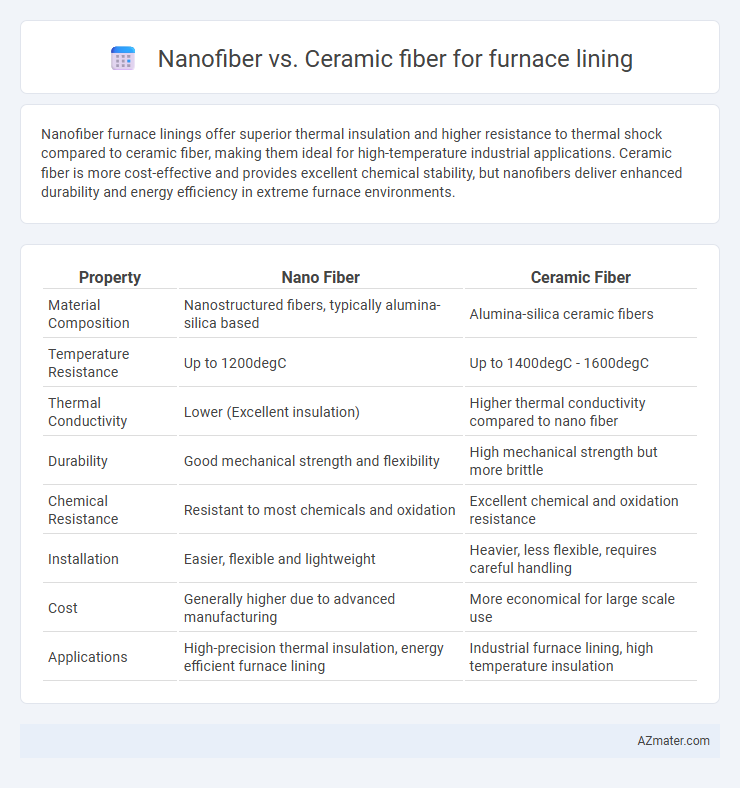
Nanofiber furnace linings offer superior thermal insulation and higher resistance to thermal shock compared to ceramic fiber, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Ceramic fiber is more cost-effective and provides excellent chemical stability, but nanofibers deliver enhanced durability and energy efficiency in extreme furnace environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nano Fiber | Ceramic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Nanostructured fibers, typically alumina-silica based | Alumina-silica ceramic fibers |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 1200degC | Up to 1400degC - 1600degC |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower (Excellent insulation) | Higher thermal conductivity compared to nano fiber |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength and flexibility | High mechanical strength but more brittle |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to most chemicals and oxidation | Excellent chemical and oxidation resistance |
| Installation | Easier, flexible and lightweight | Heavier, less flexible, requires careful handling |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced manufacturing | More economical for large scale use |
| Applications | High-precision thermal insulation, energy efficient furnace lining | Industrial furnace lining, high temperature insulation |
Introduction to Furnace Lining Materials
Furnace lining materials play a crucial role in thermal insulation and energy efficiency, with nano fibers offering ultra-fine fiber diameters that enhance thermal resistance and reduce heat loss compared to traditional ceramic fibers. Ceramic fibers, known for their high-temperature stability and chemical inertness, provide robust insulation but tend to have coarser fibers resulting in slightly lower thermal efficiency. Selecting between nano fiber and ceramic fiber linings depends on factors such as maximum operating temperature, thermal conductivity, and mechanical durability required for specific furnace applications.
Overview of Nano Fiber Technology
Nano fiber technology for furnace lining offers superior thermal insulation and enhanced mechanical strength compared to conventional ceramic fibers. These fibers, with diameters typically less than 100 nanometers, provide higher surface area and reduced thermal conductivity, resulting in better energy efficiency and prolonged furnace lifespan. The advanced nanoscale structure also improves resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making nano fiber linings ideal for high-temperature industrial applications.
What is Ceramic Fiber?
Ceramic fiber is a high-temperature insulation material composed primarily of alumina and silica, widely used for furnace lining due to its excellent heat resistance and low thermal conductivity. It offers superior durability, chemical stability, and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring temperature insulation up to 1,260degC (2,300degF). Compared to nano fiber, ceramic fiber provides a cost-effective, robust solution for furnace linings, ensuring energy efficiency and extended service life.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Nano fibers exhibit superior thermal insulation properties compared to ceramic fibers due to their ultra-fine diameter, which reduces thermal conductivity and enhances heat retention in furnace linings. Ceramic fibers, although effective at high temperatures, have larger fiber diameters that result in higher thermal conductivity and slightly reduced insulating efficiency. Nano fiber linings provide lower heat loss and improved energy efficiency, making them ideal for advanced high-temperature applications in industrial furnaces.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nanofiber insulation for furnace lining offers superior mechanical strength due to its fine fiber diameter and high tensile properties, resulting in enhanced resistance to abrasion and deformation under thermal stress. Ceramic fiber, while traditionally used for high-temperature insulation, tends to have lower toughness and is more prone to brittleness and mechanical degradation over prolonged exposure to thermal cycling. The durability of nanofiber materials in furnace linings significantly surpasses that of ceramic fibers, providing longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in industrial high-temperature environments.
Energy Efficiency Benefits
Nano fiber insulation exhibits superior thermal resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to ceramic fiber, resulting in enhanced energy efficiency for furnace linings. Its finer fiber structure reduces heat loss and improves temperature retention, leading to decreased fuel consumption and operating costs. Ceramic fibers, while durable, typically have higher heat penetration rates, making nano fibers a more effective choice for maximizing furnace energy savings.
Resistance to Chemical and Thermal Shock
Nano fiber furnace linings offer superior resistance to chemical corrosion and thermal shock due to their high surface area and enhanced bonding properties, resulting in prolonged service life under aggressive operating conditions. Ceramic fiber linings provide excellent thermal insulation but may exhibit lower resilience to rapid temperature fluctuations and chemical degradation, leading to potential cracking or erosion over time. Advances in nano fiber technology deliver improved durability and stability in harsh furnace environments, optimizing maintenance cycles and operational efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Nano fiber insulation offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making installation in furnace lining easier and quicker compared to the rigid and heavier ceramic fiber materials. Maintenance of nano fiber linings is less frequent due to their enhanced resistance to thermal shock and reduced fiber degradation, whereas ceramic fibers often require periodic replacement and more careful handling to prevent fiber damage. Additionally, nano fiber systems produce less dust during installation and maintenance, improving workplace safety and reducing cleanup time compared to traditional ceramic fiber linings.
Cost Comparison: Nano Fiber vs. Ceramic Fiber
Nano fiber insulation offers higher thermal efficiency and lower heat loss compared to ceramic fiber, resulting in energy savings despite its higher initial cost. Ceramic fiber remains a cost-effective option for furnace lining due to its lower upfront price and widespread availability, making it suitable for budget-sensitive projects. Evaluating long-term operational expenses alongside initial investment is crucial in choosing between nano fiber and ceramic fiber for furnace applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Furnace Lining
Nano fiber insulation offers superior thermal stability and lower thermal conductivity compared to ceramic fiber, making it ideal for high-temperature furnace linings requiring efficient energy retention. Ceramic fiber, while cost-effective and widely used, has a higher thermal conductivity and lower mechanical strength, which may result in reduced lifespan under extreme thermal cycling conditions. Selecting the best material depends on furnace operating temperatures, energy efficiency goals, and budget constraints, with nano fiber providing enhanced performance in demanding industrial applications.
Infographic: Nano fiber vs Ceramic fiber for Furnace lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com