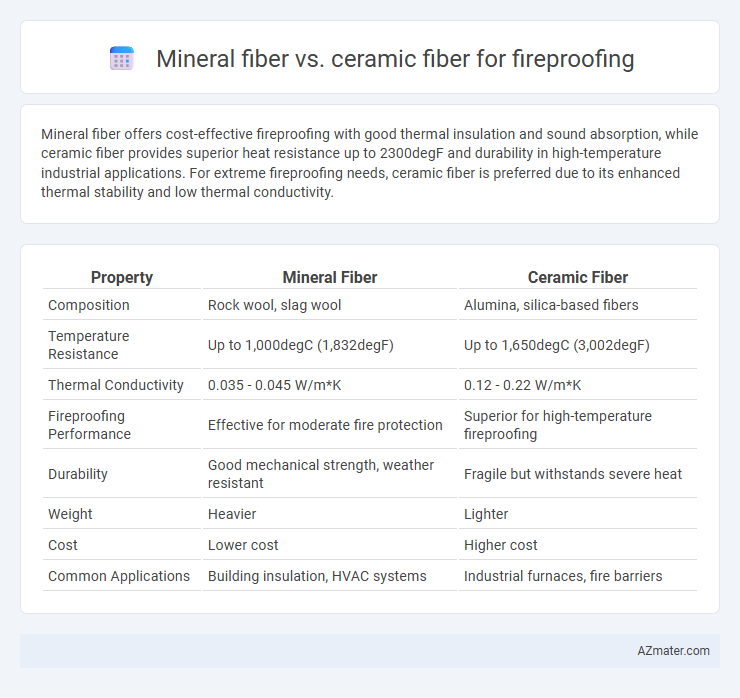
Mineral fiber offers cost-effective fireproofing with good thermal insulation and sound absorption, while ceramic fiber provides superior heat resistance up to 2300degF and durability in high-temperature industrial applications. For extreme fireproofing needs, ceramic fiber is preferred due to its enhanced thermal stability and low thermal conductivity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mineral Fiber | Ceramic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Rock wool, slag wool | Alumina, silica-based fibers |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1,000degC (1,832degF) | Up to 1,650degC (3,002degF) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K | 0.12 - 0.22 W/m*K |
| Fireproofing Performance | Effective for moderate fire protection | Superior for high-temperature fireproofing |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, weather resistant | Fragile but withstands severe heat |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Applications | Building insulation, HVAC systems | Industrial furnaces, fire barriers |
Introduction to Fireproofing Materials
Mineral fiber and ceramic fiber are key fireproofing materials widely used for thermal insulation and fire resistance. Mineral fiber, derived from molten rock or slag, provides cost-effective, durable insulation with excellent heat resistance up to approximately 1000degC. Ceramic fiber, made from alumina and silica, offers superior thermal stability and can withstand temperatures exceeding 1400degC, making it ideal for high-temperature fireproofing applications in industrial settings.
Overview of Mineral Fiber
Mineral fiber, composed primarily of basalt and diabase rock, offers excellent fireproofing properties due to its high melting point above 1000degC and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for insulation in industrial and commercial applications. Its non-combustible nature and resistance to chemical corrosion ensure durability and safety in fire-sensitive environments. Mineral fiber's sound absorption capabilities and environmental sustainability further enhance its appeal compared to ceramic fiber alternatives.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature insulation material composed primarily of alumina and silica, known for its excellent thermal stability and low thermal conductivity up to 2300degF (1260degC). Compared to mineral fiber, ceramic fiber offers superior heat resistance, making it ideal for extreme fireproofing applications in industrial furnaces, kilns, and fireproof barriers. Its lightweight and flexible nature also contribute to easy installation and enhanced durability in high-temperature environments.
Key Properties Comparison
Mineral fiber fireproofing offers high thermal resistance up to 1200degC and excellent sound absorption, while ceramic fiber withstands temperatures above 1400degC with superior thermal insulation and low thermal conductivity. Mineral fibers are denser and more durable for structural applications, whereas ceramic fibers provide lightweight, flexible, and corrosion-resistant solutions ideal for refractory linings. Both materials exhibit good chemical inertness, but ceramic fiber outperforms in rapid thermal cycling and high-temperature stability for extreme fireproofing needs.
Fire Resistance Performance
Mineral fiber offers excellent fire resistance with high melting points typically around 1,000degC to 1,200degC, providing effective insulation and structural protection during high-temperature exposure. Ceramic fiber outperforms mineral fiber in fire resistance, with melting points exceeding 1,400degC to 1,650degC, enabling superior thermal stability and prolonged fireproofing performance. The enhanced fire resistance of ceramic fiber makes it the preferred choice for extreme fireproofing applications in industrial and commercial settings.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Mineral fiber offers excellent thermal insulation with a high melting point around 1000degC, making it suitable for general fireproofing applications requiring moderate to high temperature resistance. Ceramic fiber outperforms mineral fiber in thermal insulation, withstanding temperatures up to 1400degC or higher, providing superior heat retention and lower thermal conductivity in extreme temperature environments. The choice between mineral and ceramic fiber depends on the specific fireproofing needs, where ceramic fiber is preferred for high-temperature industrial settings, while mineral fiber suits commercial and residential insulation requirements.
Durability and Longevity
Mineral fiber offers excellent fireproofing properties with high resistance to thermal degradation, making it durable for long-term applications in insulation and fire protection. Ceramic fiber provides superior heat resistance and maintains its structural integrity at higher temperatures, enhancing its longevity in extreme fireproofing environments. Both materials exhibit strong durability, but ceramic fiber generally outperforms mineral fiber in longevity under intense thermal conditions.
Health and Safety Considerations
Mineral fiber and ceramic fiber both offer strong fireproofing capabilities, but ceramic fiber poses higher health risks due to its fine, respirable dust that can irritate the respiratory system and skin. Mineral fiber generally has lower biopersistence and is considered safer, as it releases fewer hazardous fibers during installation and removal. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilation are critical when handling either material to minimize exposure to potentially harmful airborne particles.
Cost and Installation Factors
Mineral fiber fireproofing offers a cost-effective solution with relatively simple installation, making it a popular choice for large-scale commercial projects. Ceramic fiber, although more expensive, provides superior thermal resistance and durability, often justifying higher upfront costs in high-temperature environments. Installation of ceramic fiber requires specialized skills and protective measures due to its fragile and irritant nature, while mineral fiber is easier and faster to apply, reducing labor costs.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Project
Mineral fiber offers excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for fireproofing in commercial buildings and industrial applications where durability and sound absorption are critical. Ceramic fiber withstands higher temperatures and provides superior thermal shock resistance, best suited for high-temperature environments such as furnaces and kilns. Evaluating project requirements, including maximum operating temperature, insulation performance, and budget constraints, ensures selecting the right fiber for effective fireproofing.
Infographic: Mineral fiber vs Ceramic fiber for Fireproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com