choice between hemp and kenaf for paper production hinges on balancing hemp's superior fiber quality against kenaf's cost-effective yield and abundance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hemp fiber offers a significantly lower environmental footprint than kenaf fiber due to its rapid growth cycle, requiring fewer pesticides and less water, which reduces soil degradation and conserves natural resources. Kenaf fiber, while also sustainable, demands intensive agricultural inputs and longer maturation, increasing energy consumption and carbon emissions during cultivation. The superior cellulose content and recyclability of hemp fiber further enhance its viability for eco-friendly paper production, promoting a circular economy with reduced deforestation pressure.
Paper Quality: Strength, Texture, and Appearance
Hemp fiber outperforms kenaf fiber in paper strength due to its longer and coarser fibers, which enhance tear resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-quality archival paper. Kenaf fiber produces smoother paper with a finer texture, suitable for printing applications requiring uniformity and brightness. While hemp paper boasts a natural off-white appearance with a rustic feel, kenaf paper tends to have a brighter, whiter finish, appealing for commercial and packaging uses.
Industrial Applications in Papermaking
Hemp fiber offers superior tensile strength and durability compared to Kenaf fiber, making it highly suitable for producing high-quality industrial paper products such as packaging and specialty papers. Kenaf fiber, with its fast growth cycle and high cellulose content, provides cost-effective raw material advantages, ideal for large-scale paper manufacturing where sustainability and resource efficiency are prioritized. Both fibers contribute uniquely to the papermaking industry by enhancing the mechanical properties and recyclability of paper, with hemp favored for its strength and Kenaf for its eco-friendly production attributes.
Economic Viability and Market Trends
Hemp fiber offers higher tensile strength and durability than kenaf fiber, contributing to longer-lasting paper products and promising greater economic viability in premium paper markets. Kenaf fiber boasts faster growth cycles and lower cultivation costs, making it an economically attractive choice for large-scale paper production focused on cost efficiency. Market trends indicate a growing demand for sustainable paper sources, with hemp benefiting from increasing legalization and eco-conscious consumer preferences, while kenaf remains favored in regions emphasizing rapid renewable resource turnover.
Future Prospects for Hemp and Kenaf Paper
Hemp fiber and kenaf fiber both exhibit strong potential for sustainable paper production due to their fast growth and high cellulose content. Future prospects for hemp paper include advancements in environmentally friendly pulping techniques and increased demand driven by eco-conscious markets. Kenaf paper benefits from robust fiber strength and versatility, with ongoing research focusing on improving yield efficiency and expanding industrial applications in packaging and specialty papers.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Kenaf fiber for Paper
 azmater.com
azmater.com