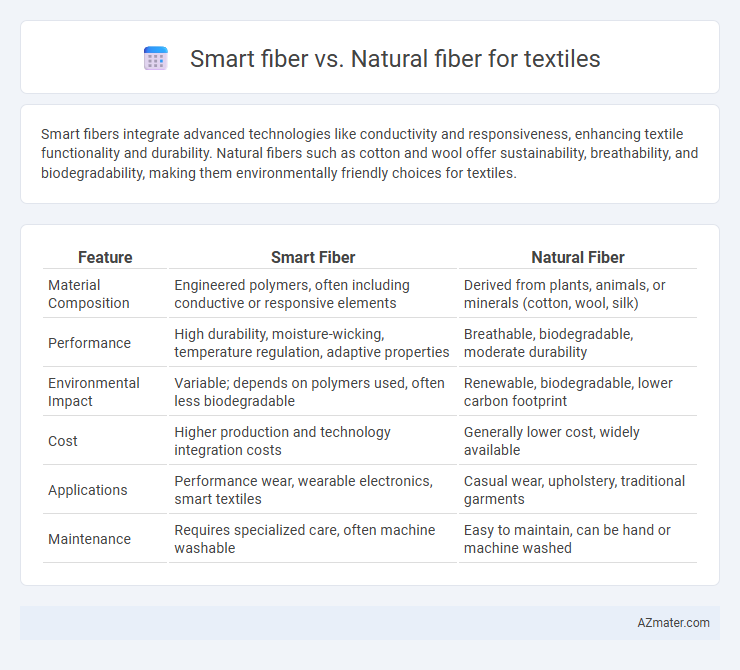
Smart fibers integrate advanced technologies like conductivity and responsiveness, enhancing textile functionality and durability. Natural fibers such as cotton and wool offer sustainability, breathability, and biodegradability, making them environmentally friendly choices for textiles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Natural Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Engineered polymers, often including conductive or responsive elements | Derived from plants, animals, or minerals (cotton, wool, silk) |
| Performance | High durability, moisture-wicking, temperature regulation, adaptive properties | Breathable, biodegradable, moderate durability |
| Environmental Impact | Variable; depends on polymers used, often less biodegradable | Renewable, biodegradable, lower carbon footprint |
| Cost | Higher production and technology integration costs | Generally lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | Performance wear, wearable electronics, smart textiles | Casual wear, upholstery, traditional garments |
| Maintenance | Requires specialized care, often machine washable | Easy to maintain, can be hand or machine washed |
Introduction to Smart Fibers and Natural Fibers
Smart fibers are advanced textile materials engineered to respond to environmental stimuli such as temperature, moisture, and pressure, enhancing functionality in apparel and technical fabrics. Natural fibers, derived from plants and animals like cotton, wool, and silk, offer biodegradability, breathability, and comfort, making them sustainable choices in textile production. The integration of smart fibers in textiles provides innovative performance features, whereas natural fibers emphasize eco-friendliness and traditional wearability.
Defining Smart Fibers: Technology and Functionality
Smart fibers are engineered textiles integrated with advanced technologies such as sensors, conductive materials, and microprocessors to provide functionalities beyond traditional fabric properties. These fibers can respond to environmental stimuli like temperature, humidity, or mechanical stress, enabling applications in health monitoring, adaptive clothing, and interactive wearables. Unlike natural fibers derived from plants or animals, smart fibers combine material science and electronics to enhance performance, durability, and user experience in textile products.
Characteristics of Natural Fibers in Textiles
Natural fibers in textiles, such as cotton, wool, silk, and flax, are prized for their breathability, moisture absorption, and biodegradability, enhancing wearer comfort and environmental sustainability. These fibers exhibit excellent thermal regulation and hypoallergenic properties, making them ideal for sensitive skin and variable climates. Their inherent strength, elasticity, and dye affinity contribute to durability and vibrant textile colors, contrasting with the often synthetic feel of smart fibers.
Performance Comparison: Strength, Durability, and Flexibility
Smart fibers, engineered with advanced polymers and nanomaterials, exhibit superior strength and enhanced durability compared to natural fibers like cotton or wool, which are prone to environmental degradation. The flexibility of smart fibers can be precisely tailored during manufacturing to optimize performance for specific textile applications, whereas natural fibers have inherent variability influenced by their biological origin. In textile performance, smart fibers offer consistent mechanical properties and long-term resilience, outperforming natural fibers in strength retention and resistance to wear and tear.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart fibers, engineered for enhanced performance and durability, contribute to sustainability by extending textile lifespan and reducing waste through advanced properties like self-cleaning or biodegradability. Natural fibers such as organic cotton, wool, and hemp are prized for their renewable sources and biodegradability but often require significant water and land use, impacting environmental sustainability. The choice between smart and natural fibers depends on balancing lifecycle environmental impacts, resource consumption, and recycling potential within textile manufacturing.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Smart fibers, engineered with advanced polymers and responsive materials, offer superior moisture management, temperature regulation, and elasticity, enhancing overall comfort and wearability in textiles. Natural fibers like cotton, wool, and silk provide breathability, softness, and hypoallergenic properties, making them ideal for sensitive skin and prolonged wear. Combining smart fiber technology with natural fibers results in textiles that optimize comfort, durability, and adaptability across various environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis: Smart Fibers vs Natural Fibers
Smart fibers, incorporating advanced technologies like conductive or shape-memory materials, generally incur higher production costs due to complex manufacturing processes and expensive raw materials. Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and flax offer cost advantages with lower material expenses and simpler processing, but may lack the enhanced functionalities seen in smart fibers. Considering total cost of ownership, smart fibers can offer long-term savings through durability and specialized applications, while natural fibers remain favored for affordability in mass-market textile production.
Innovations and Applications in the Textile Industry
Smart fibers incorporate advanced technologies such as microcapsules, shape-memory polymers, and conductive materials, enabling textiles to respond dynamically to environmental stimuli like temperature, moisture, and electric current. Natural fibers, valued for their sustainability and biodegradability, have been enhanced through innovations like enzyme treatments and nanotechnology to improve durability, moisture management, and antimicrobial properties. These advancements expand applications in sportswear, medical textiles, and wearable electronics, blending eco-friendly materials with high-performance functionalities.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Smart fibers, embedded with advanced technologies like conductivity and responsiveness, appeal to tech-savvy consumers seeking innovative textile functionalities such as moisture management and temperature regulation. Natural fibers such as cotton, wool, and silk remain favored for their breathability, sustainability, and comfort, aligning with growing eco-conscious consumer trends. Market analysis indicates a rising demand for hybrid textiles combining smart fiber technology with natural fiber benefits, reflecting a consumer preference for performance-enhanced yet environmentally friendly fabrics.
Future Prospects: Evolution of Textile Materials
Smart fibers, engineered with embedded sensors and responsive capabilities, are poised to revolutionize the textile industry by enabling interactive and adaptive clothing, enhancing wearer comfort and performance monitoring. Natural fibers, celebrated for their biodegradability and sustainability, continue to evolve through bioengineering to improve durability and functionality while maintaining environmental benefits. The future of textile materials lies in hybrid innovations that combine smart fiber technology with the eco-friendly properties of natural fibers, driving sustainable and high-performance fabric solutions.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Natural fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com