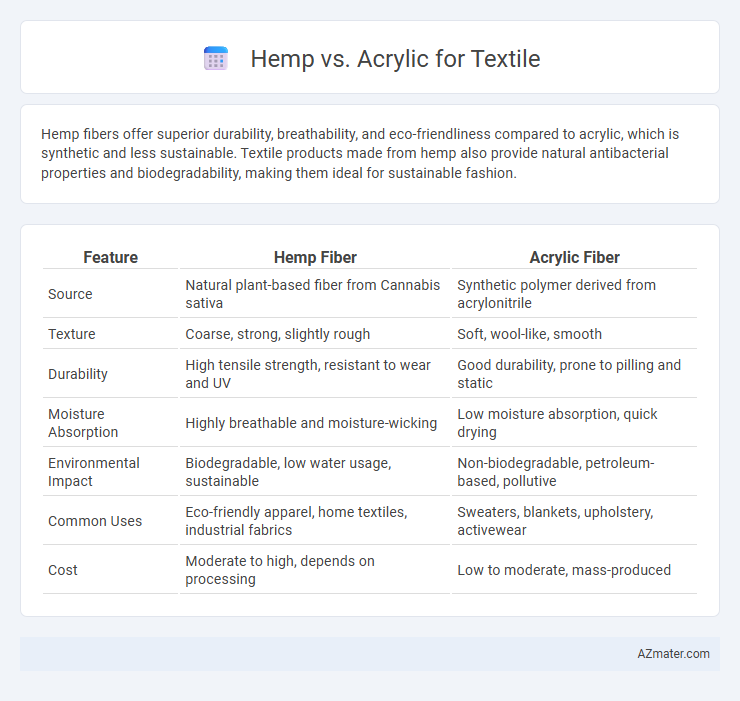
Hemp fibers offer superior durability, breathability, and eco-friendliness compared to acrylic, which is synthetic and less sustainable. Textile products made from hemp also provide natural antibacterial properties and biodegradability, making them ideal for sustainable fashion.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural plant-based fiber from Cannabis sativa | Synthetic polymer derived from acrylonitrile |
| Texture | Coarse, strong, slightly rough | Soft, wool-like, smooth |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear and UV | Good durability, prone to pilling and static |
| Moisture Absorption | Highly breathable and moisture-wicking | Low moisture absorption, quick drying |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low water usage, sustainable | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based, pollutive |
| Common Uses | Eco-friendly apparel, home textiles, industrial fabrics | Sweaters, blankets, upholstery, activewear |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depends on processing | Low to moderate, mass-produced |
Introduction to Hemp and Acrylic Fibers
Hemp fibers, derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, are renowned for their durability, breathability, and eco-friendly qualities, making them a sustainable choice in textile production. Acrylic fibers, synthetic polymers made from polyacrylonitrile, offer lightweight, soft, and wool-like characteristics widely used in clothing and home textiles. Comparing hemp and acrylic highlights differences in environmental impact, texture, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability crucial for sustainable and functional fabric selection.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Acrylic
Hemp textiles have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to acrylic fibers, as hemp cultivation requires minimal water, pesticides, and synthetic fertilizers while promoting soil health and carbon sequestration. Acrylic is a synthetic fiber derived from petroleum, contributing to non-renewable resource depletion and releasing microplastics into water systems during washing, causing long-term pollution. Choosing hemp over acrylic supports sustainable fashion by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.
Raw Material Sourcing and Sustainability
Hemp is derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, offering a renewable and biodegradable raw material with low water and pesticide requirements, making it highly sustainable. Acrylic fibers are synthetic, produced from petroleum-based polymers through energy-intensive chemical processes, resulting in higher carbon emissions and non-biodegradable waste. Choosing hemp over acrylic significantly reduces environmental impact by promoting natural fiber sourcing and enhancing textile sustainability.
Production Processes Compared
Hemp production involves eco-friendly processes with low water usage, minimal pesticides, and natural retting that breaks down the stalks to extract fibers, resulting in sustainable and biodegradable textiles. Acrylic production relies on petrochemicals and energy-intensive polymerization, producing synthetic fibers through chemical spinning, which leads to higher carbon emissions and less environmental friendliness. Choosing hemp over acrylic drastically reduces the ecological footprint of textile manufacturing due to hemp's renewable cultivation and biodegradable fiber properties.
Durability and Longevity of Hemp and Acrylic
Hemp fabric outperforms acrylic in durability due to its natural resistance to wear, UV light, and mildew, making it ideal for long-lasting textile applications. Acrylic fibers are synthetic and prone to pilling and fading over time, reducing their lifespan compared to hemp. The tensile strength of hemp fibers contributes to superior longevity, maintaining structural integrity even after repeated washing and heavy use.
Comfort and Breathability in Wear
Hemp fibers offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making garments cooler and more comfortable to wear in warm climates. Acrylic textiles tend to trap heat and moisture, often resulting in less ventilation and increased discomfort during prolonged wear. The natural structure of hemp enhances airflow and skin dryness, while acrylic's synthetic nature can cause overheating and irritation.
Moisture Absorption and Quick Drying
Hemp fibers exhibit superior moisture absorption compared to acrylic, absorbing up to 20% of their weight in water, which enhances comfort in textiles. Hemp also dries faster due to its natural breathability and porous structure, preventing the retention of moisture. Acrylic, while lightweight, tends to hold moisture on the surface, resulting in slower drying times and less effective moisture management.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Hemp fibers generally cost more than acrylic due to sustainable cultivation and eco-friendly processing methods, while acrylic remains cheaper because of large-scale synthetic production. Market availability of hemp is limited compared to acrylic, which dominates the textile sector with widespread presence in fast fashion and industrial applications. Consumers seeking sustainable textiles face higher prices and less variety with hemp, whereas acrylic offers affordability and mass-market accessibility.
Applications in Fashion and Home Textiles
Hemp fibers offer exceptional durability, breathability, and natural antimicrobial properties, making them ideal for sustainable fashion and eco-friendly home textiles such as upholstery, curtains, and rugs. Acrylic, known for its lightweight, vibrant color retention, and wool-like feel, is widely used in affordable sweaters, scarves, and blankets that require ease of care and vibrant aesthetics. The choice between hemp and acrylic in fashion and home textiles depends on factors like environmental impact, performance needs, and fabric texture preferences.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Hemp and Acrylic
Innovations in hemp textiles are advancing with biodegradable fiber treatments and enhanced durability, positioning hemp as a sustainable alternative in eco-conscious markets. Acrylic developments focus on improving softness, moisture-wicking properties, and blending capabilities to meet evolving fashion and athletic demands. Both fibers are integrating nanotechnology and chemical modifications to enhance performance, signaling strong future prospects in sustainable and high-performance textile applications.
Infographic: Hemp vs Acrylic for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com