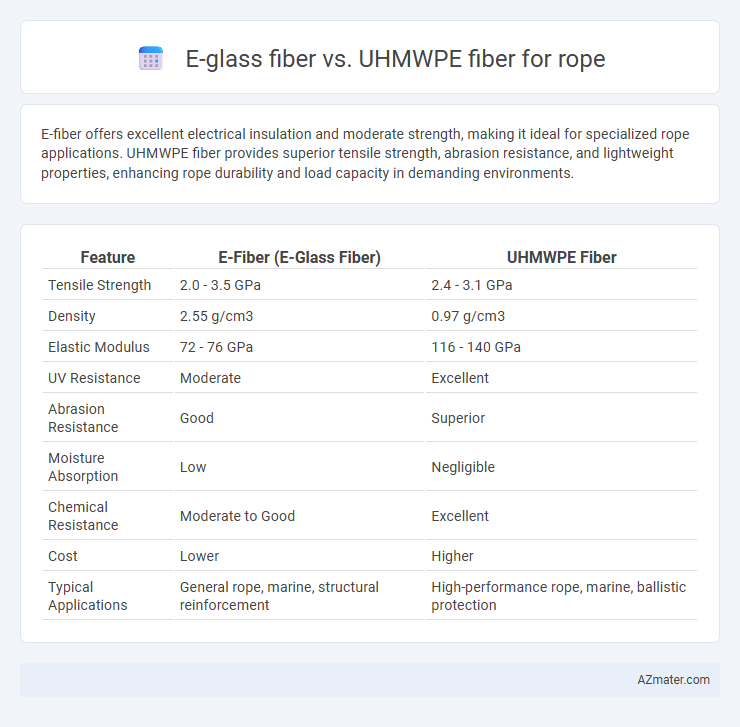
E-fiber offers excellent electrical insulation and moderate strength, making it ideal for specialized rope applications. UHMWPE fiber provides superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and lightweight properties, enhancing rope durability and load capacity in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | E-Fiber (E-Glass Fiber) | UHMWPE Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2.0 - 3.5 GPa | 2.4 - 3.1 GPa |
| Density | 2.55 g/cm3 | 0.97 g/cm3 |
| Elastic Modulus | 72 - 76 GPa | 116 - 140 GPa |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Negligible |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate to Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | General rope, marine, structural reinforcement | High-performance rope, marine, ballistic protection |
Introduction to E-fiber and UHMWPE Fiber
E-fiber, known for its high tensile strength and lightweight properties, is commonly utilized in composite materials and advanced rope manufacturing due to its excellent resistance to heat and chemical corrosion. UHMWPE fiber, or Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene, offers exceptional abrasion resistance, low moisture absorption, and outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for high-performance ropes used in marine, industrial, and tactical applications. Both fibers provide superior durability and performance, but UHMWPE fibers are particularly favored for their lower density and higher energy absorption capacity in rope engineering.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
E-fiber, composed primarily of alumina and silica, offers high tensile strength and excellent thermal stability, making it suitable for demanding rope applications. UHMWPE fiber consists of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and chemical resistance, produced through gel-spinning to align polymer chains for maximum durability. Manufacturing E-fiber involves high-temperature processing to draw and stabilize the fibers, while UHMWPE fiber requires controlled cooling and tension during gel-spinning to optimize molecular orientation and performance in ropes.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
E-fiber typically exhibits higher tensile strength and modulus compared to UHMWPE fiber, making it more resistant to stretching and deformation under load. UHMWPE fibers offer exceptional impact resistance and energy absorption but generally have lower tensile strength than E-fiber. In rope applications requiring maximum mechanical strength, E-fiber provides superior performance in terms of load-bearing capacity and durability.
Weight and Density Differences
E-fiber offers a density of approximately 2.5 g/cm3, whereas UHMWPE fiber features a significantly lower density near 0.97 g/cm3, making UHMWPE ropes substantially lighter than E-fiber ropes. This weight advantage enhances UHMWPE's suitability for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios, such as marine and aerospace uses. The lower density of UHMWPE fibers contributes to reduced rope weight without compromising tensile strength, offering increased efficiency compared to heavier E-fiber alternatives.
Durability and Abrasion Resistance
UHMWPE fiber exhibits superior durability and abrasion resistance compared to E-fiber, making it ideal for ropes subjected to extreme wear and harsh environmental conditions. UHMWPE fibers have high tensile strength and low elongation properties, maintaining performance even under repeated stress and friction. In contrast, E-fiber, while strong and lightweight, tends to degrade faster when exposed to abrasive surfaces and UV radiation.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
E-fiber ropes exhibit superior flexibility due to their finer filament structure, allowing for easier manipulation and knotting compared to UHMWPE fibers. UHMWPE fiber ropes, while offering exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, tend to be stiffer and have a lower elasticity, which can make handling less intuitive in dynamic applications. The choice between E-fiber and UHMWPE fiber ropes depends significantly on the required balance between flexibility and load capacity, with E-fiber favored in scenarios demanding enhanced handling characteristics.
Environmental Resistance: UV, Chemical, and Moisture
E-fiber ropes exhibit moderate UV resistance but can degrade faster under prolonged sunlight exposure compared to UHMWPE fiber ropes, which are highly resistant to UV radiation, maintaining strength and integrity over time. Chemically, UHMWPE fibers outperform E-fibers with superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and solvents, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. In terms of moisture absorption, E-fiber ropes tend to absorb more water, leading to potential weakening and rot, while UHMWPE fibers are hydrophobic, ensuring minimal moisture uptake and sustained durability in marine and humid conditions.
Cost Analysis: E-fiber vs UHMWPE Fiber
E-fiber offers a lower initial material cost compared to UHMWPE fiber, making it cost-effective for budget-sensitive rope manufacturing. UHMWPE fiber, although priced higher, provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced abrasion resistance, leading to longer service life and reduced replacement expenses. Considering total lifecycle costs, UHMWPE may offer better value despite its premium price due to durability and maintenance savings.
Applications in Industry and Marine Settings
E-fiber offers high tensile strength and excellent resistance to chemicals, making it suitable for industrial applications requiring durable, lightweight rope such as in construction and manufacturing. UHMWPE fiber exhibits superior abrasion resistance, low water absorption, and exceptional impact resistance, which enhances its performance in marine settings including mooring lines, fishing nets, and rescue operations. The choice between E-fiber and UHMWPE fiber depends on specific environmental demands; UHMWPE excels in harsh, wet conditions while E-fiber is often preferred for general industrial durability and chemical exposure.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Rope Needs
E-fiber offers excellent electrical insulation and lightweight properties, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal conductivity and moderate strength. UHMWPE fiber excels in tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and chemical stability, providing superior durability for demanding environments and heavy loads. Selecting the right fiber depends on whether the priority is electrical insulation and lightness or maximum strength and durability for harsh conditions.
Infographic: E-fiber vs UHMWPE Fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com