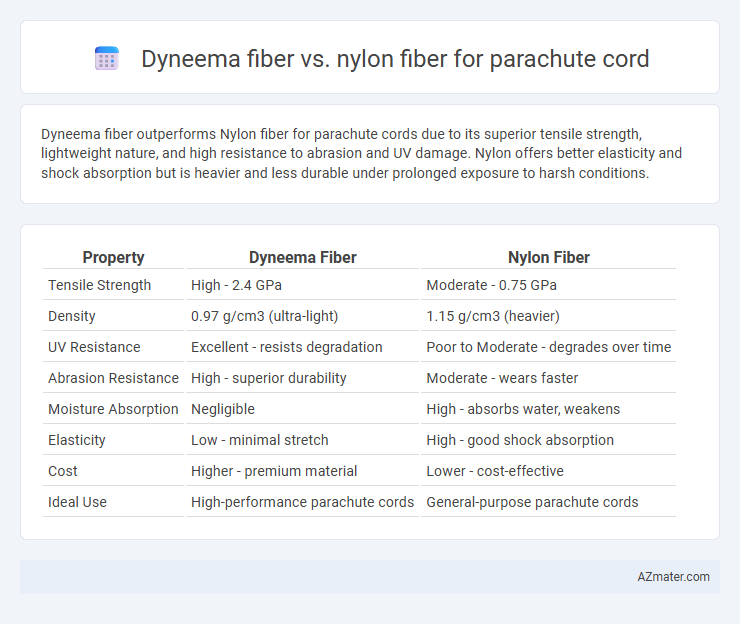
Dyneema fiber outperforms Nylon fiber for parachute cords due to its superior tensile strength, lightweight nature, and high resistance to abrasion and UV damage. Nylon offers better elasticity and shock absorption but is heavier and less durable under prolonged exposure to harsh conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Dyneema Fiber | Nylon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High - 2.4 GPa | Moderate - 0.75 GPa |
| Density | 0.97 g/cm3 (ultra-light) | 1.15 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| UV Resistance | Excellent - resists degradation | Poor to Moderate - degrades over time |
| Abrasion Resistance | High - superior durability | Moderate - wears faster |
| Moisture Absorption | Negligible | High - absorbs water, weakens |
| Elasticity | Low - minimal stretch | High - good shock absorption |
| Cost | Higher - premium material | Lower - cost-effective |
| Ideal Use | High-performance parachute cords | General-purpose parachute cords |
Introduction to Parachute Cord Materials
Parachute cords rely on high-strength, lightweight fibers such as Dyneema and Nylon to ensure durability and safety. Dyneema fiber offers superior tensile strength and exceptional resistance to abrasion and UV damage, making it ideal for critical load-bearing applications. Nylon fiber provides excellent elasticity and shock absorption, which helps absorb sudden forces during deployment and landing.
Overview of Dyneema Fiber
Dyneema fiber is an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for parachute cords where durability and lightweight performance are critical. It offers superior tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and low stretch compared to traditional nylon fibers, enhancing safety and reliability in demanding airborne applications. The fiber's resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and chemicals ensures long-lasting functionality even in harsh environments.
Overview of Nylon Fiber
Nylon fiber, widely used in parachute cords, offers high tensile strength, excellent elasticity, and superior abrasion resistance, making it a reliable choice for dynamic loads and shock absorption during parachute deployment. Its water resistance and durability under varying environmental conditions ensure consistent performance and longevity. Compared to Dyneema, nylon provides greater stretch, which can be beneficial in impact scenarios but may result in heavier and less stiff cords.
Strength and Load-Bearing Comparison
Dyneema fiber exhibits a tensile strength up to 15 times greater than nylon, making it exceptionally suited for parachute cords requiring maximal load-bearing capability. With a higher strength-to-weight ratio, Dyneema offers superior durability and can handle greater loads without stretching or weakening under stress. In contrast, nylon fibers have moderate strength but are more elastic, which can reduce reliability under heavy or sustained loads in parachuting applications.
Weight and Density Differences
Dyneema fiber offers a significantly lower weight and density compared to nylon fiber, making it ideal for parachute cords requiring lightweight strength. With a density of approximately 0.97 g/cm3, Dyneema is about 40% lighter than nylon, which has a density near 1.15 g/cm3. This reduced density translates to enhanced portability and less bulk in parachute systems without compromising tensile strength.
Weather and UV Resistance
Dyneema fiber offers superior weather and UV resistance compared to Nylon fiber, maintaining strength and durability in harsh environmental conditions. Its molecular structure provides excellent resistance to moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals, ensuring long-term performance without significant degradation. Nylon tends to absorb water and weaken under prolonged UV exposure, making Dyneema a more reliable choice for parachute cords used in extreme outdoor settings.
Flexibility and Handling
Dyneema fiber offers superior flexibility and lightweight handling compared to nylon fiber, making it highly suitable for parachute cords requiring easy packing and quick deployment. While nylon provides good elasticity and abrasion resistance, Dyneema's low stretch and high tensile strength result in more precise control and less elongation under load. This combination of flexibility and strength in Dyneema enhances overall cord performance and durability in demanding aerial applications.
Water Absorption and Performance
Dyneema fiber exhibits significantly lower water absorption compared to nylon fiber, maintaining its strength and lightweight properties even in wet conditions, which enhances parachute cord reliability and performance. Nylon fibers absorb more water, leading to increased weight and reduced tensile strength, potentially compromising cord durability during high-moisture operations. The superior moisture resistance of Dyneema ensures consistent performance, making it the preferred choice for parachute cords in demanding environments.
Durability and Lifespan
Dyneema fiber offers superior durability for parachute cords due to its high tensile strength and exceptional resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and moisture compared to nylon fiber. Nylon fiber, while strong and elastic, is more susceptible to wear and degradation over time, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Consequently, Dyneema parachute cords provide a longer lifespan and maintain performance under extreme stress, making them a preferred choice for critical applications.
Cost and Practical Applications
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and abrasion resistance compared to Nylon fiber, making it ideal for high-performance parachute cords but at a significantly higher cost. Nylon remains popular for general-purpose parachute cord due to its affordability, elasticity, and durability in diverse environments. Cost-sensitive applications typically favor Nylon, while Dyneema is preferred in situations requiring maximum strength and minimal weight.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Nylon fiber for Parachute cord
 azmater.com
azmater.com