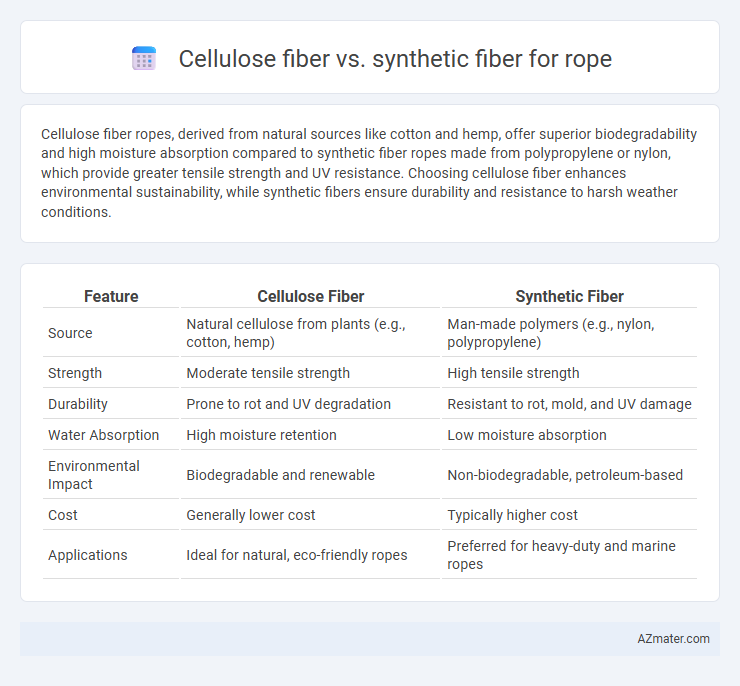
Cellulose fiber ropes, derived from natural sources like cotton and hemp, offer superior biodegradability and high moisture absorption compared to synthetic fiber ropes made from polypropylene or nylon, which provide greater tensile strength and UV resistance. Choosing cellulose fiber enhances environmental sustainability, while synthetic fibers ensure durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cellulose Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural cellulose from plants (e.g., cotton, hemp) | Man-made polymers (e.g., nylon, polypropylene) |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Durability | Prone to rot and UV degradation | Resistant to rot, mold, and UV damage |
| Water Absorption | High moisture retention | Low moisture absorption |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and renewable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Applications | Ideal for natural, eco-friendly ropes | Preferred for heavy-duty and marine ropes |
Introduction to Rope Materials: Cellulose vs Synthetic Fibers
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton, hemp, and jute, offer excellent biodegradability, breathability, and grip for rope applications, making them ideal for traditional, eco-friendly uses. Synthetic fibers such as nylon, polyester, and polypropylene provide superior strength, resistance to moisture, UV rays, and chemicals, ensuring durability and longer lifespan in harsh environments. Choosing between cellulose and synthetic fibers depends on specific requirements like strength, environmental impact, and handling characteristics for rope material.
Composition and Structure of Cellulose Fiber Ropes
Cellulose fiber ropes are primarily composed of natural fibers derived from plant cell walls, such as hemp, jute, and sisal, which consist mainly of cellulose polymer chains arranged in microfibrils providing high tensile strength and flexibility. The structure of cellulose fibers features a hierarchical arrangement of crystalline and amorphous regions, contributing to their durability and resistance to abrasion, while allowing moisture absorption that affects rope performance. In contrast, synthetic fiber ropes, made from polymers like nylon or polyester, exhibit uniform molecular structures offering enhanced resistance to rot, chemicals, and UV degradation but lack the natural absorbency found in cellulose fibers.
Synthetic Fiber Ropes: Types and Properties
Synthetic fiber ropes, including nylon, polyester, and polypropylene, offer superior strength, durability, and resistance to moisture compared to cellulose fiber ropes like hemp or jute. Nylon ropes boast high elasticity and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for dynamic loads, while polyester ropes provide excellent UV stability and low stretch under load. Polypropylene ropes are lightweight and float on water, making them suitable for marine applications, with overall synthetic options outperforming natural fibers in longevity and maintenance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Cellulose fibers, such as cotton and hemp, offer moderate strength and biodegradability but generally exhibit lower tensile strength and wear resistance compared to synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester. Synthetic fibers provide superior durability, higher resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and abrasion, making them ideal for heavy-duty rope applications requiring long-term reliability. Strength measurements indicate synthetic ropes can achieve tensile strengths 2 to 3 times greater than cellulose-based ropes, enhancing performance in industrial and marine environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources such as cotton, jute, and hemp, are biodegradable and have a lower carbon footprint compared to synthetic fibers made from petrochemicals like nylon or polyester. The production of synthetic fibers involves significant energy consumption and releases greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental pollution and microplastic contamination in marine ecosystems. Choosing cellulose fiber ropes promotes sustainability by reducing dependence on fossil fuels and enabling natural decomposition, thereby minimizing long-term ecological damage.
Water and Weather Resistance
Cellulose fibers such as cotton and jute absorb water readily, leading to swelling, weakening, and increased susceptibility to mildew and rot when exposed to moisture and harsh weather conditions. Synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester exhibit superior water resistance, maintaining tensile strength and durability even after prolonged exposure to wet environments and UV radiation. This enhanced resistance makes synthetic ropes ideal for marine, outdoor, and industrial applications where consistent performance under variable weather conditions is critical.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Cellulose fibers such as hemp and cotton offer natural flexibility and excellent grip, making ropes easier to handle in wet or dry conditions. Synthetic fibers like nylon and polypropylene provide superior elasticity and strength, enhancing durability but sometimes resulting in a slicker surface that can challenge grip. The choice between these fibers depends on specific handling requirements, with cellulose fibers preferred for tasks needing tactile control and synthetics favored for strength and resistance.
Cost Analysis: Cellulose Fiber vs Synthetic Fiber
Cellulose fibers, such as cotton and sisal, typically have lower initial costs compared to synthetic fibers like nylon and polyester, making them more budget-friendly for rope manufacturing. However, synthetic fibers offer better durability, resistance to moisture, and longer lifespan, which can reduce replacement frequency and overall costs in the long term. Evaluating total cost of ownership, synthetic ropes may provide better value despite higher upfront expenses due to their superior performance and maintenance savings.
Common Applications and Industry Preferences
Cellulose fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton and hemp, are commonly used in marine and agricultural ropes due to their biodegradability and grip properties. Synthetic fibers such as nylon and polypropylene dominate in industrial applications including climbing, rescue operations, and heavy lifting, valued for their high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Industry preferences increasingly favor synthetic fibers for performance-critical roles, while cellulose fibers remain preferred in eco-friendly and traditional uses where environmental impact is a primary concern.
Choosing the Right Rope: Key Considerations
Cellulose fiber ropes, such as those made from hemp or jute, offer biodegradability and excellent grip, making them ideal for environmentally conscious applications and decorative uses. Synthetic fiber ropes like nylon or polypropylene provide superior strength, resistance to moisture, and durability under harsh conditions, suitable for marine and industrial purposes. When choosing the right rope, consider factors such as tensile strength, environmental impact, abrasion resistance, and application-specific requirements to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Cellulose fiber vs Synthetic fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com