Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to traditional cotton fiber, which relies on water-intensive cultivation. Ingeo fiber also provides enhanced durability and biodegradability, making it a sustainable alternative for eco-conscious textile manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
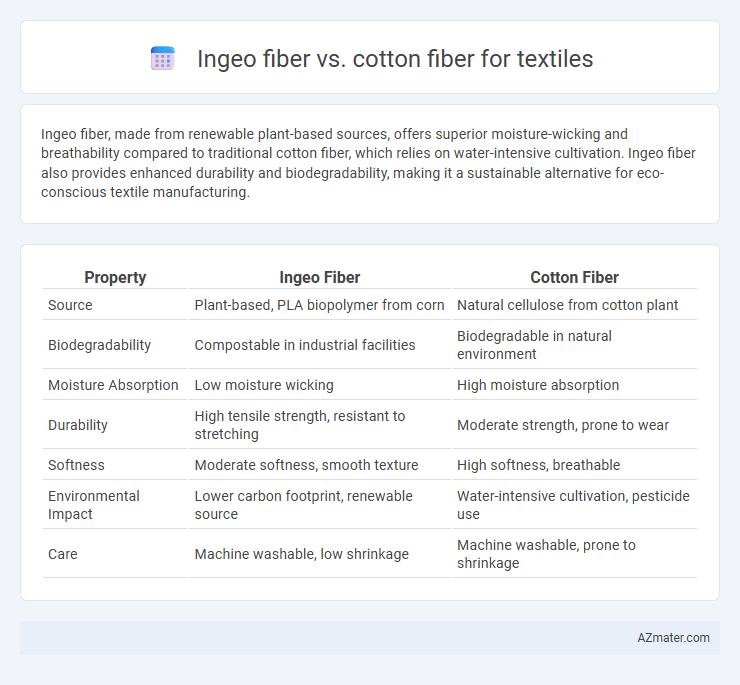
| Property | Ingeo Fiber | Cotton Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based, PLA biopolymer from corn | Natural cellulose from cotton plant |
| Biodegradability | Compostable in industrial facilities | Biodegradable in natural environment |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture wicking | High moisture absorption |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to stretching | Moderate strength, prone to wear |
| Softness | Moderate softness, smooth texture | High softness, breathable |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, renewable source | Water-intensive cultivation, pesticide use |
| Care | Machine washable, low shrinkage | Machine washable, prone to shrinkage |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Cotton Fiber
Ingeo fiber, derived from polylactic acid (PLA) biopolymer made through fermentation of renewable plant sugars, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional fibers. Cotton fiber, sourced from the seed hairs of the cotton plant, is widely recognized for its natural softness, breathability, and versatility in textile applications. The comparison between Ingeo fiber and cotton fiber in textiles involves assessing factors such as environmental impact, moisture management, durability, and lifecycle performance.
Origin and Production Processes
Ingeo fiber is a biopolymer derived from renewable plant-based resources like corn fermentation, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fibers. Cotton fiber originates from the natural cotton plant, harvested through extensive agricultural practices involving irrigation, pesticides, and mechanical picking. The production of Ingeo fiber involves microbial fermentation and biopolymer extraction, whereas cotton fiber production relies on ginning, cleaning, and spinning raw cotton fibers into textile yarns.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, significantly reduces carbon emissions and water usage compared to conventional cotton fiber, which requires extensive irrigation and pesticide application. The biodegradability of Ingeo fiber contributes to lower environmental persistence, while cotton cultivation often leads to soil degradation and high chemical inputs. Life cycle assessments highlight Ingeo's lower overall ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable choice for textile manufacturing.
Physical Properties and Performance
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, exhibits high tensile strength and excellent moisture-wicking properties compared to conventional cotton fiber, which is known for its softness and natural breathability. Ingeo fibers demonstrate superior wrinkle resistance and quicker drying times, enhancing fabric durability and comfort during wear, while cotton fibers offer better thermal insulation and skin-friendly softness ideal for sensitive skin. Textile manufacturers often prefer Ingeo for sustainable, performance-driven applications whereas cotton remains favored for classic comfort and natural fiber content.
Comfort and Wearability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to traditional cotton fiber, enhancing overall comfort in textile applications. Its natural elasticity and softness provide a lightweight feel that reduces skin irritation and improves wearability during extended use. While cotton fibers remain valued for their durability and natural texture, Ingeo's sustainable composition delivers a more consistent comfort experience ideal for activewear and everyday clothing.
Durability and Lifespan
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers enhanced durability compared to conventional cotton fiber, exhibiting higher tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear in textile applications. Cotton fiber, while breathable and soft, tends to deteriorate faster under frequent washing and environmental exposure, leading to a shorter lifespan. The inherent biodegradability of Ingeo fiber combined with its structural resilience makes it an increasingly preferred choice for sustainable textiles requiring long-lasting performance.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Factors
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant starches, exhibits faster biodegradability compared to conventional cotton fiber, typically decomposing within months under industrial composting conditions. Cotton fiber, while natural and biodegradable, often relies on agricultural inputs like pesticides and water, influencing its overall environmental footprint. End-of-life management of Ingeo promotes closed-loop composting systems, reducing landfill waste, whereas cotton's disposal often leads to slower degradation in landfills, especially if blended with synthetic fibers.
Cost and Market Availability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, generally has higher production costs compared to traditional cotton fiber, which benefits from established large-scale cultivation and processing infrastructure. Cotton fiber remains more widely available and cost-effective in global textile markets due to its long-standing supply chains and lower raw material expenses. Market demand for Ingeo fiber is growing, driven by sustainability trends, but its higher price point still limits widespread adoption compared to the more accessible and economical cotton fiber.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Ingeo fiber offers a sustainable alternative to cotton fiber with its biodegradable and renewable properties, making it ideal for eco-friendly textile applications such as sportswear, casual apparel, and home textiles. Cotton fiber remains dominant due to its natural softness, breathability, and durability, widely used in everyday clothing, denim, and high-quality textile products. Combining Ingeo with cotton enhances fabric strength and moisture management, expanding its application in performance textiles and fashion segments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber
Ingeo fiber offers superior sustainability with biodegradable properties and lower carbon emissions compared to traditional cotton fiber, making it an eco-friendly choice for textile manufacturing. Cotton fiber provides natural breathability and softness, preferred for comfort and durability in garments. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing environmental impact with end-use requirements, where Ingeo suits eco-conscious brands and cotton remains favored for classic textile applications.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Cotton fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com