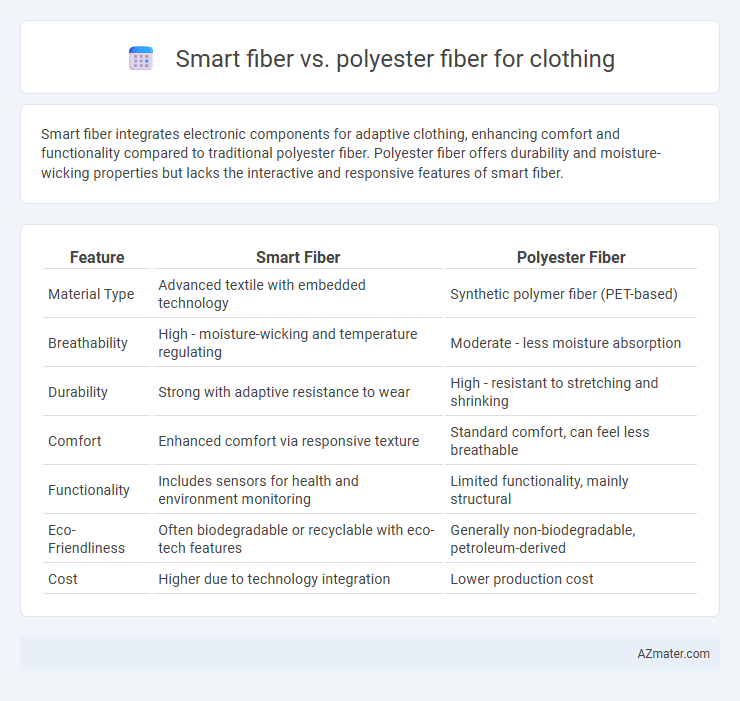
Smart fiber integrates electronic components for adaptive clothing, enhancing comfort and functionality compared to traditional polyester fiber. Polyester fiber offers durability and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the interactive and responsive features of smart fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Advanced textile with embedded technology | Synthetic polymer fiber (PET-based) |
| Breathability | High - moisture-wicking and temperature regulating | Moderate - less moisture absorption |
| Durability | Strong with adaptive resistance to wear | High - resistant to stretching and shrinking |
| Comfort | Enhanced comfort via responsive texture | Standard comfort, can feel less breathable |
| Functionality | Includes sensors for health and environment monitoring | Limited functionality, mainly structural |
| Eco-Friendliness | Often biodegradable or recyclable with eco-tech features | Generally non-biodegradable, petroleum-derived |
| Cost | Higher due to technology integration | Lower production cost |
Introduction to Smart Fibers and Polyester Fibers
Smart fibers, integrating advanced technology such as sensors or conductive materials, offer adaptive properties like temperature regulation and moisture management in clothing. Polyester fibers, derived from synthetic polymers, provide durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking capabilities widely used in mainstream apparel. Comparing their functionality, smart fibers enable responsive performance enhancements, while polyester serves as a reliable, cost-effective base material for everyday garments.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Smart fiber clothing incorporates advanced materials like phase-change or conductive fibers, enabling temperature regulation and moisture management, whereas polyester fiber is a synthetic polymer primarily composed of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), known for durability and wrinkle resistance. Smart fibers often integrate nanotechnology or microcapsules to enhance performance such as breathability and odor control, while polyester's consistent chemical structure offers strong tensile strength and color retention. The distinct material compositions result in smart fibers providing adaptive comfort and functionality, contrasting with polyester's cost-effective, straightforward fiber architecture suitable for mass-produced apparel.
Performance and Functionality Comparison
Smart fiber clothing offers advanced moisture-wicking, temperature regulation, and odor resistance, outperforming traditional polyester fiber in adaptability and comfort during physical activities. Polyester fibers are durable, lightweight, and cost-effective, but lack the responsive capabilities of smart fibers that actively enhance wearer performance and functionality. Choosing smart fiber garments can significantly improve breathability and thermal management, making them ideal for high-performance sportswear and outdoor apparel.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Smart fiber offers enhanced moisture-wicking and temperature regulation compared to traditional polyester fiber, significantly improving comfort during prolonged wear. Polyester fiber is durable and wrinkle-resistant but may trap heat and moisture, reducing breathability and causing discomfort in warm conditions. Advanced smart fibers integrate sensory technology and adaptive materials to optimize body temperature and enhance overall wearability in diverse environments.
Moisture Management Capabilities
Smart fiber outperforms polyester fiber in moisture management, offering enhanced sweat-wicking and faster drying properties due to advanced breathable and hydrophobic technologies. Polyester fiber tends to retain moisture longer, which can lead to discomfort and increased drying times during physical activities. Smart fiber's superior moisture regulation contributes to improved thermal comfort and reduces the risk of skin irritation, making it ideal for activewear and performance clothing.
Durability and Longevity of Fabrics
Smart fiber materials incorporate advanced nanotechnology and moisture-wicking properties, significantly enhancing fabric durability and resistance to wear compared to traditional Polyester fiber. Polyester fiber, while durable and resistant to stretching and shrinking, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV light and repeated washing. Smart fibers maintain structural integrity and color vibrancy longer, making them superior for long-lasting clothing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Smart fibers, often engineered with biodegradable or recyclable materials, offer a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional polyester fibers, which are derived from non-renewable petroleum resources and contribute significantly to microplastic pollution. Polyester production involves high energy consumption and releases greenhouse gases, whereas smart fibers can incorporate sustainable practices such as reduced water usage and lower emissions during manufacturing. As the fashion industry moves towards sustainability, smart fibers present a promising alternative by enhancing biodegradability and supporting circular economy principles.
Cost Implications in Clothing Production
Smart fibers generally incur higher production costs due to advanced materials and integrated technologies, impacting the overall expense of clothing manufacturing. Polyester fibers remain cost-effective and widely used because of their low price, durability, and ease of mass production. Manufacturers weigh the high initial investment of smart fibers against long-term value in performance benefits versus the affordability and scalability of polyester for bulk apparel production.
Innovations in Smart Fiber Technology
Smart fiber technology incorporates advanced materials such as phase-change materials, conductive polymers, and nanotechnology to create fabrics that adapt to environmental conditions, regulate temperature, and monitor biometric data. Polyester fiber, a widely used synthetic material, offers durability and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the responsive functionalities inherent in smart fibers. Innovations in smart fiber technology are driving the development of clothing that enhances comfort, performance, and health tracking, positioning it as a transformative alternative to traditional polyester fibers.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Clothing Needs
Smart fiber incorporates advanced materials like phase-change compounds or conductive yarns, enhancing moisture management and temperature regulation for activewear and performance clothing. Polyester fiber offers durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying properties, making it ideal for everyday garments and budget-friendly options. Selecting the right fiber depends on your priority--opt for smart fiber for enhanced comfort and technology integration, or polyester for resilience and affordability in clothing.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Polyester fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com