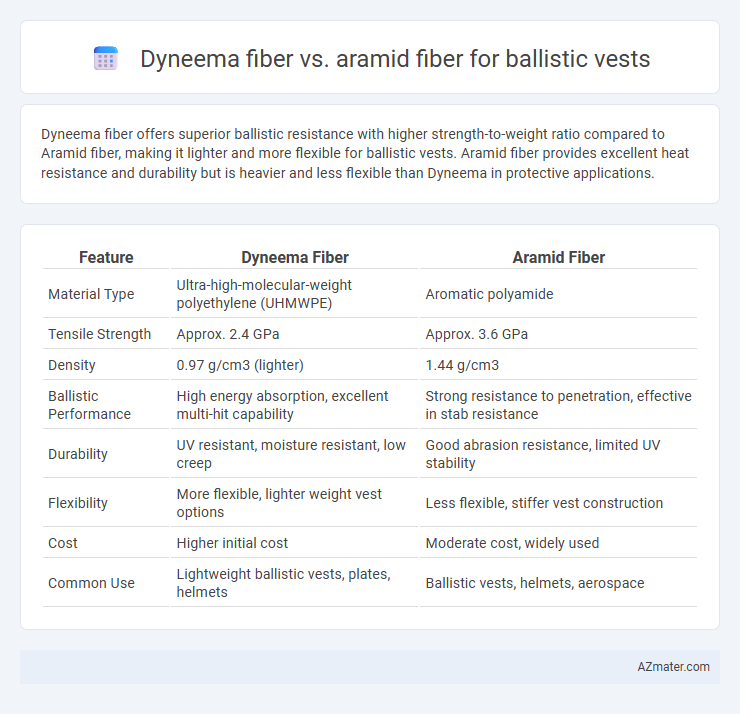
Dyneema fiber offers superior ballistic resistance with higher strength-to-weight ratio compared to Aramid fiber, making it lighter and more flexible for ballistic vests. Aramid fiber provides excellent heat resistance and durability but is heavier and less flexible than Dyneema in protective applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dyneema Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Aromatic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | Approx. 2.4 GPa | Approx. 3.6 GPa |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (lighter) | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Ballistic Performance | High energy absorption, excellent multi-hit capability | Strong resistance to penetration, effective in stab resistance |
| Durability | UV resistant, moisture resistant, low creep | Good abrasion resistance, limited UV stability |
| Flexibility | More flexible, lighter weight vest options | Less flexible, stiffer vest construction |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Moderate cost, widely used |
| Common Use | Lightweight ballistic vests, plates, helmets | Ballistic vests, helmets, aerospace |
Introduction to Ballistic Vest Materials
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it a preferred choice for ballistic vests requiring high mobility and durability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent impact resistance and thermal stability, widely used for their proven performance in ballistic protection. Both materials enhance the overall efficacy of ballistic vests by combining strength, flexibility, and abrasion resistance.
What is Dyneema Fiber?
Dyneema fiber, a high-performance polyethylene fiber known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, is widely used in ballistic vests due to its lightweight and superior energy absorption capabilities compared to traditional fibers. Unlike aramid fibers, Dyneema offers enhanced resistance to moisture and UV degradation, maintaining ballistic protection in harsh environmental conditions. Its ultra-high molecular weight and unique molecular chain structure enable superior tensile strength, making it ideal for flexible, lightweight ballistic armor applications.
What is Aramid Fiber?
Aramid fiber is a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers used extensively in ballistic vests for its exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance. Known commercially as Kevlar or Twaron, aramid fibers offer superior protection against bullets and shrapnel through their high durability and lightweight properties. Compared to Dyneema fiber, aramid fibers provide better thermal stability and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for multi-threat ballistic applications.
Key Properties Comparison: Dyneema vs Aramid
Dyneema fiber offers superior tensile strength and is lightweight with exceptional cut and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for ballistic vests that require high mobility and comfort. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide excellent thermal stability and impact resistance, maintaining performance under high temperatures and repeated ballistic impacts. Both materials excel in energy absorption, but Dyneema leads in moisture resistance while Aramid fibers sustain structural integrity better under extreme heat conditions.
Ballistic Protection Performance
Dyneema fiber offers superior ballistic protection performance due to its exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, enabling lightweight, high-impact resistance in ballistic vests. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent energy absorption and thermal stability but generally result in heavier vests with slightly lower blunt force trauma resistance. Dyneema's ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene structure delivers enhanced multi-hit capability and greater resistance to fragmentation compared to Aramid fibers, making it ideal for advanced ballistic protection systems.
Weight and Comfort Analysis
Dyneema fiber offers significantly lower weight compared to Aramid fiber, making ballistic vests lighter and less bulky for extended wear. Its ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composition provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance, enhancing overall comfort during prolonged use. In contrast, Aramid fibers like Kevlar are heavier and less breathable, which can lead to discomfort and heat retention in high-intensity scenarios.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Dyneema fiber offers superior durability due to its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composition, resulting in high tensile strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and impact over time. Its inherent chemical resistance ensures outstanding environmental resilience against moisture, UV exposure, and chemicals, maintaining ballistic integrity in harsh conditions. In contrast, Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide strong ballistic protection but degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and moisture, reducing lifespan and requiring careful environmental handling.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Dyneema fiber offers a lightweight ballistic solution but typically comes at a higher cost than Aramid fibers such as Kevlar, impacting budget-sensitive procurement. Availability of Aramid fibers is generally greater due to established global manufacturing and supply chains, facilitating faster production and replenishment of ballistic vests. Budget constraints and supply chain reliability often lead law enforcement and military agencies to prefer Aramid fiber options despite Dyneema's superior weight-to-strength ratio.
Real-World Applications and Industry Usage
Dyneema fiber is widely used in ballistic vests for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, offering enhanced mobility and comfort in real-world law enforcement and military operations. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, remain prevalent in ballistic protection due to their proven heat resistance and durability under high-impact conditions, particularly in military and tactical gear. Industry usage often pairs Dyneema for lightweight, flexible armor solutions with aramids in multi-layered vests where thermal stability and multi-hit performance are critical.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fiber for Ballistic Vests
Dyneema fiber offers superior lightweight properties and high tensile strength, enabling ballistic vests with enhanced mobility and comfort without compromising protection. Aramid fiber provides excellent thermal resistance and proven durability, making it suitable for intense combat environments and sustained use. Selecting the best fiber depends on the operational requirements, where Dyneema suits mobility-focused applications and aramid excels in settings demanding heat resistance and long-term reliability.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Aramid fiber for Ballistic vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com