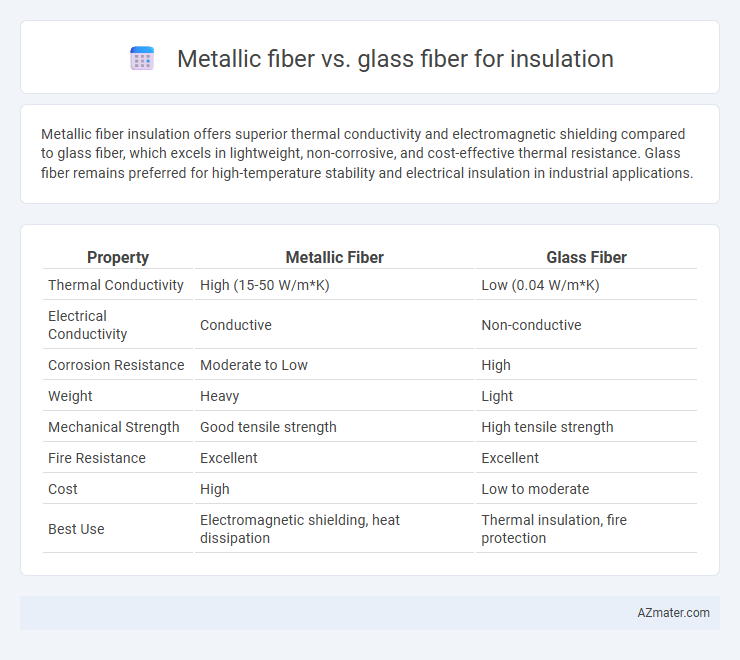
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding compared to glass fiber, which excels in lightweight, non-corrosive, and cost-effective thermal resistance. Glass fiber remains preferred for high-temperature stability and electrical insulation in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (15-50 W/m*K) | Low (0.04 W/m*K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive | Non-conductive |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate to Low | High |
| Weight | Heavy | Light |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength | High tensile strength |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | High | Low to moderate |
| Best Use | Electromagnetic shielding, heat dissipation | Thermal insulation, fire protection |
Introduction to Metallic Fiber and Glass Fiber Insulation
Metallic fiber insulation consists of fine metal strands designed to reflect radiant heat, making it highly effective in high-temperature applications and electromagnetic interference shielding. Glass fiber insulation, composed of spun glass fibers, excels in thermal resistance, sound absorption, and fire retardancy, commonly used in residential and industrial settings. Both materials offer distinct advantages: metallic fibers provide superior conductivity and durability, while glass fibers offer lightweight thermal insulation with excellent fire safety.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Metallic fiber insulation is composed primarily of fine metal strands such as aluminum or stainless steel, produced through processes like wire drawing and weaving to create flexible, conductive mats ideal for thermal and electromagnetic shielding. Glass fiber insulation consists of spun silica-based fibers formed by melting raw materials followed by fiberizing through rapid cooling and attenuation, resulting in non-metallic, highly effective thermal and acoustic barriers. The manufacturing distinction, metal drawing versus glass melting and fiberizing, directly influences the fibers' thermal conductivity, durability, and application in insulation technology.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior thermal conductivity, efficiently dissipating heat, while glass fiber insulation provides excellent thermal resistance by trapping air within its fibers, reducing heat transfer. Glass fiber's low thermal conductivity ranges typically between 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K, making it effective for minimizing heat loss, whereas metallic fibers, due to their high conductivity (often above 200 W/m*K), are less effective as insulators but beneficial in applications requiring heat dissipation. The choice between metallic and glass fiber insulation depends on the required balance between thermal resistance and conductivity for specific temperature management needs.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Metallic fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to glass fibers, with enhanced tensile strength and resistance to deformation under stress. Their durability is notable, as metals withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion better than glass, which can be brittle and prone to cracking under mechanical stress. Consequently, metallic fiber insulation offers longer service life and improved reliability in demanding industrial applications.
Fire Resistance Performance
Metallic fibers exhibit superior fire resistance performance compared to glass fibers due to their high melting points and non-combustible nature, making them ideal for applications requiring enhanced thermal protection. Glass fibers, while also fire-resistant and capable of withstanding temperatures up to approximately 1,000degC, can become brittle and degrade under prolonged high heat exposure. The inherent metallic conductivity further aids in dissipating heat quickly, reducing the risk of fire propagation in insulated materials.
Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
Metallic fibers exhibit limited moisture resistance and are prone to corrosion when exposed to high humidity or water, which can degrade their insulating properties over time. Glass fibers offer superior moisture resistance and do not corrode, maintaining their structural integrity and insulation efficiency in damp environments. For applications requiring long-term durability against moisture and corrosion, glass fiber insulation is the preferred choice.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Metallic fibers offer superior thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding but tend to be heavier and less flexible compared to glass fibers, which are lightweight and provide excellent flexibility for insulation applications. Glass fibers reduce overall structural weight, making them ideal for aerospace and automotive insulation, while metallic fibers, due to their higher density, are better suited for applications requiring durability and enhanced heat dissipation. The choice between these fibers depends on balancing weight constraints and the need for mechanical flexibility in specific insulation projects.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Viability
Metallic fiber insulation offers higher thermal conductivity but comes at a significantly higher initial cost compared to glass fiber, which remains more cost-efficient due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses. Glass fiber insulation provides superior economic viability for large-scale applications, benefiting from widespread availability and lower installation costs. Despite the premium price, metallic fiber's durability and potential for reuse can offset expenses in specialized industrial contexts where long-term performance is critical.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Metallic fibers exhibit higher recyclability and durability compared to glass fibers, contributing to reduced environmental waste in insulation applications. Glass fibers, while energy-intensive to produce, offer better thermal insulation efficiency, lowering long-term energy consumption and carbon emissions. Sustainable insulation solutions increasingly favor recyclable metallic fibers due to their potential for reducing landfill accumulation and supporting circular economy principles.
Best Applications for Metallic and Glass Fiber Insulation
Metallic fiber insulation excels in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and high-temperature environments, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and industrial applications requiring durability and thermal resistance. Glass fiber insulation offers superior thermal performance and soundproofing, commonly used in residential, commercial buildings, and HVAC systems for energy efficiency and noise reduction. Selecting between metallic and glass fiber insulation depends on specific needs such as conductivity, temperature tolerance, and acoustic properties.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Glass fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com