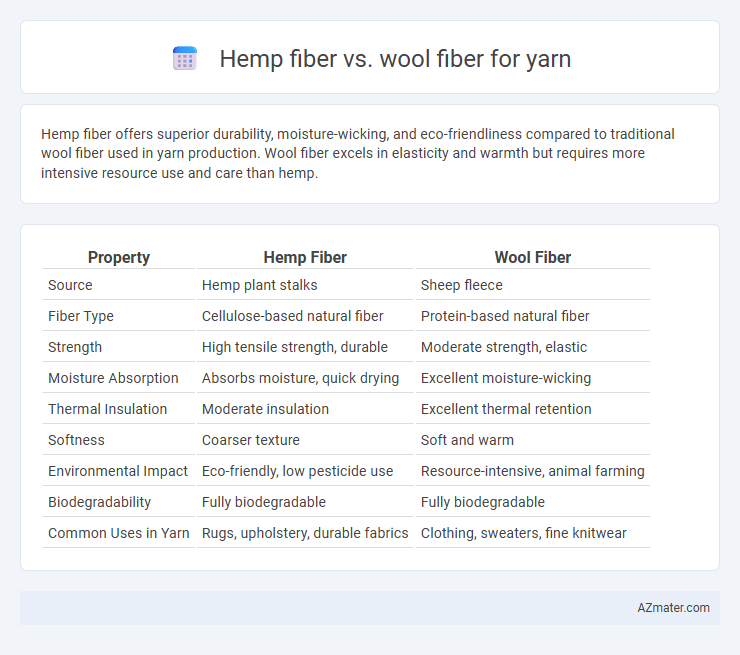
Hemp fiber offers superior durability, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendliness compared to traditional wool fiber used in yarn production. Wool fiber excels in elasticity and warmth but requires more intensive resource use and care than hemp.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Hemp Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hemp plant stalks | Sheep fleece |
| Fiber Type | Cellulose-based natural fiber | Protein-based natural fiber |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, elastic |
| Moisture Absorption | Absorbs moisture, quick drying | Excellent moisture-wicking |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate insulation | Excellent thermal retention |
| Softness | Coarser texture | Soft and warm |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, low pesticide use | Resource-intensive, animal farming |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Fully biodegradable |
| Common Uses in Yarn | Rugs, upholstery, durable fabrics | Clothing, sweaters, fine knitwear |
Introduction to Hemp and Wool Fibers
Hemp fiber, derived from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its exceptional strength, durability, and natural resistance to pests and mildew, making it a sustainable choice for yarn production. Wool fiber, obtained from the fleece of sheep, offers excellent elasticity, warmth, and moisture-wicking properties, which contribute to comfort and insulation in textile applications. Both fibers present distinct benefits for yarn manufacturing, with hemp emphasizing sustainability and longevity, while wool is prized for its softness and thermal regulation.
Origin and Sustainability of Hemp vs Wool
Hemp fiber originates from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, known for its rapid growth and minimal need for pesticides or herbicides, making it a highly sustainable option for yarn production. Wool fiber is derived from the fleece of sheep, requiring land, water, and energy-intensive animal husbandry practices that contribute to a larger environmental footprint. Hemp's low-impact cultivation and biodegradability position it as an eco-friendly alternative to wool, which involves resource-heavy farming and methane emissions from livestock.
Fiber Structure and Composition Comparison
Hemp fiber consists of long, coarse bast fibers with high cellulose content, providing strength and durability ideal for coarse yarns, while wool fiber is composed of overlapping, scaly protein-based keratin with high elasticity and crimp, resulting in softer, insulating yarns. The cellulose structure in hemp leads to moisture-wicking and mildew-resistant properties, contrasting with wool's natural lanolin coating that enhances water repellency and warmth retention. Differences in fiber diameter and surface texture influence the yarn's texture, with hemp producing stiff, rough yarns and wool yielding soft, pliable yarns suitable for lightweight, flexible textiles.
Spinning Qualities: Hemp Yarn vs Wool Yarn
Hemp fiber offers superior strength and durability compared to wool fiber, making hemp yarn ideal for producing long-lasting, abrasion-resistant textiles. Wool fiber provides greater elasticity and softness, resulting in yarns that are easy to spin with excellent loft and insulation properties. While hemp yarn tends to be stiffer and coarser, it yields a smooth, strong thread suited for sturdy fabrics, whereas wool yarn produces a warmer, more flexible fabric with enhanced moisture-wicking capabilities.
Texture and Softness Differences
Hemp fiber is coarser and more rigid than wool fiber, providing a rougher texture ideal for durable, sturdy yarn. Wool fiber offers exceptional softness and elasticity, resulting in yarn that feels smooth and comfortable against the skin. The natural lanolin in wool enhances softness, whereas hemp's cellulose structure contributes to its firmness and breathability.
Durability and Longevity of Each Fiber
Hemp fiber boasts exceptional durability due to its long, strong bast fibers, making it highly resistant to wear and tear in yarn applications compared to wool. Wool fibers, while providing excellent elasticity and moisture-wicking properties, tend to be less abrasion-resistant and may degrade faster with frequent use. Hemp yarns offer superior longevity in harsh conditions, whereas wool yarns excel in comfort but require more careful maintenance to preserve their lifespan.
Breathability and Moisture-wicking Properties
Hemp fiber excels in breathability and moisture-wicking due to its natural hollow structure, allowing air circulation and rapid moisture evaporation, making it ideal for warm, humid conditions. Wool fiber, particularly merino wool, offers superior moisture management by absorbing up to 30% of its weight in moisture while retaining warmth and promoting breathability through its crimped fiber structure. Both fibers contribute to comfort in yarn applications, with hemp favored for cooling breathability and wool for balanced moisture retention and thermal regulation.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Hemp fiber requires minimal maintenance due to its natural resistance to mold, mildew, and UV damage, making it ideal for durable yarn products. Wool fiber demands careful care, including gentle washing and avoidance of high heat to prevent shrinking and felting, which can compromise the yarn's integrity. Hemp's durability contrasts with wool's need for frequent conditioning to maintain softness and elasticity during repeated use.
Uses and Applications in Textile Industry
Hemp fiber is highly durable, moisture-wicking, and resistant to mold, making it ideal for eco-friendly textiles such as upholstery, denim, and canvas, while wool fiber offers excellent insulation, elasticity, and moisture absorption, commonly used in knitwear, suits, and high-end outerwear. Hemp's natural strength and biodegradability suit it for sustainable fashion and industrial textile applications, whereas wool's warmth and softness excel in cold-weather clothing and luxury fabrics. Both fibers serve distinct roles in the textile industry, with hemp favored for robust, durable goods and wool prized for comfort and thermal properties.
Environmental Impact and Ethical Considerations
Hemp fiber offers a significantly lower environmental impact than wool fiber due to its rapid growth, minimal water requirements, and reduced need for pesticides, making it a highly sustainable choice for yarn production. Wool fiber, while renewable, raises ethical concerns related to livestock farming practices, animal welfare, and greenhouse gas emissions from sheep. Choosing hemp yarn supports eco-friendly manufacturing and cruelty-free textile solutions, aligning with sustainable fashion and ethical consumerism trends.
Infographic: Hemp fiber vs Wool fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com