Wool offers natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and durability, making it ideal for cold-weather apparel, while Modal provides a soft, breathable, and lightweight fabric suitable for comfortable, moisture-absorbent clothing in warmer climates. Wool's sustainability and antimicrobial properties contrast Modal's eco-friendly production from beech trees and superior color retention.
Table of Comparison
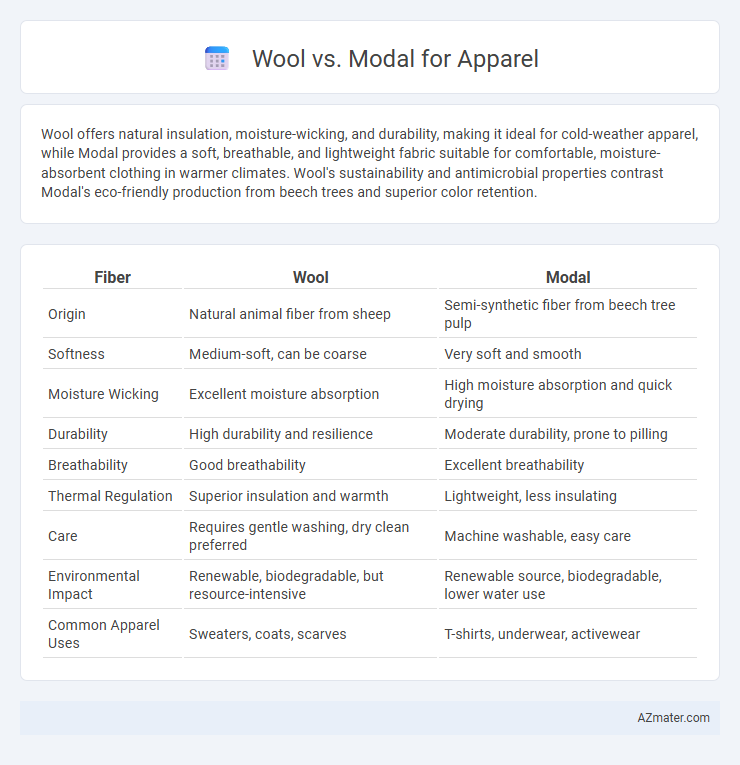
| Fiber | Wool | Modal |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural animal fiber from sheep | Semi-synthetic fiber from beech tree pulp |
| Softness | Medium-soft, can be coarse | Very soft and smooth |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent moisture absorption | High moisture absorption and quick drying |
| Durability | High durability and resilience | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Excellent breathability |
| Thermal Regulation | Superior insulation and warmth | Lightweight, less insulating |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, dry clean preferred | Machine washable, easy care |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable, biodegradable, but resource-intensive | Renewable source, biodegradable, lower water use |
| Common Apparel Uses | Sweaters, coats, scarves | T-shirts, underwear, activewear |
Introduction to Wool and Modal Fabrics
Wool, derived from sheep fleece, is renowned for its natural insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and durability, making it ideal for cold-weather apparel. Modal, a semi-synthetic fiber made from beech tree pulp, offers exceptional softness, breathability, and resistance to shrinkage, enhancing comfort in everyday clothing. Both fibers present unique benefits: wool excels in warmth and resilience, while modal provides a lightweight, smooth texture suited for versatile fashion.
Origin and Production Process
Wool originates from the fleece of sheep and undergoes shearing, scouring, carding, and spinning to create natural, durable fibers ideal for insulation and moisture-wicking. Modal is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from beech tree pulp, produced through a chemical-intensive process involving cellulose extraction, spinning, and regeneration into soft, breathable fabric. The natural origin and artisanal production of wool contrast with modal's more industrial, sustainable-focused manufacturing rooted in renewable wood sources.
Texture and Comfort Comparison
Wool offers a natural, breathable texture with excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for cold weather apparel. Modal, derived from beech tree fibers, provides a silky-smooth feel, superior softness, and better drape, enhancing comfort and wearability in casual or lightweight clothing. Both fabrics excel in comfort, but wool is preferred for warmth and durability, while modal is favored for its smooth texture and lightweight breathability.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Wool excels in breathability and moisture management due to its natural crimp and porous fiber structure, which allows air circulation and absorbs up to 30% of moisture without feeling damp. Modal, a type of rayon made from beech tree pulp, offers excellent moisture-wicking properties by pulling sweat away from the body and drying faster than cotton, though it lacks wool's insulating qualities. For activewear and outdoor apparel, wool provides superior temperature regulation and odor resistance alongside breathability, whereas modal is favored in lightweight, soft fabrics ideal for casual wear.
Durability and Longevity
Wool offers exceptional durability due to its natural resilience, maintaining shape and insulating properties over extended use, making it ideal for winter apparel and outerwear. Modal, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from beech trees, provides excellent resistance to shrinkage and pilling but generally wears out faster than wool under heavy abrasion or frequent washing. Choosing between wool and modal for longevity depends on the specific garment use, with wool excelling in rugged, long-lasting applications and modal favored for softness with moderate durability.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Wool provides superior warmth and natural insulation due to its crimped fibers that trap air, making it ideal for cold-weather apparel. Modal, a semi-synthetic fabric derived from beech trees, offers moderate insulation with a smooth, breathable texture but lacks the thermal retention characteristics of wool. For optimal cold-weather clothing, wool's moisture-wicking and heat-retention properties outperform modal, ensuring better temperature regulation in challenging conditions.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Wool requires gentle hand washing with cold water or dry cleaning to prevent shrinking and maintain its natural fibers, while Modal is machine washable, durable, and resistant to shrinking and fading, making it lower maintenance. Wool's natural lanolin provides some water resistance but demands careful drying flat to avoid misshaping, whereas Modal's synthetic fibers dry quickly and retain shape well. For longevity, wool garments benefit from airing out to reduce odor, while Modal clothing withstands frequent washing without significant quality loss.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Wool, a natural fiber derived from sheep, offers biodegradability and renewable qualities, but its environmental impact includes significant land use, methane emissions, and water consumption during production. Modal, a semi-synthetic fiber made from beech tree cellulose, is biodegradable and requires less water and land compared to wool, with efficient chemical recycling processes reducing pollution. Both fibers contribute to sustainability in apparel, yet modal's lower resource demand and renewable sourcing present a greener alternative to traditional wool production.
Cost and Affordability
Wool garments tend to be more expensive due to the labor-intensive shearing and processing required, with prices often ranging from $100 to over $500 for high-quality apparel. Modal fabric offers a more affordable alternative, typically costing 30-50% less while maintaining softness and durability, making it popular for budget-conscious consumers. Wool's natural insulation and breathability justify its higher price point in premium markets, whereas modal's cost-effectiveness suits everyday wear and mass production.
Best Use Cases and Recommendations
Wool excels in cold-weather apparel due to its natural insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and durability, making it ideal for sweaters, outerwear, and thermal base layers. Modal, a semi-synthetic fabric made from beech tree pulp, offers exceptional softness, breathability, and drape, perfect for lightweight shirts, underwear, and casual wear that require comfort and moisture management. For activewear and layering, wool provides warmth and odor resistance, while modal is best suited for everyday garments needing a smooth, silky feel and easy care.
Infographic: Wool vs Modal for Apparel
 azmater.com
azmater.com