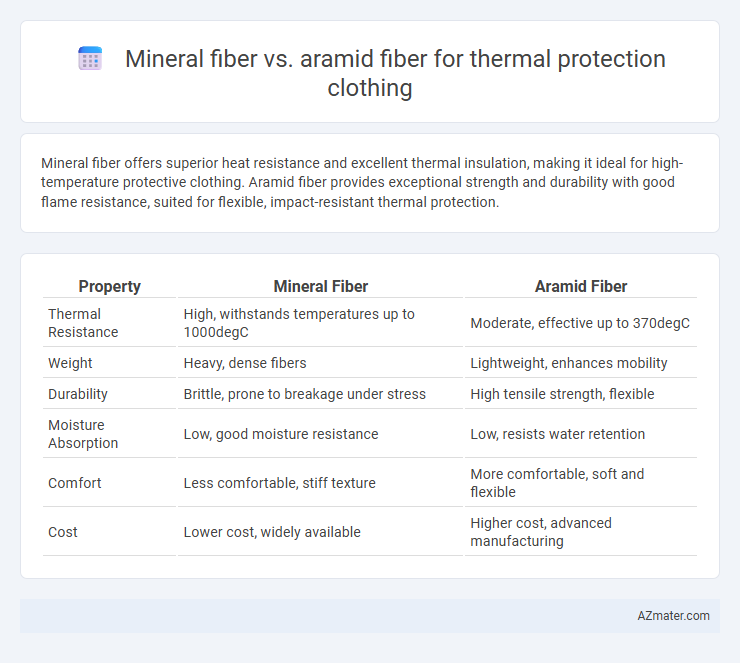
Mineral fiber offers superior heat resistance and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for high-temperature protective clothing. Aramid fiber provides exceptional strength and durability with good flame resistance, suited for flexible, impact-resistant thermal protection.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mineral Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | High, withstands temperatures up to 1000degC | Moderate, effective up to 370degC |
| Weight | Heavy, dense fibers | Lightweight, enhances mobility |
| Durability | Brittle, prone to breakage under stress | High tensile strength, flexible |
| Moisture Absorption | Low, good moisture resistance | Low, resists water retention |
| Comfort | Less comfortable, stiff texture | More comfortable, soft and flexible |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, advanced manufacturing |
Introduction to Thermal Protection Clothing
Thermal protection clothing relies heavily on advanced materials like mineral fiber and aramid fiber to safeguard against extreme heat. Mineral fiber offers excellent insulation and high-temperature resistance, suitable for environments with intense radiant heat, while aramid fiber provides superior strength, durability, and cut resistance, making it ideal for high-performance protective gear. Selecting the appropriate fiber enhances thermal protection clothing's effectiveness in firefighters, industrial workers, and military personnel exposed to hazardous thermal conditions.
Overview of Mineral Fiber Properties
Mineral fibers, such as fiberglass and basalt, exhibit excellent thermal resistance, withstanding temperatures often exceeding 1000degC, making them ideal for high-temperature protective clothing. These fibers offer low thermal conductivity, effective insulation, and inherent flame retardancy, ensuring superior protection against heat and fire hazards. Their chemical stability and resistance to oxidation further enhance durability and performance in extreme thermal environments.
Aramid Fiber Characteristics Explained
Aramid fiber, known for its exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, is widely used in thermal protection clothing due to its inherent flame-retardant properties and durability under extreme temperatures. Unlike mineral fiber, aramid fibers maintain flexibility and lightweight comfort while providing superior resistance to heat, abrasion, and chemical exposure. These fibers exhibit excellent thermal stability up to 500degC and are often utilized in firefighter suits and industrial safety gear for enhanced protection and performance.
Thermal Resistance: Mineral vs. Aramid Fiber
Mineral fibers, such as basalt and glass fibers, exhibit high thermal resistance and excellent insulating properties, making them ideal for extreme heat exposure. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior thermal stability and flame resistance with lower thermal conductivity, enhancing durability in high-temperature environments. Comparing thermal resistance, aramid fibers offer more flexibility and stronger performance in dynamic thermal protection clothing, whereas mineral fibers excel in static insulation applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to mineral fibers, making them ideal for thermal protection clothing subjected to intense mechanical stress. Their high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and resistance to degradation under prolonged high temperatures surpass mineral fibers, which tend to be brittle and less resilient under repetitive strain. This durability ensures longer-lasting protective garments with sustained thermal and mechanical performance in harsh environments.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Mineral fiber, known for its high thermal resistance, offers excellent insulation but tends to be stiff and less breathable, potentially reducing wearer comfort during extended use. Aramid fiber provides superior flexibility and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort and wearability in thermal protection clothing without compromising heat resistance. The lightweight nature and soft texture of aramid fibers make them ideal for applications requiring prolonged wear and mobility.
Flame and Heat Resistance Performance
Mineral fibers exhibit superior thermal insulation and high-temperature resistance up to 1000degC, making them ideal for flame-resistant clothing in extreme heat environments. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, offer excellent flame resistance and self-extinguishing properties, withstanding temperatures up to 370degC while maintaining strength and flexibility. The choice between mineral and aramid fibers depends on the required balance of heat resistance, durability, and comfort in protective apparel for fire hazards.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Mineral fibers exhibit excellent chemical resistance, particularly to acids and alkalis, making them suitable for harsh industrial environments, while aramid fibers provide superior resistance to organic solvents and degradation from UV exposure. Aramid fibers demonstrate outstanding thermal stability and flame retardant properties without melting or dripping, whereas mineral fibers offer better resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion but can be brittle. Both fibers deliver durable environmental protection, with aramid favored for flexibility and impact resistance and mineral fibers lauded for superior chemical inertness in extreme conditions.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Mineral fiber used in thermal protection clothing generally offers a lower cost and wider availability compared to aramid fiber, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale applications. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are typically more expensive due to their advanced manufacturing processes and superior heat resistance qualities, yet they provide enhanced durability and flame retardancy. Availability of mineral fibers is more consistent across global markets, whereas aramid fibers may face supply constraints and higher price volatility driven by specialized demand and production limitations.
Selecting the Right Fiber for Thermal Protection Clothing
Mineral fiber excels in thermal protection due to its inherent non-combustibility and high melting point, making it ideal for environments with extreme heat exposure. Aramid fiber offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, providing enhanced durability and cut resistance while maintaining excellent thermal stability. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific application needs: mineral fiber suits high-temperature insulation, whereas aramid fiber is preferred for protective garments requiring a balance of heat resistance and mechanical performance.
Infographic: Mineral fiber vs Aramid fiber for Thermal protection clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com