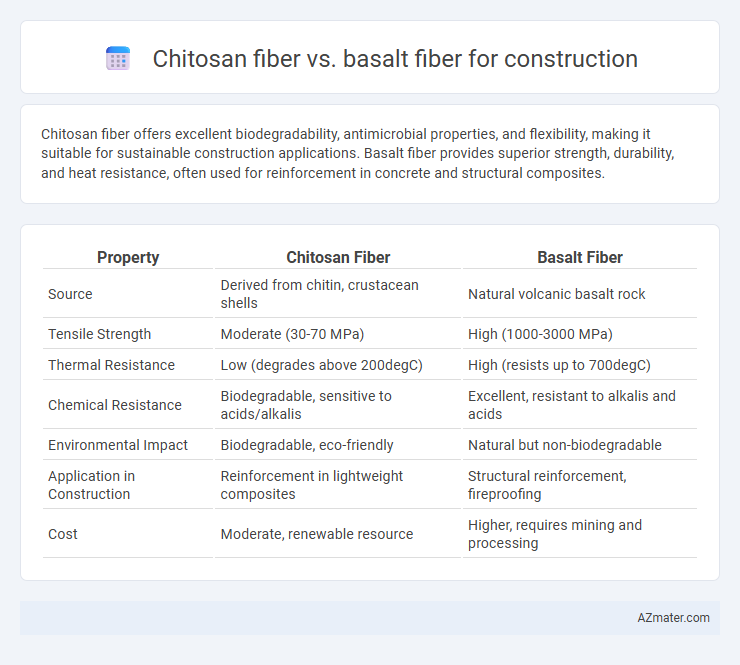
Chitosan fiber offers excellent biodegradability, antimicrobial properties, and flexibility, making it suitable for sustainable construction applications. Basalt fiber provides superior strength, durability, and heat resistance, often used for reinforcement in concrete and structural composites.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Chitosan Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from chitin, crustacean shells | Natural volcanic basalt rock |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (30-70 MPa) | High (1000-3000 MPa) |
| Thermal Resistance | Low (degrades above 200degC) | High (resists up to 700degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Biodegradable, sensitive to acids/alkalis | Excellent, resistant to alkalis and acids |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Natural but non-biodegradable |
| Application in Construction | Reinforcement in lightweight composites | Structural reinforcement, fireproofing |
| Cost | Moderate, renewable resource | Higher, requires mining and processing |
Introduction to Chitosan and Basalt Fibers in Construction
Chitosan fiber, derived from crustacean shells, offers excellent biodegradability, antimicrobial properties, and strong tensile strength, making it a sustainable choice for eco-friendly construction materials. Basalt fiber, produced from volcanic rock, provides superior thermal resistance, high durability, and excellent mechanical performance, making it ideal for reinforcing concrete and structural applications. Both fibers contribute to enhancing construction longevity and environmental sustainability through their unique physical and chemical properties.
Chemical Composition and Source Comparison
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, consists primarily of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine units, offering biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, while basalt fiber is produced from volcanic basalt rock, composed mainly of silica, aluminum oxide, and iron oxide, providing high thermal stability and mechanical strength. The natural origin of chitosan fiber from marine biowaste contrasts with basalt fiber's geological source, influencing their sustainability profiles and chemical resistance in construction applications. Basalt fiber's inorganic composition delivers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to the organic chitosan fiber, making each material suitable for distinct structural requirements.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Chitosan fiber exhibits excellent tensile strength and biodegradability, making it suitable for eco-friendly construction applications but often lacks the robustness required for heavy structural loads. Basalt fiber offers superior mechanical strength, high tensile strength up to 4840 MPa, and exceptional durability against chemical corrosion and temperature extremes, making it ideal for reinforcing concrete and enhancing long-term structural performance. The choice between chitosan and basalt fibers depends on the balance between sustainability goals and the need for mechanical resilience in construction projects.
Thermal Behavior and Fire Resistance
Chitosan fiber exhibits superior thermal insulation properties due to its natural polymer structure, making it highly effective for reducing heat transfer in construction applications. Basalt fiber demonstrates exceptional fire resistance with a melting point above 1400degC, maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat conditions. Comparative thermal behavior reveals chitosan's biodegradability and flame-retardant additives enhance fire resistance, while basalt fiber offers long-term durability with minimal thermal degradation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Chitosan fiber, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, offers superior biodegradability and minimal environmental footprint compared to basalt fiber, which is mined from volcanic rock and requires high energy for processing. The renewable nature of chitosan fiber supports sustainable construction by reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles, whereas basalt fiber, despite its durability and resistance to corrosion, contributes to higher carbon emissions during production. Incorporating chitosan fiber in construction materials enhances eco-friendly building practices by lowering toxicity and improving end-of-life recyclability relative to conventional basalt fiber.
Cost-Effectiveness and Market Availability
Chitosan fiber offers superior biodegradability and antimicrobial properties but remains limited in large-scale construction applications due to higher production costs and restricted market availability. Basalt fiber provides a cost-effective, eco-friendly alternative with widespread availability and excellent mechanical strength, making it favorable for reinforced concrete and structural composites. Evaluating construction projects, basalt fiber consistently delivers greater cost-efficiency and accessibility compared to chitosan fiber.
Ease of Processing and Fabrication Techniques
Chitosan fiber offers superior biodegradability and ease of chemical modification, allowing for versatile wet spinning and electrospinning fabrication methods suited to customized construction composites. Basalt fiber, derived from natural volcanic rock, requires high-temperature melting and extrusion processes, making its production more energy-intensive but yielding fibers with excellent strength and thermal resistance. In terms of processing, chitosan fibers enable simpler integration with bio-based matrices, while basalt fibers demand specialized equipment for handling their stiffness and brittleness during composite fabrication.
Applications in Modern Construction Projects
Chitosan fiber, derived from natural biopolymers, offers excellent biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, making it ideal for sustainable construction materials and eco-friendly coatings in modern buildings. Basalt fiber, produced from volcanic rock, provides superior tensile strength, thermal stability, and corrosion resistance, widely used in structural reinforcement, concrete composites, and seismic retrofitting of infrastructure. Both fibers enhance durability and environmental performance, with chitosan fiber promoting green building initiatives and basalt fiber ensuring long-term structural integrity in advanced construction projects.
Long-Term Performance and Maintenance
Chitosan fiber exhibits excellent biodegradability and antimicrobial properties that enhance long-term durability in construction by resisting mold and bacterial growth, reducing maintenance costs. Basalt fiber offers superior mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability, ensuring structural integrity and minimal degradation over time in harsh environmental conditions. For long-term performance, basalt fiber requires less frequent inspections and repairs, while chitosan fiber supports sustainable maintenance through its eco-friendly properties and slower environmental impact.
Future Prospects and Research Directions
Chitosan fiber shows promising biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, making it suitable for sustainable construction materials innovation. Basalt fiber offers superior mechanical strength and thermal resistance, driving research towards lightweight, high-performance composites for infrastructure durability. Future prospects emphasize hybrid composites combining chitosan's eco-friendliness with basalt's robustness to enhance structural functionality and environmental impact.
Infographic: Chitosan fiber vs Basalt fiber for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com