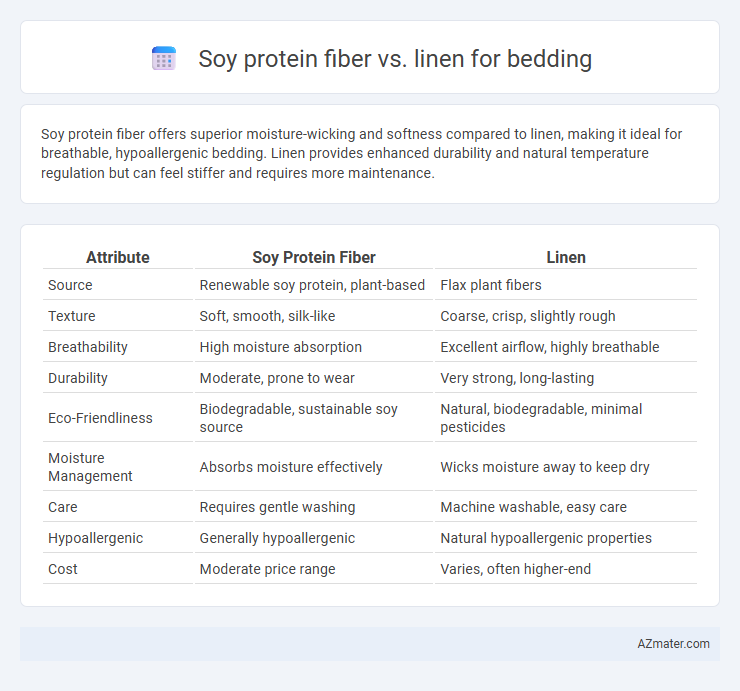
Soy protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and softness compared to linen, making it ideal for breathable, hypoallergenic bedding. Linen provides enhanced durability and natural temperature regulation but can feel stiffer and requires more maintenance.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Soy Protein Fiber | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Renewable soy protein, plant-based | Flax plant fibers |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like | Coarse, crisp, slightly rough |
| Breathability | High moisture absorption | Excellent airflow, highly breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear | Very strong, long-lasting |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, sustainable soy source | Natural, biodegradable, minimal pesticides |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs moisture effectively | Wicks moisture away to keep dry |
| Care | Requires gentle washing | Machine washable, easy care |
| Hypoallergenic | Generally hypoallergenic | Natural hypoallergenic properties |
| Cost | Moderate price range | Varies, often higher-end |
Introduction to Soy Protein Fiber and Linen for Bedding
Soy protein fiber, derived from soybeans, offers a sustainable and biodegradable option for bedding with natural moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties. Linen, made from flax fibers, is renowned for its durability, breathability, and temperature-regulating abilities, making it a highly sought-after material for high-quality bedding. Both materials provide eco-friendly alternatives to synthetic fibers, catering to environmentally conscious consumers seeking comfort and functionality in bedding.
Origin and Production Process of Soy Protein Fiber
Soy protein fiber is derived from soybeans through a process that extracts proteins from soybean meal, followed by spinning these proteins into fibers using wet or dry spinning techniques. Linen originates from flax plants, harvested and processed by retting, drying, and weaving the flax fibers into fabric. The production of soy protein fiber involves sustainable agricultural practices and bio-based extraction methods, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional plant-based fibers like linen.
Overview of Linen: Source and Manufacturing
Linen is a natural textile derived from the fibers of the flax plant, cultivated primarily in Europe, particularly Belgium and Ireland. The manufacturing process involves harvesting flax fibers, retting to separate the fibers from the stem, and spinning them into yarn, producing a durable and breathable fabric. Linen bedding is prized for its moisture-wicking properties and strength, offering a sustainable and long-lasting option compared to synthetic or protein-based fibers like soy protein fiber.
Comfort and Feel: Soy Protein Fiber vs Linen
Soy protein fiber bedding offers a silky soft texture with excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for those who prefer smooth, breathable sheets that stay cool and comfortable. Linen bedding is renowned for its natural breathability and durability, providing a crisp yet slightly textured feel that softens with each wash while maintaining excellent airflow. Both materials excel in comfort, but soy protein fiber leans towards a luxuriously silky touch, whereas linen delivers a more rustic, airy sensation ideal for warm climates.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Soy protein fiber offers excellent breathability due to its natural moisture-wicking properties, making it highly effective at regulating body temperature during sleep. Linen, derived from flax plants, is renowned for its superior airflow and quick-drying capabilities, providing a cool and fresh sleeping environment. Both fibers enhance comfort by promoting ventilation, but linen generally excels in heat dissipation for warmer climates while soy protein fiber balances warmth and cooling for varied temperatures.
Moisture-Wicking and Absorbency Qualities
Soy protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties compared to linen, drawing sweat away from the skin to keep sleepers dry throughout the night. Linen, known for its high absorbency, can quickly soak up moisture but may feel damp longer, affecting overall comfort. Soy protein fiber's ability to manage moisture efficiently makes it an excellent choice for bedding in warm or humid climates.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Soy protein fiber bedding offers moderate durability with a soft texture but tends to wear faster over time compared to linen. Linen, made from flax fibers, is renowned for its exceptional strength and longevity, often lasting several years with proper care. The natural resilience and moisture-wicking properties of linen contribute to its superior durability and extended lifespan in bedding applications.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability Factors
Soy protein fiber, derived from the byproducts of soybean processing, offers a biodegradable and renewable option for bedding, reducing reliance on synthetic fibers and minimizing environmental impact. Linen, made from flax plants, boasts exceptional sustainability due to its low water consumption, natural pest resistance, and full biodegradability, making it a highly eco-friendly choice. Both fibers support sustainable farming practices, but linen's longer durability and minimal resource requirements often position it as the superior option for eco-conscious bedding.
Care, Maintenance, and Ease of Cleaning
Soy protein fiber bedding offers superior softness and natural moisture-wicking properties, requiring gentle machine wash cycles with mild detergents and air drying to maintain fiber integrity. Linen bedding is highly durable and becomes softer with each wash but needs gentle washing in cold water to prevent shrinkage and fiber breakage, often benefiting from line drying or low heat tumble drying. Both materials resist bacteria and allergens, but soy protein fiber demands more delicate care compared to the robust nature and easy maintenance of linen.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Soy protein fiber bedding offers a cost-efficient alternative to linen, with prices typically 20-30% lower due to its lower cultivation and manufacturing expenses. Market availability of soy protein fiber is expanding rapidly, driven by increasing demand for sustainable textiles, while linen remains a premium, niche product with limited large-scale distribution. Consumers seeking affordability and eco-friendly options often find soy protein fiber more accessible through online retailers and specialty bedding stores compared to traditional linen products.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Linen for Bedding
 azmater.com
azmater.com