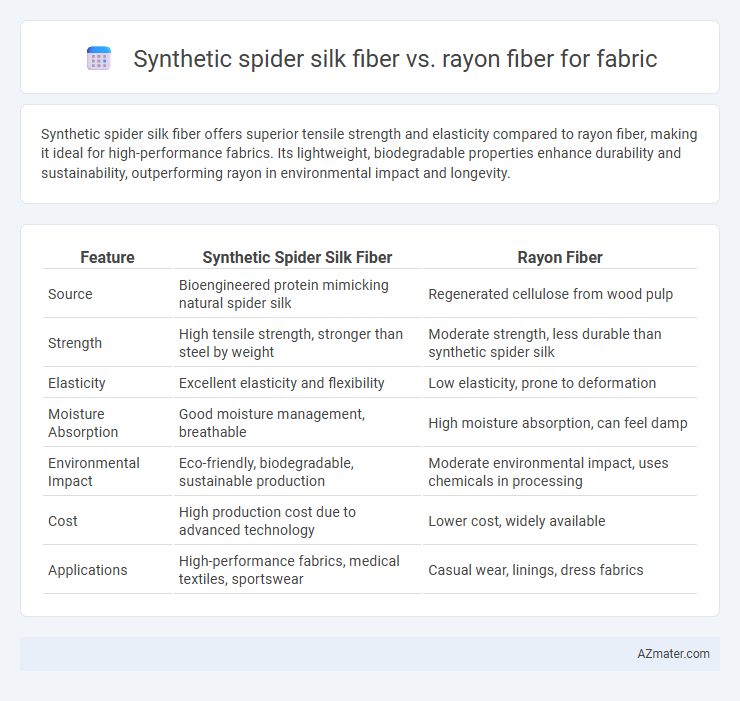
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to rayon fiber, making it ideal for high-performance fabrics. Its lightweight, biodegradable properties enhance durability and sustainability, outperforming rayon in environmental impact and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Rayon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Bioengineered protein mimicking natural spider silk | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp |
| Strength | High tensile strength, stronger than steel by weight | Moderate strength, less durable than synthetic spider silk |
| Elasticity | Excellent elasticity and flexibility | Low elasticity, prone to deformation |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture management, breathable | High moisture absorption, can feel damp |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, sustainable production | Moderate environmental impact, uses chemicals in processing |
| Cost | High production cost due to advanced technology | Lower cost, widely available |
| Applications | High-performance fabrics, medical textiles, sportswear | Casual wear, linings, dress fabrics |
Introduction to Synthetic Spider Silk and Rayon Fibers
Synthetic spider silk fiber, engineered to mimic the natural protein structure of spider silk, offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a revolutionary material in textiles and advanced fabrics. Rayon fiber, a semi-synthetic cellulose-based fabric derived from wood pulp, provides a smooth, breathable, and absorbent alternative commonly used in apparel and home textiles. The distinct molecular compositions of synthetic spider silk and rayon fibers influence their durability, environmental impact, and applications in high-performance versus everyday fabric markets.
Origins and Production Processes
Synthetic spider silk fiber is engineered through biomimetic techniques that replicate the natural proteins found in spider silk, involving genetic modification of host organisms such as bacteria or yeast to produce fibroin proteins, which are then spun into fibers. Rayon fiber originates from cellulose derived mainly from wood pulp through a chemical-intensive viscose or lyocell process, where the cellulose is dissolved, regenerated, and spun into fibers. The biotechnological production of synthetic spider silk is more sustainable and innovative compared to rayon's traditional chemical methods, which often require harsh solvents and extensive processing steps.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Synthetic spider silk fiber consists primarily of repetitive amino acid sequences such as glycine and alanine, forming beta-sheet crystal structures that provide exceptional strength and elasticity. Rayon fiber is composed of regenerated cellulose derived from natural cellulose polymers, featuring hydroxyl groups that contribute to moisture absorption and dye affinity but lack the molecular organization for high tensile strength. The unique protein-based chemical structure of synthetic spider silk offers superior mechanical properties compared to the polysaccharide-based composition of rayon fibers.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to rayon fiber, boasting tensile strengths up to 1.3 GPa, far exceeding rayon's typical range of 0.3 to 0.6 GPa. The durability of synthetic spider silk is enhanced by its exceptional elasticity and resistance to wear, enabling fabrics to withstand repeated stress without significant degradation. Rayon fiber, while versatile and cost-effective, lacks the resilience and long-term performance of synthetic spider silk, making the latter a preferred choice for high-performance textile applications.
Flexibility and Comfort in Textiles
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior flexibility and exceptional tensile strength compared to rayon fiber, making it ideal for high-performance textiles that require durability and ease of movement. Its natural elasticity enhances wearer comfort, allowing fabrics to stretch and recover without losing shape, unlike rayon which tends to be less resilient and more prone to deformation. The moisture-wicking and breathable properties of synthetic spider silk further contribute to comfort by maintaining temperature regulation and reducing skin irritation during prolonged wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers significant environmental advantages over rayon fiber, as it is typically produced using bioengineered proteins that require less water and fewer harsh chemicals during manufacturing. Rayon fiber, derived from cellulose in wood pulp, often involves intensive water use, chemical treatments, and deforestation, contributing to higher ecological footprints. The biodegradability and renewable sourcing of synthetic spider silk further enhance its sustainability profile compared to the chemically intensive and resource-heavy rayon production process.
Cost and Scalability of Fabric Production
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers higher tensile strength and superior elasticity compared to rayon fiber, but its production cost remains significantly higher due to complex bioengineering processes. Rayon fiber benefits from well-established manufacturing infrastructure, enabling large-scale production at a lower cost and wider market availability. Scaling synthetic spider silk to compete with rayon's volume requires substantial advancements in biotechnological efficiency and cost reduction strategies.
Applications in Fashion and Industrial Sectors
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it ideal for high-performance fashion garments and advanced industrial uses such as protective clothing, medical sutures, and reinforced composites. Rayon fiber, derived from regenerated cellulose, offers affordability and a smooth, breathable texture favored in mainstream fashion for casual wear and home textiles but lacks the durability and strength required for demanding industrial applications. The fusion of synthetic spider silk's durability with rayon's softness is driving innovation in hybrid fabrics, expanding possibilities in sustainable fashion and resilient industrial textiles.
Comparison of Performance in Everyday Use
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, outperforming rayon fiber in durability and resistance to wear during everyday use. Rayon fiber, while softer and more breathable, tends to lose shape and degrade faster when exposed to frequent washing and friction. The superior moisture-wicking and lightweight properties of synthetic spider silk enhance comfort and longevity, making it ideal for activewear and high-performance fabrics.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary material for sustainable fabric innovations compared to rayon fiber, which relies on chemically intensive production from wood pulp. Advances in bioengineering and genetically modified organisms enhance production scalability of synthetic spider silk, promising breakthroughs in high-performance textiles with minimal environmental impact. Future prospects include integrating synthetic spider silk fibers into wearable technology and medical textiles, surpassing rayon's traditional applications with superior durability and eco-friendly properties.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Rayon fiber for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com