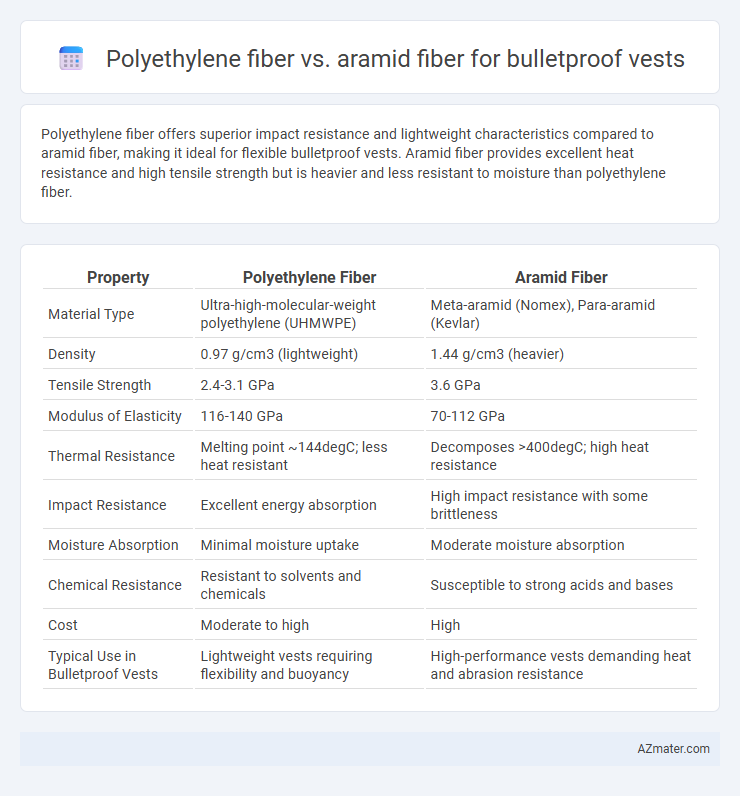
Polyethylene fiber offers superior impact resistance and lightweight characteristics compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for flexible bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber provides excellent heat resistance and high tensile strength but is heavier and less resistant to moisture than polyethylene fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | Meta-aramid (Nomex), Para-aramid (Kevlar) |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 1.44 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Tensile Strength | 2.4-3.1 GPa | 3.6 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 116-140 GPa | 70-112 GPa |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~144degC; less heat resistant | Decomposes >400degC; high heat resistance |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent energy absorption | High impact resistance with some brittleness |
| Moisture Absorption | Minimal moisture uptake | Moderate moisture absorption |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to solvents and chemicals | Susceptible to strong acids and bases |
| Cost | Moderate to high | High |
| Typical Use in Bulletproof Vests | Lightweight vests requiring flexibility and buoyancy | High-performance vests demanding heat and abrasion resistance |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Polyethylene fiber and aramid fiber are prominent materials used in bulletproof vests due to their high tensile strength and lightweight properties. Polyethylene fiber, known for its ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composition, offers superior ballistic resistance while maintaining low weight and buoyancy. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, provide excellent thermal stability and durability, making them ideal for multi-threat protection in personal armor systems.
Overview of Polyethylene Fiber
Polyethylene fiber, specifically ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it a popular choice for bulletproof vests due to its lightweight and high impact resistance. Its chemical resistance and low moisture absorption increase durability under various environmental conditions. Compared to aramid fiber, polyethylene fiber provides superior ballistic performance with significantly reduced weight, enhancing wearer mobility and comfort.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber, a synthetic polymer known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, is widely used in bulletproof vests due to its high tensile strength and resistance to impact and heat. Unlike polyethylene fiber, aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer superior thermal stability and durability, making them ideal for multi-threat ballistic protection. Their molecular structure enables the absorption and dispersion of kinetic energy, effectively stopping high-velocity projectiles while maintaining flexibility and lightweight comfort.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Polyethylene fibers, specifically Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), consist of long chains of polyethylene molecules aligned to provide exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar or Twaron, are aromatic polyamides characterized by rigid, rod-like molecular chains that offer high tensile strength and heat resistance. While polyethylene fibers excel in energy absorption and are highly resistant to moisture, aramid fibers provide better thermal stability and greater resistance to abrasion and impact at elevated temperatures.
Ballistic Performance Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength and low weight, providing excellent ballistic energy absorption and shrapnel resistance, making it ideal for lightweight bulletproof vests. Aramid fiber offers superior thermal stability and impact resistance, maintaining structural integrity under high-velocity impacts and enhancing multi-hit capability in tactical applications. Ballistic performance comparison shows polyethylene fiber excels in blunt force trauma reduction and weight savings, while aramid fiber delivers greater durability against fragmentation and heat exposure.
Weight and Comfort Considerations
Polyethylene fiber offers significantly lighter weight compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for bulletproof vests where mobility and reduced fatigue are priorities. Polyethylene fibers provide higher comfort due to lower density and enhanced moisture resistance, contributing to cooler and drier wear during extended use. Aramid fiber, while heavier, delivers superior heat resistance but can be less comfortable in hot environments due to its moisture retention and stiffness.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Polyethylene fibers, such as Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer high durability with excellent impact resistance and are notably resistant to moisture and UV degradation. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar, provide superior thermal stability and maintain strength under extreme heat but are more susceptible to moisture absorption, which can reduce their durability over time. Environmental resistance of polyethylene fibers generally exceeds that of aramid fibers, making UHMWPE preferable for prolonged exposure to harsh, wet, or UV-intense conditions in bulletproof vests.
Cost and Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers a cost-effective solution for bulletproof vests due to its lower raw material expenses and efficient manufacturing processes, making it widely accessible for large-scale production. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, typically incurs higher costs because of complex synthesis and limited availability from specialized suppliers, which can restrict supply chains. Polyethylene's superior availability and affordability often make it the preferred choice in budget-sensitive applications without severe compromise on ballistic performance.
Applications in Law Enforcement and Military
Polyethylene fiber, known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent ballistic resistance, is widely used in law enforcement and military bulletproof vests for enhanced mobility and comfort during prolonged operations. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for environments with extreme temperatures and high-impact threats. Both fibers contribute significantly to personal armor systems, with polyethylene fibers preferred for lightweight tactical gear and aramid fibers favored for multi-hit protection and resistance to abrasion.
Which Fiber is Better for Bulletproof Vests?
Polyethylene fiber, such as Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers high tensile strength, low weight, and excellent resistance to moisture, making it ideal for lightweight bulletproof vests with superior comfort and mobility. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Twaron, provide exceptional heat resistance and impact absorption, making them highly effective for stopping high-velocity projectiles in traditional tactical armor. For bulletproof vests, polyethylene fibers generally perform better in terms of weight-to-protection ratio, while aramid fibers remain preferred for applications requiring enhanced thermal stability and multi-hit capability.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com