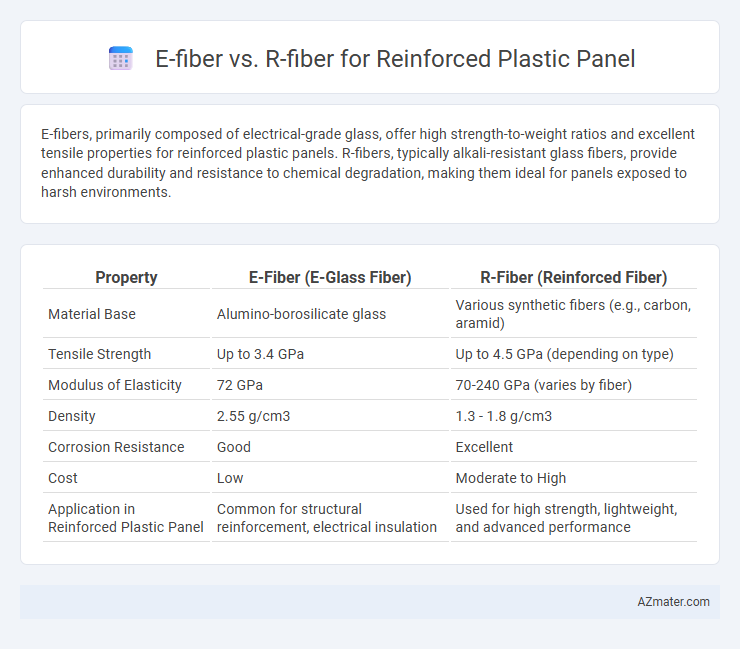
E-fibers, primarily composed of electrical-grade glass, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent tensile properties for reinforced plastic panels. R-fibers, typically alkali-resistant glass fibers, provide enhanced durability and resistance to chemical degradation, making them ideal for panels exposed to harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber (E-Glass Fiber) | R-Fiber (Reinforced Fiber) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Base | Alumino-borosilicate glass | Various synthetic fibers (e.g., carbon, aramid) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3.4 GPa | Up to 4.5 GPa (depending on type) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 72 GPa | 70-240 GPa (varies by fiber) |
| Density | 2.55 g/cm3 | 1.3 - 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Low | Moderate to High |
| Application in Reinforced Plastic Panel | Common for structural reinforcement, electrical insulation | Used for high strength, lightweight, and advanced performance |
Introduction to Reinforced Plastic Panels
E-fiber and R-fiber are key reinforcement materials in reinforced plastic panels, influencing mechanical strength and durability. E-fiber, primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate, offers excellent electrical insulation and tensile properties ideal for lightweight applications. R-fiber, made from recycled glass, provides cost-effective reinforcement with sustainable benefits while maintaining adequate structural performance in composite panels.
Overview of Fiber Types in Composites
E-fiber (Electrical grade) and R-fiber (Reinforced grade) are widely used fiber types in reinforced plastic panels, each offering distinct mechanical properties for composite applications. E-fiber is primarily composed of alumino-borosilicate glass, known for its excellent electrical insulation and high tensile strength, making it ideal for electronic and electrical components. R-fiber, designed with enhanced impact resistance and durability, is formulated to withstand harsher mechanical stresses, making it suitable for structural applications where toughness and dimensional stability are critical.
What is E-Fiber?
E-fiber, or electrical-grade glass fiber, is a type of fiberglass specifically designed for superior electrical insulation properties used in reinforced plastic panels. It provides excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for applications requiring durable and non-conductive materials. Compared to R-fiber, which is primarily aimed at reinforcement with higher tensile strength, E-fiber focuses on maintaining insulation performance within structural composites.
What is R-Fiber?
R-Fiber is a type of reinforcing fiber used in reinforced plastic panels known for its exceptional tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for enhancing structural integrity and impact resistance. Unlike standard E-fiber, which primarily offers good electrical insulation and corrosion resistance, R-fiber provides superior mechanical performance, particularly in high-stress applications such as automotive and aerospace components. The unique properties of R-fiber contribute to lightweight yet durable panels that improve overall durability and lifespan of composite materials.
Mechanical Properties: E-Fiber vs R-Fiber
E-fiber reinforced plastic panels demonstrate superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to R-fiber counterparts, making them ideal for high-load applications. R-fibers, while offering enhanced impact resistance and better energy absorption, typically exhibit lower modulus and tensile strength than E-fibers. The choice between E-fiber and R-fiber hinges on balancing mechanical requirements such as rigidity and toughness for optimal panel performance.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
E-fiber reinforced plastic panels exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to R-fiber counterparts, particularly in aggressive environments containing acids, alkalis, and solvents. The E-fiber's high purity alumino-silicate composition enhances durability against chemical degradation, making it ideal for applications involving corrosive substances. In contrast, R-fiber panels, composed of recycled materials, may show reduced resistance and potential for faster chemical wear over prolonged exposure.
Cost Analysis: E-Fiber and R-Fiber
E-fiber reinforced plastic panels typically offer a lower cost option due to the abundance and affordability of E-glass fibers, reducing raw material expenses compared to R-fiber variants. R-fiber, composed primarily of recycled or specialty fibers, often incurs higher processing costs despite potential environmental benefits. Cost analysis favors E-fiber panels for large-scale applications where budget constraints outweigh performance enhancements associated with R-fiber reinforcements.
Durability and Longevity Factors
E-fibers, primarily made from high-strength glass, offer excellent tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for reinforced plastic panels requiring long-term durability in harsh environments. R-fibers, often referring to resin-based or recycled fibers, provide moderate mechanical properties but may exhibit reduced longevity and fade resistance compared to E-fibers. The superior chemical stability and fatigue resistance of E-fibers significantly enhance the lifespan and structural integrity of reinforced plastic panels under prolonged stress and environmental exposure.
Applications of E-Fiber and R-Fiber in Plastic Panels
E-fiber, known for its high electrical insulation and tensile strength, is widely used in reinforced plastic panels for applications requiring excellent dielectric properties, such as in electronics enclosures and aerospace components. R-fiber offers superior impact resistance and durability, making it ideal for automotive body panels and outdoor structural components where mechanical stress and environmental exposure are critical factors. The choice between E-fiber and R-fiber in plastic panels depends on balancing electrical insulation needs with mechanical performance requirements.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Project
Choosing the right fiber for reinforced plastic panels depends on the application requirements and performance criteria. E-fiber, or E-glass fiber, offers excellent tensile strength, electrical insulation, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for general-purpose reinforcement. R-fiber, or R-glass fiber, provides superior mechanical properties and resistance to corrosion and impact, suitable for demanding environments needing enhanced durability.
Infographic: E-fiber vs R-fiber for Reinforced Plastic Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com