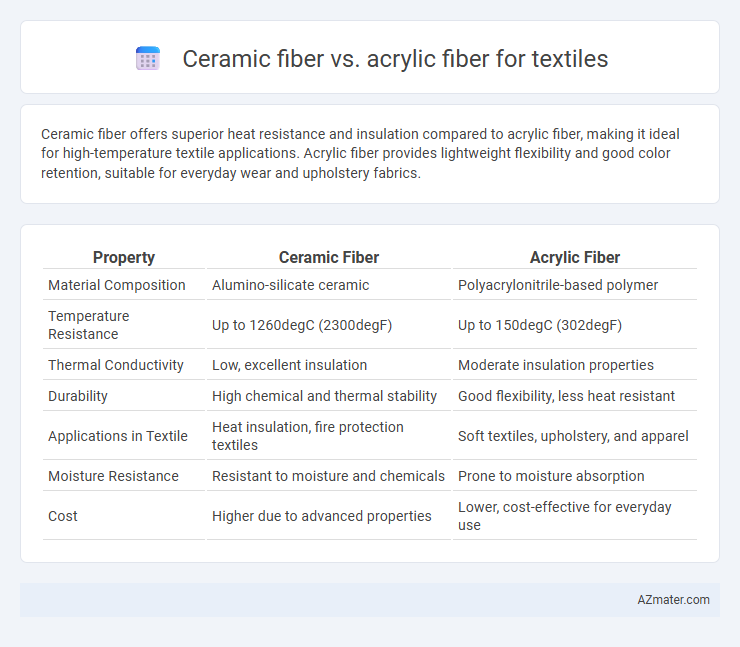
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and insulation compared to acrylic fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature textile applications. Acrylic fiber provides lightweight flexibility and good color retention, suitable for everyday wear and upholstery fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Alumino-silicate ceramic | Polyacrylonitrile-based polymer |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1260degC (2300degF) | Up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low, excellent insulation | Moderate insulation properties |
| Durability | High chemical and thermal stability | Good flexibility, less heat resistant |
| Applications in Textile | Heat insulation, fire protection textiles | Soft textiles, upholstery, and apparel |
| Moisture Resistance | Resistant to moisture and chemicals | Prone to moisture absorption |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced properties | Lower, cost-effective for everyday use |
Introduction to Ceramic Fiber and Acrylic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is an inorganic, heat-resistant material widely used in high-temperature insulation and textile applications due to its excellent thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer fiber, is valued in textiles for its lightweight, softness, and resistance to moisture and UV damage. Comparing ceramic fiber and acrylic fiber highlights the distinct advantages of ceramic fibers in heat insulation and durability versus the flexibility and comfort offered by acrylic fibers in clothing and upholstery.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Ceramic fiber primarily consists of alumina and silica, produced through sol-gel or melting-spinning methods, resulting in high-temperature resistance and thermal insulation properties. Acrylic fiber is composed of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) polymers, created via wet spinning or dry spinning processes, offering flexibility, softness, and moisture-wicking features. The distinct compositions and manufacturing techniques define their applications, with ceramic fibers suited for heat resistance in industrial textiles and acrylic fibers favored in apparel and home textiles for comfort.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Ceramic fiber exhibits exceptional thermal stability, high tensile strength, and excellent resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for high-temperature textile applications. Acrylic fiber offers superior elasticity, lightweight properties, and resistance to ultraviolet light, yet it has lower thermal resistance and tensile strength compared to ceramic fiber. The mechanical durability of ceramic fiber enables use in harsh industrial environments, whereas acrylic fiber is preferred for flexible, lightweight textiles requiring moderate strength and improved comfort.
Thermal Resistance and Insulation
Ceramic fiber exhibits superior thermal resistance withstanding temperatures up to 1260degC, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation in industrial textiles. Acrylic fiber offers moderate thermal insulation, suitable for temperatures below 150degC, emphasizing comfort and lightweight applications in apparel and home textiles. Ceramic fiber's low thermal conductivity and excellent heat retention outperform acrylic fiber, which is better suited for thermal insulation in everyday clothing rather than extreme heat environments.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior chemical resistance compared to acrylic fibers, effectively withstanding harsh acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for high-performance textile applications in aggressive environments. Acrylic fibers have moderate chemical resistance but degrade faster when exposed to strong chemicals or prolonged UV radiation, limiting their use in chemically intense or outdoor conditions. Ceramic fibers also offer exceptional environmental stability, maintaining structural integrity and thermal performance over wide temperature ranges and extended exposure, unlike acrylic fibers which can become brittle and lose strength under UV and oxidative stress.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Ceramic fibers offer outstanding thermal insulation and chemical resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature protective clothing and industrial filtration textiles. Acrylic fibers provide excellent softness, colorfastness, and moisture-wicking properties, commonly used in apparel, upholstery, and outdoor fabrics. In textile manufacturing, ceramic fibers excel in heat-retaining applications, while acrylic fibers enhance comfort and durability in everyday wear and decorative textiles.
Safety and Health Considerations
Ceramic fiber in textiles offers superior heat resistance and minimal off-gassing, making it safer for high-temperature applications compared to acrylic fiber, which can emit harmful fumes when burned. Acrylic fiber poses respiratory risks due to potential formaldehyde-based finishes and releases toxic gases such as hydrogen cyanide during combustion. Prioritizing ceramic fiber in safety-critical environments reduces health hazards linked to toxic exposure and improves workplace air quality.
Cost Comparison and Economic Viability
Ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to acrylic fiber, which is more affordable and widely used for everyday textile applications. Acrylic fiber provides economic viability in large-scale production due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses, making it suitable for cost-sensitive markets. For high-temperature industrial textiles, ceramic fiber justifies its price through enhanced performance and longer service life, despite the initial investment.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ceramic fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and recyclability compared to acrylic fibers, making them more sustainable for high-temperature textile applications. Acrylic fibers, derived from petrochemicals, contribute to microplastic pollution and have a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive production processes. Choosing ceramic fibers supports reduced environmental impact through enhanced durability, lower emissions, and improved waste management in the textile industry.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Textile Applications
Ceramic fiber offers exceptional heat resistance and durability, making it ideal for high-temperature textile applications such as protective clothing and industrial insulation. Acrylic fiber excels in softness, colorfastness, and moisture-wicking properties, which are preferred for everyday apparel and home textiles. Selecting the right fiber depends on the specific requirements of heat tolerance, comfort, and durability in the intended textile use.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com