Recycled fiber in yarn production significantly reduces environmental impact by conserving resources and lowering carbon emissions compared to virgin fiber, which requires extensive water, energy, and raw materials. Choosing recycled fiber enhances sustainability without compromising yarn quality or durability.
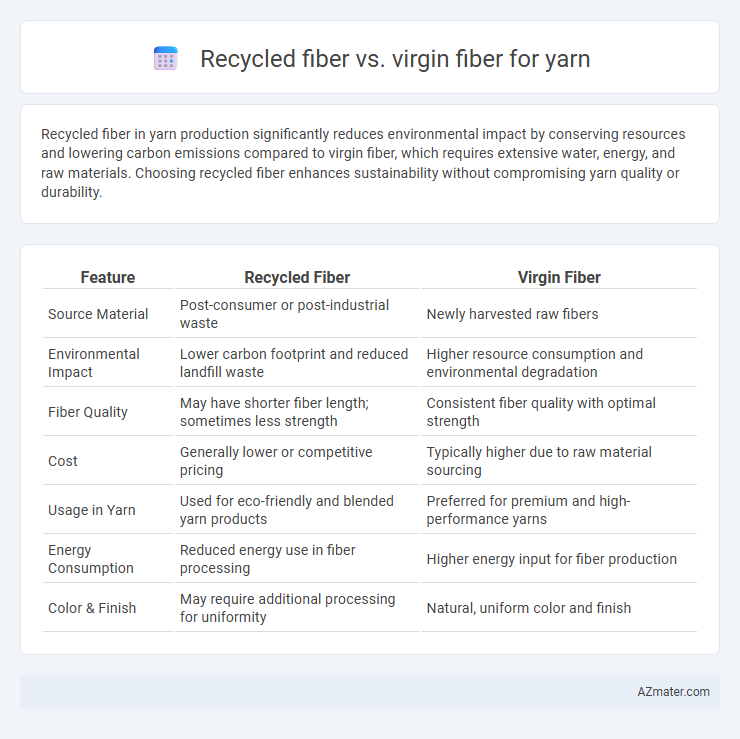
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Fiber | Virgin Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Post-consumer or post-industrial waste | Newly harvested raw fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint and reduced landfill waste | Higher resource consumption and environmental degradation |
| Fiber Quality | May have shorter fiber length; sometimes less strength | Consistent fiber quality with optimal strength |
| Cost | Generally lower or competitive pricing | Typically higher due to raw material sourcing |
| Usage in Yarn | Used for eco-friendly and blended yarn products | Preferred for premium and high-performance yarns |
| Energy Consumption | Reduced energy use in fiber processing | Higher energy input for fiber production |
| Color & Finish | May require additional processing for uniformity | Natural, uniform color and finish |
Introduction to Yarn Fibers
Yarn fibers are primarily categorized into recycled fiber and virgin fiber, each offering distinct environmental and performance attributes. Virgin fiber, sourced directly from natural materials such as cotton or wool, provides superior strength and uniformity essential for high-quality yarn production. Recycled fiber, derived from post-consumer or post-industrial waste, contributes to sustainability by reducing landfill waste and lowering energy consumption during manufacturing.
What Are Virgin Fibers?
Virgin fibers are natural or synthetic fibers produced directly from raw materials without prior processing or use, ensuring superior strength and uniformity in yarn production. Common virgin fibers include cotton, wool, and polyester, which provide consistent quality and are essential for applications requiring high durability and performance. Unlike recycled fibers, virgin fibers maintain original fiber length and integrity, resulting in smoother and stronger yarns ideal for premium textile products.
Understanding Recycled Fibers
Recycled fibers in yarn production are derived from post-consumer or post-industrial textile waste, offering an eco-friendly alternative to virgin fibers by reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing landfill waste. These fibers undergo processes such as mechanical shredding and chemical recycling to restore fiber quality, though the resulting yarn may exhibit variations in strength and texture compared to virgin fibers made from fresh natural or synthetic sources. Understanding recycled fibers involves recognizing their sustainability benefits, potential limitations in performance, and applications in creating eco-conscious textiles without compromising quality.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Fiber
Recycled fiber significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin fiber production, which typically requires extensive water use and chemical treatments. Manufacturing yarn from recycled fibers minimizes landfill waste and decreases the depletion of natural resources such as trees and petroleum-based materials. Studies show that recycled fiber can reduce carbon footprints by up to 70%, making it a more sustainable choice in the textile industry.
Production Process Differences
Recycled fiber production involves collecting post-consumer or post-industrial textile waste, cleaning, and mechanically or chemically breaking it down before re-spinning into yarn, significantly reducing raw material extraction. Virgin fiber production starts with raw natural fibers such as cotton or synthetic polymers, which undergo processes like ginning, carding, and spinning, demanding more energy and water resources. The recycled fiber process typically emits fewer greenhouse gases and consumes less water, making it a more sustainable option compared to the energy-intensive virgin fiber production.
Quality and Performance Comparison
Virgin fiber yarn offers superior strength, softness, and durability compared to recycled fiber, making it ideal for high-quality textile applications requiring long-lasting performance. Recycled fiber yarn, while more sustainable and cost-effective, tends to have shorter staple lengths and increased fiber damage, which can result in reduced tensile strength and slight variations in texture. Advances in recycling technology are improving the quality of recycled fibers, but virgin fibers still dominate in performance-critical yarn production.
Cost Analysis: Recycled vs Virgin Yarn
Recycled fiber yarn typically costs 20-30% less than virgin fiber due to reduced raw material expenses and lower energy consumption during processing. Virgin fiber yarn, derived from new natural or synthetic fibers, incurs higher costs related to agricultural production or petrochemical refinement, driving up overall pricing. Despite initial cost savings, recycled yarn may require additional processing to maintain quality, slightly impacting final manufacturing expenses.
Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Market demand for recycled fiber yarn is rapidly increasing due to growing consumer preference for sustainable and eco-friendly products. Brands are shifting towards recycled fibers to meet regulations and appeal to environmentally conscious buyers, resulting in a surge in recycled fiber yarn production. Virgin fiber yarn remains preferred for high-performance textiles, but the market balance is shifting as recycled alternatives improve in quality and availability.
Sustainability and Certifications
Recycled fiber for yarn significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and water usage compared to virgin fiber production, contributing to sustainable textile manufacturing. Certifications such as GRS (Global Recycled Standard) and OEKO-TEX(r) ensure recycled fibers meet strict environmental and social criteria, promoting transparency and quality. Virgin fiber, while often certified under standards like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), typically has a higher carbon footprint, making recycled fiber the preferred choice for eco-friendly yarn production.
Future Trends in Yarn Fiber Choices
Future trends in yarn fiber choices highlight a growing shift towards recycled fibers due to sustainability demands and regulatory pressures reducing reliance on virgin fibers sourced from petroleum-based or environmentally impactful materials. Innovations in recycling technology enable higher-quality recycled yarns that meet performance standards in textiles, expanding applications in fashion and industrial fabrics. Market projections indicate increasing consumer preference and brand commitments to circular economy principles will accelerate adoption of recycled fibers, challenging the dominance of traditional virgin fiber production.
Infographic: Recycled fiber vs Virgin fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com