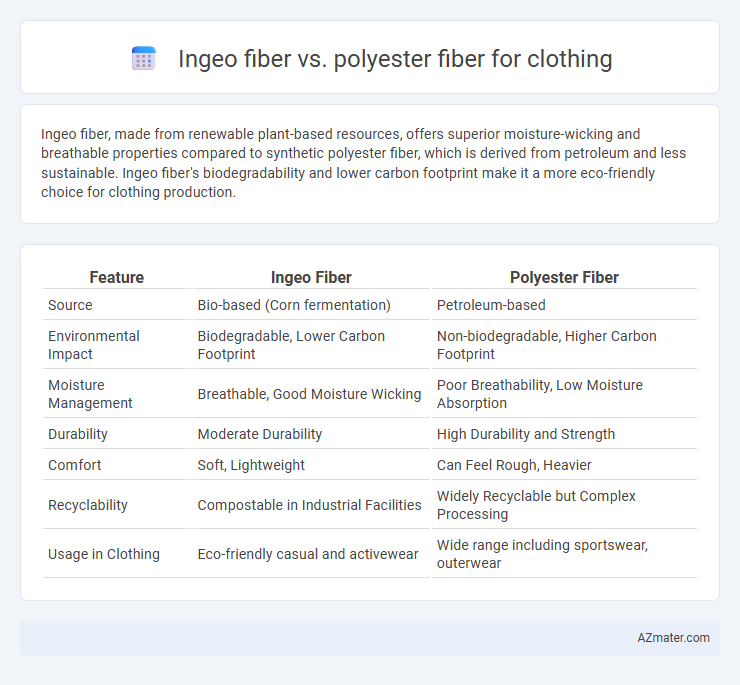
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based resources, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathable properties compared to synthetic polyester fiber, which is derived from petroleum and less sustainable. Ingeo fiber's biodegradability and lower carbon footprint make it a more eco-friendly choice for clothing production.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bio-based (Corn fermentation) | Petroleum-based |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, Lower Carbon Footprint | Non-biodegradable, Higher Carbon Footprint |
| Moisture Management | Breathable, Good Moisture Wicking | Poor Breathability, Low Moisture Absorption |
| Durability | Moderate Durability | High Durability and Strength |
| Comfort | Soft, Lightweight | Can Feel Rough, Heavier |
| Recyclability | Compostable in Industrial Facilities | Widely Recyclable but Complex Processing |
| Usage in Clothing | Eco-friendly casual and activewear | Wide range including sportswear, outerwear |
Introduction to Ingeo and Polyester Fibers
Ingeo fiber is a biopolymer made from renewable plant-based materials, primarily corn starch, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional synthetic fibers. Polyester fiber, derived from petrochemicals, is widely used in clothing due to its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Ingeo fibers provide biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint, while polyester focuses on performance and longevity in textile applications.
What is Ingeo Fiber?
Ingeo fiber is a sustainable textile made from renewable plant-based resources, primarily corn fermentation, which results in a biodegradable and eco-friendly fabric alternative to traditional polyester fiber derived from petroleum. It offers excellent moisture-wicking, breathability, and softness, making it ideal for comfortable and environmentally conscious clothing. Ingeo fibers reduce carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels while providing similar durability and versatility to synthetic polyester in apparel manufacturing.
What is Polyester Fiber?
Polyester fiber is a synthetic textile made from petrochemical-derived polymers, primarily polyethylene terephthalate (PET), widely used in clothing due to its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties. Compared to Ingeo fiber, which is derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn starch, polyester fiber relies on non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to higher environmental impact and longer biodegradation times. The choice between polyester and Ingeo fibers significantly affects sustainability, comfort, and garment performance in the textile industry.
Production Processes Compared
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials through a low-energy, carbon-efficient fermentation process, offers a more sustainable alternative to traditional polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and produced via energy-intensive petrochemical methods. The Ingeo production reduces greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, aligning with eco-friendly textile manufacturing goals. Polyester production, while cost-effective and durable, relies on non-renewable resources and emits higher levels of pollutants throughout its creation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials like corn, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and biodegradability compared to conventional polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and contributes to microplastic pollution. The production of Ingeo fiber consumes less energy and water, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation associated with synthetic fibers. Choosing Ingeo fiber supports circular fashion initiatives by promoting compostable textiles and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing overall sustainability in clothing manufacturing.
Performance and Durability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based resources, offers excellent moisture-wicking and breathability compared to traditional polyester fiber, enhancing comfort in activewear and casual clothing. Polyester fiber demonstrates superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, ensuring long-lasting durability and color retention even after repeated washing. While Ingeo provides a sustainable alternative with decent performance, polyester remains the preferred choice for garments requiring maximum resilience and heavy-duty performance.
Comfort and Wearability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant material, offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional polyester fiber, enhancing overall comfort in clothing applications. The natural structure of Ingeo fibers allows for better temperature regulation and softness against the skin, reducing irritation during extended wear. Polyester fiber, while durable and wrinkle-resistant, often lacks the same level of moisture management, which can lead to discomfort in warm or active conditions.
Cost Analysis: Ingeo vs Polyester
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant materials, generally incurs higher production costs compared to petroleum-based polyester fiber due to more complex and resource-intensive manufacturing processes. Polyester fiber benefits from established large-scale production leading to lower raw material and processing expenses, making it more cost-effective for mass-market clothing. Cost analysis reveals that despite higher upfront costs, Ingeo fiber may provide long-term value through sustainability and consumer demand for eco-friendly apparel.
Applications in Clothing Industry
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior breathability, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability compared to traditional polyester fiber, making it ideal for sustainable activewear and casual clothing. Polyester fiber excels in durability, wrinkle resistance, and color retention, widely used in performance sportswear and fashion garments requiring longevity. The clothing industry leverages Ingeo for eco-friendly lines targeting environmentally-conscious consumers, while polyester remains dominant in mass-produced apparel due to cost-efficiency and versatile fabric properties.
Which Fiber is Best for Clothing?
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior breathability and biodegradability compared to synthetic polyester fiber, which is petroleum-based and less environmentally friendly. Ingeo fiber excels in moisture-wicking and odor resistance, making it ideal for activewear and comfortable everyday clothing. Polyester fiber remains favored for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and cost-effectiveness, but Ingeo's sustainable properties make it the best choice for eco-conscious clothing consumers.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Polyester fiber for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com