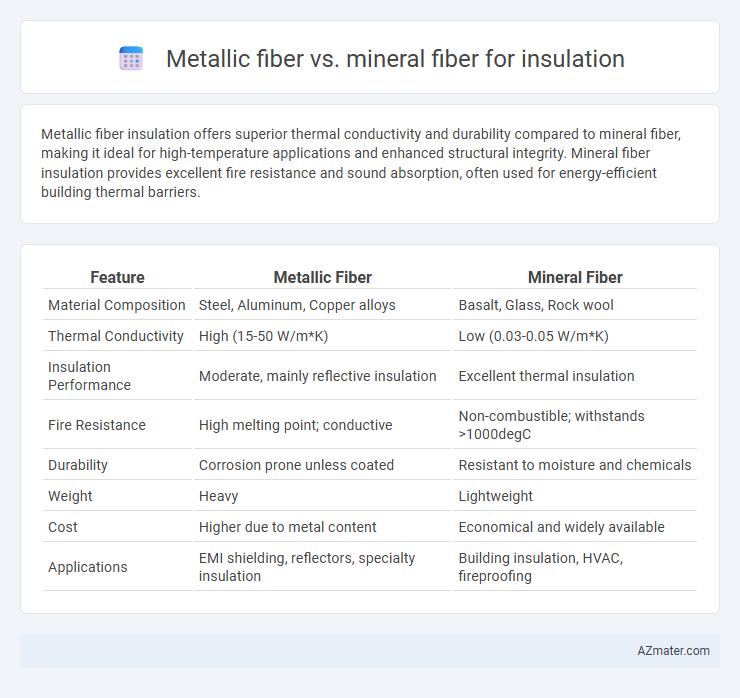
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior thermal conductivity and durability compared to mineral fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature applications and enhanced structural integrity. Mineral fiber insulation provides excellent fire resistance and sound absorption, often used for energy-efficient building thermal barriers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metallic Fiber | Mineral Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Steel, Aluminum, Copper alloys | Basalt, Glass, Rock wool |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (15-50 W/m*K) | Low (0.03-0.05 W/m*K) |
| Insulation Performance | Moderate, mainly reflective insulation | Excellent thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | High melting point; conductive | Non-combustible; withstands >1000degC |
| Durability | Corrosion prone unless coated | Resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher due to metal content | Economical and widely available |
| Applications | EMI shielding, reflectors, specialty insulation | Building insulation, HVAC, fireproofing |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior thermal conductivity control and fire resistance compared to mineral fiber, which is commonly made from rock or glass and excels in sound absorption and thermal resistance. Mineral fibers such as fiberglass and rock wool are non-combustible and widely used for thermal and acoustic insulation in residential and industrial applications. Metallic fibers, often composed of stainless steel or aluminum, provide enhanced durability and electromagnetic shielding properties, making them suitable for specialized insulation needs in high-temperature or hazardous environments.
Overview of Metallic Fiber Insulation
Metallic fiber insulation provides superior thermal conductivity and excellent fire resistance compared to traditional mineral fiber options, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Its durability and corrosion resistance contribute to longer service life in harsh environments, while its lightweight nature enhances ease of installation. This insulation type efficiently minimizes heat loss and maintains structural integrity under extreme thermal stress, outperforming mineral fiber insulation in performance and longevity.
Overview of Mineral Fiber Insulation
Mineral fiber insulation, commonly made from rock wool or slag wool, offers superior thermal resistance and excellent fire retardant properties, making it a reliable choice for building insulation. This non-combustible material provides efficient sound absorption and durability while resisting moisture and mold growth. Compared to metallic fiber insulation, mineral fiber is more cost-effective and environmentally sustainable, featuring high thermal performance without the conductivity associated with metals.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Metallic fibers exhibit high thermal conductivity, making them less effective for insulation compared to mineral fibers, which have low thermal conductivity values typically ranging from 0.03 to 0.05 W/m*K. Mineral fibers such as fiberglass and rock wool provide superior thermal resistance due to their porous structure that traps air, significantly reducing heat transfer. The thermal performance of mineral fiber insulation ensures better energy efficiency and consistent indoor temperature control in both residential and industrial applications.
Fire Resistance: Metallic vs Mineral Fibers
Metallic fibers exhibit superior fire resistance due to their high melting points and non-combustible nature, maintaining structural integrity under extreme heat. Mineral fibers such as fiberglass and rock wool also offer excellent fire resistance, as they are inherently non-flammable and do not produce toxic smoke when exposed to fire. Fire performance in insulation commonly favors mineral fibers for passive fire protection, while metallic fibers are chosen for applications requiring both thermal and electrical conductivity alongside fire resistance.
Acoustic Properties and Soundproofing
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior sound absorption and vibration damping due to its dense and flexible structure, making it highly effective for reducing noise in industrial settings. Mineral fiber insulation, composed of materials like fiberglass or rock wool, excels in acoustic insulation by trapping airborne sound waves and providing excellent thermal resistance, commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. While metallic fibers provide enhanced impact noise reduction, mineral fibers deliver broader frequency sound attenuation, optimizing overall soundproofing performance.
Durability and Lifespan of Each Fiber Type
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior durability due to its resistance to moisture, pests, and fire, resulting in a longer lifespan often exceeding 50 years. Mineral fiber insulation, such as fiberglass or rock wool, provides moderate durability but is prone to degradation from moisture and physical damage, typically lasting 20 to 30 years under optimal conditions. The inherent corrosion resistance and structural stability of metallic fibers make them ideal for applications requiring extended service life and minimal maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Metallic fiber insulation offers high recyclability and lower embodied energy compared to mineral fiber, which often involves energy-intensive extraction and processing of raw materials like basalt or glass. Mineral fiber insulation can release microfibers during installation and disposal, posing environmental and health risks, whereas metallic fibers, especially when sourced from recycled metals, reduce waste and resource depletion. Sustainability favors metallic fiber insulation due to its longer lifespan, better thermal performance, and circular economy compatibility, minimizing overall environmental impact over its life cycle.
Cost Analysis: Metallic vs Mineral Fiber Insulation
Metallic fiber insulation typically incurs higher initial costs compared to mineral fiber due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material expenses. Mineral fiber insulation, including glass wool and rock wool, offers cost-effective solutions with widespread availability and lower production costs. Long-term cost efficiency favors mineral fiber because of its balance between price, thermal performance, and durability in various insulation applications.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Key Considerations
Metallic fiber insulation offers superior thermal conductivity and electromagnetic shielding, making it ideal for applications requiring high heat resistance and electrical interference protection, while mineral fiber insulation excels in fire resistance, soundproofing, and thermal insulation due to its inorganic composition. Consider factors such as thermal performance, fire safety ratings, acoustic properties, and environmental impact when selecting between metallic and mineral fibers for insulation projects. Cost-effectiveness and installation flexibility also play critical roles in determining the best insulation material for specific industrial or residential applications.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Mineral fiber for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com