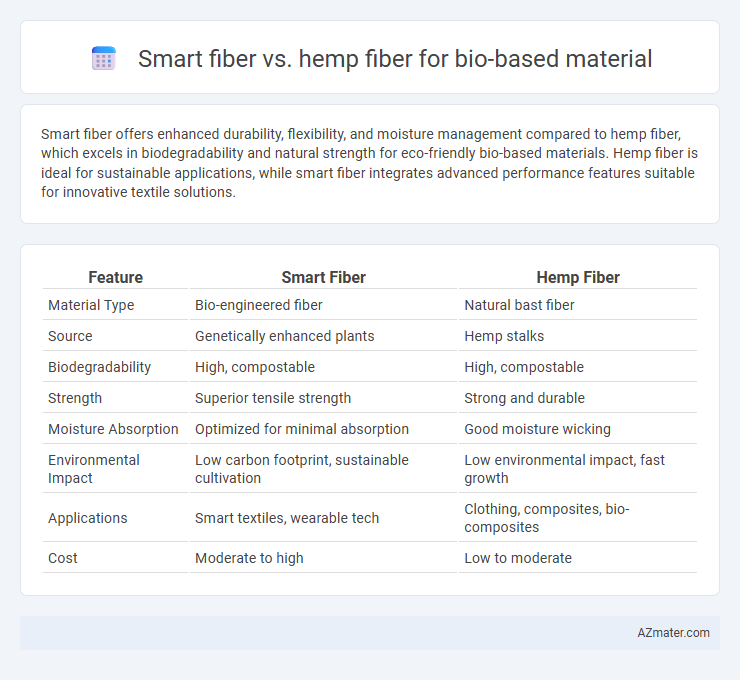
Smart fiber offers enhanced durability, flexibility, and moisture management compared to hemp fiber, which excels in biodegradability and natural strength for eco-friendly bio-based materials. Hemp fiber is ideal for sustainable applications, while smart fiber integrates advanced performance features suitable for innovative textile solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Bio-engineered fiber | Natural bast fiber |
| Source | Genetically enhanced plants | Hemp stalks |
| Biodegradability | High, compostable | High, compostable |
| Strength | Superior tensile strength | Strong and durable |
| Moisture Absorption | Optimized for minimal absorption | Good moisture wicking |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable cultivation | Low environmental impact, fast growth |
| Applications | Smart textiles, wearable tech | Clothing, composites, bio-composites |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Bio-based Materials
Bio-based materials derived from renewable sources like smart fibers and hemp fibers offer sustainable alternatives to conventional petroleum-based products. Smart fibers exhibit advanced functional properties such as self-healing and environmental responsiveness, enhancing material performance in various applications. Hemp fiber provides exceptional mechanical strength, biodegradability, and low environmental impact, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly composites and textiles in the bio-based material industry.
Overview of Smart Fiber Technology
Smart fiber technology integrates advanced materials such as conductive polymers and sensors directly into fibers, enabling real-time responsiveness and functionality within bio-based textiles. Unlike traditional hemp fiber, which offers high tensile strength and natural biodegradability, smart fibers provide enhanced properties like self-healing, environmental sensing, and adaptive insulation. This innovation positions smart fibers as a transformative solution in sustainable materials by merging the durability of natural fibers with cutting-edge technological features.
Hemp Fiber: Traditional Renewable Resource
Hemp fiber, a traditional renewable resource, offers superior biodegradability and strength, making it an ideal choice for bio-based materials. Its natural cellulose content enhances durability and moisture resistance, outperforming many synthetic fibers in ecological sustainability. Hemp cultivation requires minimal pesticides and water, contributing to its environmental benefits compared to Smart fibers engineered from synthetic polymers.
Comparative Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Smart fiber composites exhibit superior tensile strength and enhanced durability under mechanical stress compared to hemp fiber-based bioplastics, making them ideal for load-bearing bio-based applications. Hemp fibers offer high tensile strength and excellent shock absorption but tend to have lower resistance to moisture and UV degradation, which can limit their long-term durability. The enhanced interfacial bonding in smart fiber materials contributes to improved fracture toughness and longevity in aggressive environmental conditions.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart fiber, engineered with advanced biodegradable polymers, offers enhanced durability and recyclability compared to traditional hemp fiber, which is naturally renewable and requires minimal pesticides and water for cultivation. Hemp fiber sequesters significant amounts of CO2 during growth, supporting carbon-negative material production, while smart fiber's tailored degradation rates reduce long-term landfill impact. Both fibers contribute to sustainable bio-based materials by reducing dependence on fossil fuels, but hemp's low resource input and high biomass yield make it particularly advantageous for environmentally conscious manufacturing.
Processing and Manufacturing Techniques
Smart fiber processing leverages advanced techniques such as electrospinning and nanofiber fabrication, enabling precise control over fiber morphology and enhanced material properties suitable for high-performance bio-based applications. Hemp fiber manufacturing primarily involves mechanical retting, decortication, and scutching, which are cost-effective but yield coarser fibers with less uniformity compared to smart fibers. Integration of smart fiber technology with traditional hemp processing can improve fiber alignment and surface functionalization, optimizing performance while maintaining sustainability in bio-based material production.
Applications in Textile and Composite Industries
Smart fiber exhibits superior adaptability and functional properties such as moisture management and UV resistance, making it ideal for high-performance textiles and advanced composite materials. Hemp fiber offers excellent strength, biodegradability, and sustainability, widely used in eco-friendly textiles and automotive composites for durability and environmental benefits. Both fibers contribute to innovative bio-based materials, with smart fiber enhancing technical applications and hemp fiber supporting sustainable manufacturing.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Smart fiber technology enhances hemp fiber's natural properties, making it more cost-effective by reducing processing steps and increasing material durability in bio-based applications. Hemp fiber is widely available due to its rapid growth cycle and low agricultural input, but smart fiber innovations improve its market competitiveness by enabling higher performance in composites and textiles. Cost analysis reveals smart hemp composites offer lower lifecycle expenses compared to synthetic alternatives, driven by renewable sourcing and scalability in industrial production.
Innovation and Future Trends in Bio-based Fibers
Smart fiber technology in bio-based materials integrates advanced functionalities such as self-healing, responsiveness to environmental stimuli, and enhanced durability, positioning it at the forefront of innovation. Hemp fiber offers a sustainable, high-strength alternative with natural antimicrobial properties and low environmental impact, driving its adoption in eco-friendly manufacturing. Future trends highlight the convergence of smart fiber capabilities with hemp's biodegradability, creating hybrid bio-based fibers that optimize performance, sustainability, and circular economy principles in textile and composite industries.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Smart Fiber and Hemp Fiber
Choosing between smart fiber and hemp fiber for bio-based materials depends on specific application needs and desired material properties. Smart fibers offer advanced functionalities such as responsiveness to environmental stimuli, making them ideal for high-tech and adaptive uses. Hemp fiber provides superior strength, biodegradability, and sustainability, making it a cost-effective and eco-friendly option for construction, textiles, and composites.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Hemp fiber for Bio-based material
 azmater.com
azmater.com