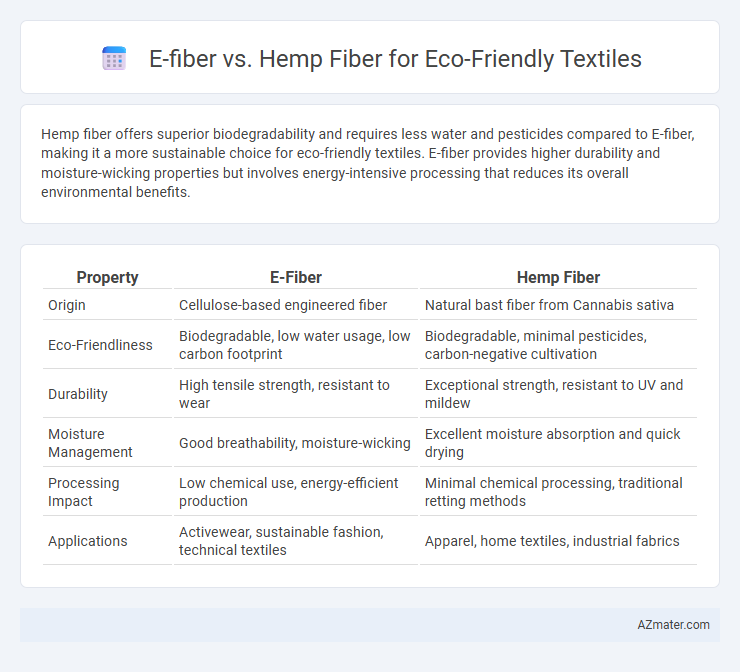
Hemp fiber offers superior biodegradability and requires less water and pesticides compared to E-fiber, making it a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly textiles. E-fiber provides higher durability and moisture-wicking properties but involves energy-intensive processing that reduces its overall environmental benefits.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Cellulose-based engineered fiber | Natural bast fiber from Cannabis sativa |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, low water usage, low carbon footprint | Biodegradable, minimal pesticides, carbon-negative cultivation |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Exceptional strength, resistant to UV and mildew |
| Moisture Management | Good breathability, moisture-wicking | Excellent moisture absorption and quick drying |
| Processing Impact | Low chemical use, energy-efficient production | Minimal chemical processing, traditional retting methods |
| Applications | Activewear, sustainable fashion, technical textiles | Apparel, home textiles, industrial fabrics |
Introduction to E-fiber and Hemp Fiber
E-fiber, derived from agricultural waste such as wheat straw and rice straw, offers a sustainable alternative by utilizing cellulose-rich byproducts to produce eco-friendly textiles with a low environmental footprint. Hemp fiber, known for its durability, biodegradability, and minimal resource requirements including low water and pesticide use, serves as a pioneering natural fiber in sustainable textile manufacturing. Both fibers contribute to reducing reliance on conventional cotton and synthetic fibers, promoting resource efficiency and waste valorization within the eco-friendly textile industry.
Sustainability Profile: E-fiber vs Hemp Fiber
E-fiber, derived from eucalyptus, offers rapid growth rates and efficient land use, resulting in lower water consumption and carbon emissions compared to traditional crops. Hemp fiber boasts strong biodegradability, requires minimal pesticides, and enhances soil health through natural nitrogen fixation, making it highly sustainable. Both fibers contribute significantly to eco-friendly textiles, with hemp excelling in regenerative farming benefits while E-fiber leads in resource-efficient production.
Cultivation Requirements and Environmental Impact
E-fiber, derived from eucalyptus trees, requires less water and fewer pesticides compared to hemp fiber, making it a more sustainable option in terms of cultivation. Hemp fiber grows rapidly and improves soil quality through phytoremediation but demands more water and pesticides in some climates, potentially increasing its environmental footprint. Both fibers offer eco-friendly textile solutions, yet E-fiber's lower resource consumption and reduced chemical use provide significant advantages in minimizing environmental impact.
Processing Methods and Resource Efficiency
E-fiber and hemp fiber differ significantly in processing methods and resource efficiency, with E-fiber typically involving advanced bioconversion techniques that require less water and chemicals compared to traditional hemp retting and decortication. Hemp fiber processing demands extensive water use and prolonged retting periods, impacting resource efficiency, whereas E-fiber production leverages enzymatic treatments to minimize environmental impact and enhance fiber quality. Resource efficiency of E-fiber is generally higher due to reduced energy consumption and lower chemical inputs, making it a more sustainable option for eco-friendly textile manufacturing.
Material Properties and Performance Comparison
E-fiber offers superior tensile strength and moisture-wicking properties compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for high-performance eco-friendly textiles. Hemp fiber excels in biodegradability and UV resistance, providing durability while maintaining environmental sustainability. Both fibers demonstrate excellent breathability, but E-fiber's lightweight nature enhances wearer comfort and versatility in sustainable apparel.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
E-fiber and hemp fiber both offer excellent biodegradability, decomposing naturally without releasing harmful residues, which makes them ideal for eco-friendly textiles. Hemp fiber provides superior durability and natural resistance to pests, enhancing its longevity and reducing chemical treatments, while E-fiber, derived from sustainable cellulose sources, ensures efficient biodegradation in industrial composting settings. Their end-of-life options support circular economy principles through composting or recycling, significantly minimizing textile waste and environmental impact.
Applications in the Eco-friendly Textile Industry
E-fiber, derived from cellulose-rich plants like flax or kenaf, offers superior softness and breathability compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for luxury eco-friendly textiles and sustainable fashion applications. Hemp fiber provides exceptional durability, UV resistance, and natural antimicrobial properties, widely utilized in outdoor apparel, upholstery, and industrial fabrics within the eco-friendly textile industry. Both fibers contribute to reduced environmental impact by supporting biodegradability and requiring fewer chemical treatments during processing, aligning with sustainable production goals.
Market Availability and Scalability
E-fiber, derived from agricultural by-products and engineered for consistency, offers growing market availability with an expanding production infrastructure tailored to industrial scalability. Hemp fiber, known for its durability and natural resistance properties, benefits from established cultivation systems but faces regulatory limitations affecting widespread adoption. Both fibers demonstrate scalable potential in eco-friendly textiles, yet E-fiber's synthetic production methods provide more controlled scalability compared to the agricultural dependency of hemp.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance
E-fiber and hemp fiber are gaining traction in eco-friendly textiles due to their sustainable sourcing and biodegradability. Consumers tend to favor hemp fiber for its natural texture and durability, associating it with organic and eco-conscious lifestyles. E-fiber, often made from recycled materials, appeals to environmentally aware buyers seeking innovative solutions but may face skepticism regarding comfort and environmental claims.
Future Trends in Sustainable Textile Fibers
E-fiber, derived from recycled electronic waste, offers a cutting-edge, resource-efficient alternative to traditional hemp fiber in sustainable textile production. Future trends highlight the growing integration of E-fiber for its lightweight, durable properties and minimal environmental impact, contrasting with hemp's established benefits of biodegradability and carbon sequestration. Innovations in blending E-fiber with hemp fiber are poised to enhance fabric performance while advancing circular economy goals in eco-friendly textiles.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Hemp fiber for Eco-friendly Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com